You are already familiar with networking if you have ever connected your laptop to Wi-Fi, shared files across computers, or competed against your friends in online games. However, have you ever thought about the different types of networking based on the distance, purpose, and technology?
In this post, we will explain types of networking and types of networking in computing systems, splitting each one down into examples, benefits, and use cases.
1. What is Networking?
Networking is the connection of two (or more) devices so they can share data, resources and services.
Simply words: Networking allows devices to “communicate” with each other.
Technically speaking: Networking encompasses both hardware (e.g. routers, switches, cables) and software (e.g. protocols, applications) that allow devices to share information.
For example: When you send an email, your computer communicates with a server over a network so that your message can be delivered.
2. Main Types of Networking
Networking can be separated, based on their specific geographical scope and needs. Here are the major types of networking that computer systems support:

2.1 Personal Area Network (PAN)
Definition: A very small network for personal networks; usually within a distance of a few meters.
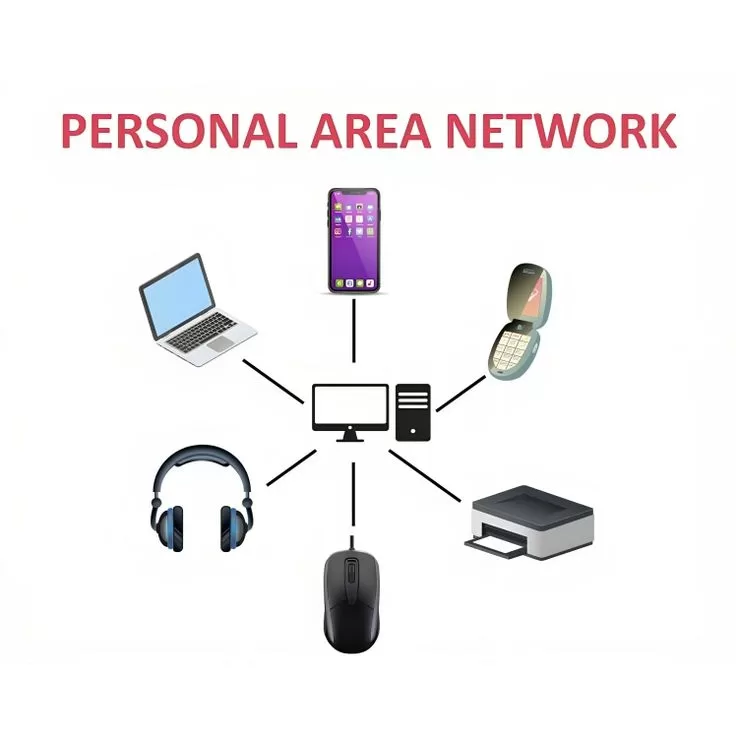
Examples:
- Connecting your phone to your wireless earphones using Bluetooth
- Connecting your laptop and smartphone using USB tethering
- Connecting Fitness trackers to a mobile device like syncing your smart watch to your mobile device
Benefits:
- Easy to set up
- Cheap
- Generate out of personal devices
Use case: Fitness trainers syncing to your phone.
2.2 Local Area Network (LAN)
Definition: A network that connects devices over a limited area, like a home, school, or office building.
Examples:
- Office computer/ into shared printer
- Home Wi-Fi network
- Gaming cafes
Benefits:
- High speed
- Secure at a small location
- Affordability on small areas
Use case: Employees work to share files between each other in office.
2.3 Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
Large Network : An area that connects multiple LAN, in a city or large Campus, larger than a LAN but smaller than a WAN.
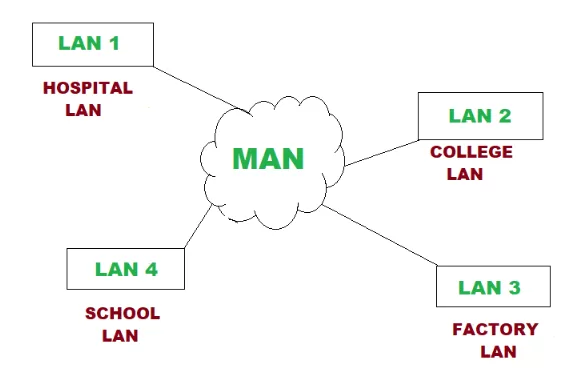
Examples:
- Public Wi-Fi available for city residents
- University campus
- Cable TV networks
Benefits:
- Connects multiple LANs in a region
- Supports fast data transfer rates
Use case: A city connecting all their branches of a company.
2.4 Wide Area Network (WAN)
Definition: A network that represents a large geographic area, often the world.
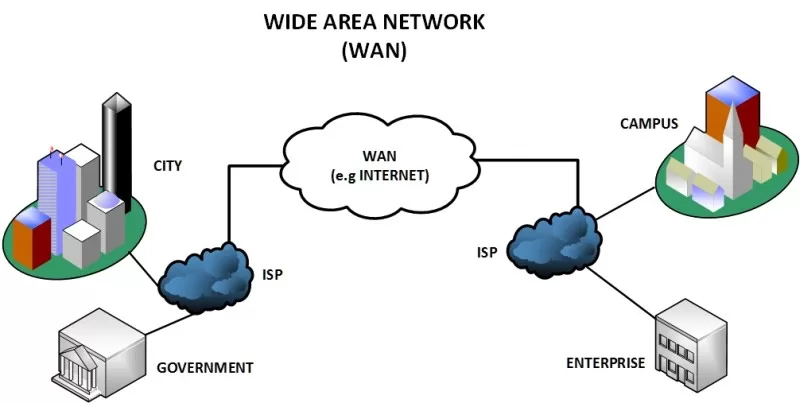
Examples:
- The Internet (the largest WAN)
- International bank networks
- Corporate connections on a global scale.
Advantages:
- It provides long distance connectivity.
- It supports large organizations.
Use Case: Data sharing by multinational companies across multiple countries.
2.5 Storage Area Network (SAN)
Definition: A high-speed network that connects shared pools of storage devices.
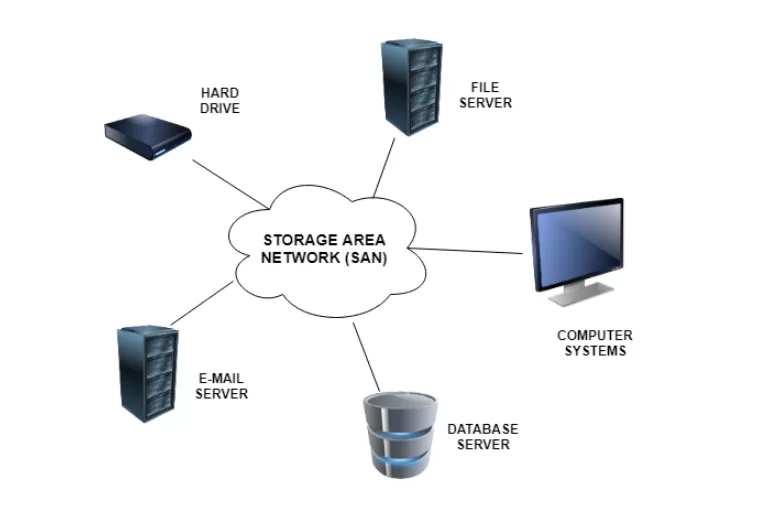
Examples:
- Data centers that contain cloud files
- Back-up servers
Advantages:
- Centralized data storage,
- Increased efficiency for processing large amounts of data .
Use Case: Cloud service providers.
3. Types of Networking Based on Architecture
In addition to geographic size, networking can also be classified based on how devices communicate:
3.1 Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Network
- All devices have equal status
- There is no central server
- Example: file sharing over Bluetooth
3.2 Client-Server Network
- One device acts as a server, the other devices are the clients
- Example: Web hosting services
4. Comparison Table: Types of Networking
| Type of Network | Range | Speed | Cost | Example |
| PAN | Few meters | High | Low | Bluetooth headset |
| LAN | 100 m – 1 km | Very High | Low-Medium | Office network |
| MAN | Up to 50 km | High | Medium | City Wi-Fi |
| WAN | Global | Varies | High | Internet |
| SAN | Local/Wide | Very High | High | Data centers |
5. Real-World Applications of Different Types of Networking
- Healthcare: Hospitals operate both LAN for all internal data and use WAN for telemedicine.
- Education: Universities operate MAN for internet service across a campus.
- Business: International companies use WAN to connect offices in other countries.
- Home: PAN connects smart devices in your home including speakers, security, etc.
6. FAQs on Types of Networking
Q1: What’s the most popular form of networking?
A: LAN is the most common, it’s used in homes and offices all around the world.
Q2: What type of networking is used for the Internet?
A: WAN.
Q3: Is Wi-Fi a type of networking?
A: Yes, it’s a wireless form of LAN or a MAN depending on range.
Final Thoughts
Learning about the types of networking and types of networking in computer systems is valuable knowledge for anyone with an interest in technology, IT careers, or digital communication. Ranging from PAN for personal devices, to WAN for global connectivity, networking is the basis of our connected world.
Whether setting up Wi-Fi in your home, managing office systems, and networking to deliver a global cloud-based project, it is important to know about the “type of networking” to make better, faster, and more secure connectivity decisions.
If the goal is to become capable of these abilities, that can be attained through attending a networking course, where you will begin to learn and get hands-on experience with real-world setups, protocols, and strategies for troubleshooting.




