Introduction to Java AWT
When I first stepped into Java GUI programming. If you’re reading this, chances are you’re trying to understand what Java AWT is, why it exists, and how you can use it to build simple graphical user interfaces.
Let me make this extremely simple.
Java AWT (Abstract Window Toolkit) is a part of Java’s standard library used to create GUI applications like windows, buttons, text fields, menus, and more.
When I started exploring desktop programming in Java, Java-AWT felt like magic. I was able to create an actual window — like a real “app window” — using just a few lines of code. And trust me, that moment stays with you.
What is Java AWT?

Java-AWT is the foundation of Java’s GUI system.
It provides:
- Components (like Button, Label, TextField)
- Containers (like Frame, Panel)
- Layout Managers (FlowLayout, BorderLayout, GridLayout)
- Event Handling (ActionListener, MouseListener, etc.)
If you’re building your first GUI app in Java, Java-AWT is the first place you should start. It helped me understand how graphical components behave, how windows render, and how events are processed.
Hierarchy of Java AWT Packages
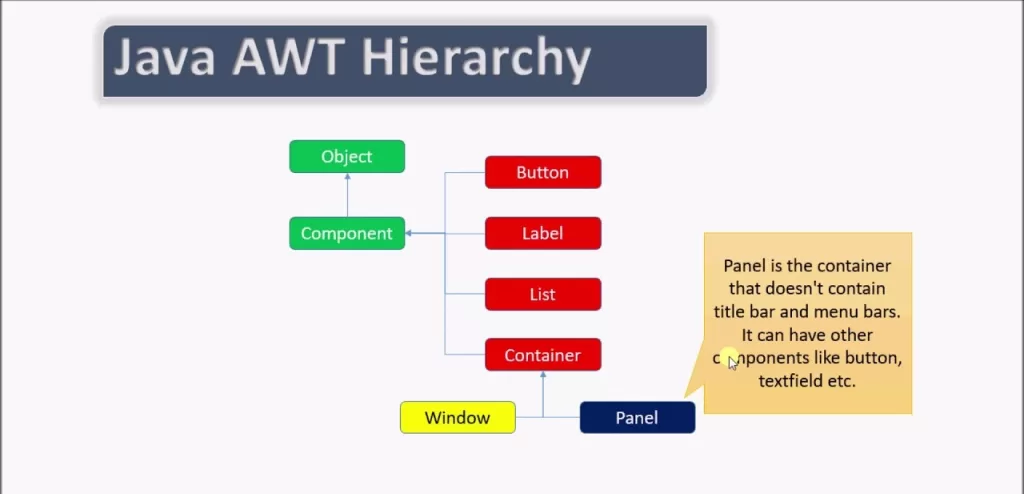
The core AWT packages are:
java.awtjava.awt.eventjava.awt.imagejava.awt.colorjava.awt.fontjava.awt.geomjava.awt.datatransfer
When I first looked at this list, it overwhelmed me.
But believe me — you don’t need all of them at once.
Just java.awt and java.awt.event are enough to get started.
Java AWT Components (The Visible UI Elements)

Components are the basic building blocks.
Anything you can see on the screen is a component.
Some commonly used Java-AWT components:
✔ Label
Used to display text.
✔ Button
Creates a clickable button.
✔ TextField
Used to take user input.
✔ TextArea
For multi-line text input.
✔ Checkbox
Represents a selection option.
✔ List
Shows a list of options.
✔ Choice
Dropdown list (like a combo box).
✔ Canvas
Used for drawing graphics.
When I built my first calculator app using java-awt, these components felt like LEGO blocks — simple yet powerful.
Java AWT Containers (The Holders of Components)
Components need containers.
I like to think of containers as “buckets” that hold interface elements.
The main containers in java awt are:
✔ Frame
A normal window. Like a desktop app window.
✔ Panel
A container inside a frame.
✔ Dialog
Popup windows.
✔ Window
Superclass of Frame and Dialog.
When I created my first AWT window, this was the code:
It was the moment where I felt, “Okay, I’m actually building GUI now!”
Java AWT Layout Managers (To Organize Components)

Java AWT gives you:
1. FlowLayout
Left-to-right arrangement.
2. BorderLayout
North, South, East, West, Center positions.
3. GridLayout
Grid of rows and columns.
4. GridBagLayout
Flexible but complex layout.
5. CardLayout
Stack of components like cards.
If you want predictable layouts, stick to FlowLayout or BorderLayout at first — that’s what I did.
Java AWT Event Handling (The Heart of GUI Programming)
A GUI is useless without interaction.
If someone clicks a button, Java needs to know.
If someone types something, Java should respond.
This is called Event Handling, and AWT uses the Delegation Event Model.
Common event listeners in java awt:
- ActionListener
- MouseListener
- MouseMotionListener
- WindowListener
- KeyListener
Here’s the simplest example of ActionListener:
Differences Between AWT and Swing (Beginner Must-Know)

I used to get confused between AWT and Swing, so here’s the simple version:
| Feature | AWT | Swing |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Heavyweight | Lightweight |
| Components | OS-dependent | Java-rendered |
| Look & feel | Native | Customizable |
| Speed | Faster for small GUIs | More features |
If you’re starting from scratch, I recommend beginning with java awt, then moving to Swing or JavaFX.
Advantages of Java AWT
- Easy to learn
- Perfect for beginners
- Great for understanding GUI basics
- Uses native OS components
- Faster rendering for basic apps
Limitations of Java AWT
- Limited components
- Not ideal for large applications
- OS-dependent look & feel
- Swing provides more features
Despite these limitations, java awt still plays a major role in learning GUI programming.
Simple Java AWT Program (Like a GFG Example)
Where is Java AWT Used Today?
Yes, AWT is older.
But it is still used in:
- Educational projects
- University lab programs
- Internal company tools
- Legacy applications
- Graphics and drawing tools
Even modern Java GUI ideas come from AWT concepts.
Final Thoughts
Learning java awt was one of my favourite phases of Java programming. It’s simple, predictable, and teaches you the real fundamentals of GUI development. If you want to build big applications later in Swing or JavaFX, start here — exactly the way I did.
Want to Learn More About Java ?, Kaashiv Infotech Offers, Full Stack Java Course, Java Course, Data Science Course, Internships & More, Visit Their Website www.kaashivinfotech.com.