Introduction
What is hypothesis testing — this was a term that sounded fearful when I was introduced to the field of data science.
What is hypothesis testing, anyway?
Is it just formulas?
Is it only for statisticians?
Would I really apply it in any real project?
If you’ve ever been unable to decide what to believe — feeling as confused as I once did — trust me, I’ve been there. In this article, I explain what is hypothesis testing in the easiest, most human way possible, based on my own experience using hypothesis testing in real data science work.
By the end of this blog, you will clearly understand:
- What is hypothesis testing
- Why hypothesis testing is important in data science
- Why this is not optional (even when you despise statistics 😅)
- How it shows up in real jobs, real projects, and real decisions
Let’s talk like friends.
No textbook tone.
No robotic explanations.
Just clarit

Definition: What is Hypothesis Testing?
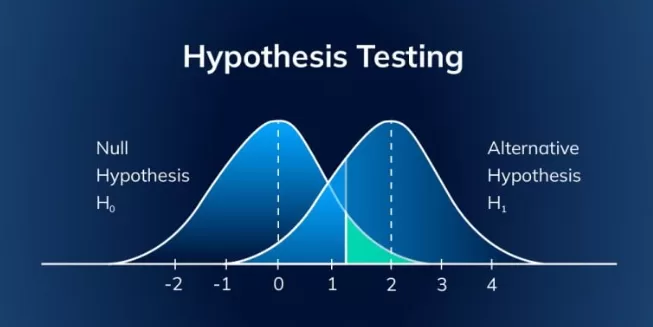
At its core, hypothesis testing in data science involves two contrasting hypotheses:
- The null hypothesis, which states that there is no effect or no difference
- The alternative hypothesis, which is what you aim to prove
Through hypothesis testing, you determine whether the observed data deviates significantly from the null hypothesis and thereby supports the alternative hypothesis.
Hypothesis Testing in Data Science: What Is This Really?
What is data science hypothesis testing?
To put it simply, hypothesis testing is how I check whether an idea is actually true using data — not intuition, not assumptions, not opinions.
Whenever I ask questions like:
- Did this new feature improve user engagement?
- Is this marketing campaign actually working?
- Was my ML model really better, or was it just luck?
…I’m already stepping into the world of hypothesis testing.
Hypothesis testing in data science is a systematic way to make decisions about a large population using sample data — with a measurable level of confidence.
And honestly?
This is where data science stops being analysis and starts becoming decision-making.
Why I Care About the Importance of Hypothesis Testing in Data Science 🤔
Let me be honest.
There was a time when I trusted dashboards blindly.
Big numbers.
Fancy charts.
Lots of confidence.
But confidence without proof?
That’s dangerous.
This is why the importance of hypothesis testing in data science cannot be overstated:
- It protects you from false conclusions
- It helps you say no to bad ideas (politely 🙂)
- It turns opinions into evidence
- It saves companies money, time, and reputation
In real-world data science, decisions affect:
- Revenue 💰
- Users 👥
- Products 📦
- People ❤️
Hypothesis testing gives me the confidence to say:
“This result is statistically valid. Let’s move forward.”
What is Hypothesis Testing: The Core Idea
At its heart, hypothesis testing comes down to one simple idea:
I start with an assumption — and then I use data to challenge it.
There are always two sides.
🔴 Null Hypothesis (H₀)
This assumes nothing unusual is happening.
Example:
The new website design does not affect conversions.
🟢 Alternative Hypothesis (H₁)
This is what I hope or expect to be true.
Example:
The new website design improves conversions.
Hypothesis testing helps me decide which side the data supports.
Why Hypothesis Testing Is Important in Data Science – A Real Example
Let me share a real experience.
I once ran an A/B test on a landing page.
Version B showed a higher conversion rate.
Everyone was excited 🎉
But I paused.
I asked:
- Is this difference real?
- Or is it just random chance?
This is where hypothesis testing in data science saved us.
After running the test correctly:
- The p-value was high
- The result was not statistically significant
If we had launched Version B blindly, we would’ve wasted time and money.
👉 This is exactly why hypothesis testing matters in real jobs.
Types of Hypotheses -Explained Simply
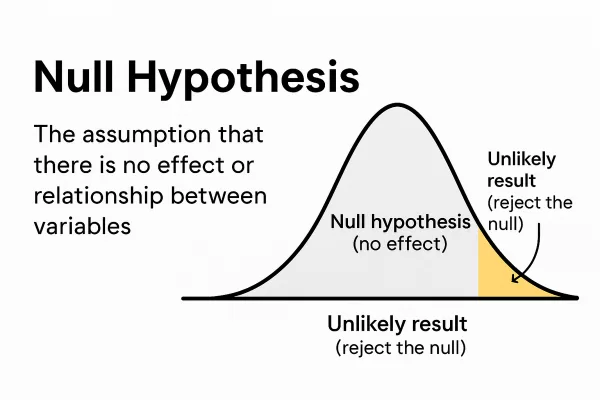
1. Null Hypothesis
The null hypothesis, denoted as H0, proposes no statistical significance or effect between the variables under study. It serves as the default position in hypothesis testing, suggesting that any observed differences are due to chance.
For example, if you’re testing the effectiveness of a new teaching method, the null hypothesis would state that this method does not affect a student’s performance compared to the conventional approach.
2. Alternative Hypothesis
Contrary to the null hypothesis, the alternative hypothesis, denoted as Ha or H1, asserts that there is a significant effect or relationship between the variables.

It is what researchers aim to prove through their data analysis. For instance, in the context of the teaching method example, the alternative hypothesis would suggest that the new method does significantly improve student performance.
3. Non-directional Hypothesis
A non-directional hypothesis does not specify the direction of the expected effect or relationship. It simply predicts that there will be a difference or relationship, without stating whether it will be positive or negative.
This type of hypothesis is suitable when the direction of the outcome is not known beforehand, allowing for an open-ended exploration of the data.
4. Directional Hypothesis
In contrast, a directional hypothesis specifies the expected direction of the relationship or effect between variables. It might predict, for example, that one group will score higher or lower than another based on some intervention.

This hypothesis is used when prior research or theory suggests a particular outcome direction.
5. Statistical Hypothesis
Statistical hypotheses are used to make inferences about a population based on sample data. These include both the null and alternative hypotheses.
Statistical hypothesis testing involves calculating the probability of observing the sample data if the null hypothesis is true. This process helps in deciding whether to accept or reject the null hypothesis based on the evidence provided by the data.
What is Hypothesis Testing: Step-by-Step
Here’s how hypothesis testing looks in my real workflow 👇
Step 1: Ask a Clear Question ❓
Bad question = bad analysis.
Did Feature X improve retention?
Step 2: Define the Hypotheses 📝
- H₀: Feature X did not improve retention
- H₁: Feature X improved retention
Step 3: Choose the Significance Level (α) 🎯
Usually 0.05 — a balance between confidence and risk.
Step 4: Collect Data 📊
Garbage data = garbage results. Always.
Step 5: Pick the Right Test 🧪
- T-test → comparing means
- Chi-square → categorical data
- Z-test → large samples
This is where understanding what is hypothesis testing truly pays off.
Step 6: Look at the P-Value 🔍
- p ≤ 0.05 → reject H₀
- p > 0.05 → don’t jump to conclusions
Mistakes I’ve Made -So You Don’t Have To 🚫
Let me save you some pain:
- Blindly trusting p-values
- Ignoring sample size
- Testing without clear hypotheses
- Confusing correlation with causation
Understanding the importance of hypothesis testing in data science also means respecting its limitations.
Hypothesis Testing in Machine Learning 🤖
Yes — machine learning uses hypothesis testing more than most people realize.
Examples include:
- Comparing model accuracy before and after tuning
- Validating feature importance
- Checking if performance improvements are statistically meaningful
Even behind cross-validation and A/B testing, hypothesis testing works quietly in the background.
Must-Know Terminology for Hypothesis Testing
1. Parameter
A fixed value describing a population characteristic.
2. Statistic
A value describing a sample, used to estimate a parameter.
3. Sampling Distribution
A probability distribution of a statistic from repeated sampling.
4. Standard Error
Measures how much a statistic varies from the population parameter.
5. Type I Error
Rejecting a true null hypothesis (false positive).
6. Type II Error
Failing to reject a false null hypothesis (false negative).
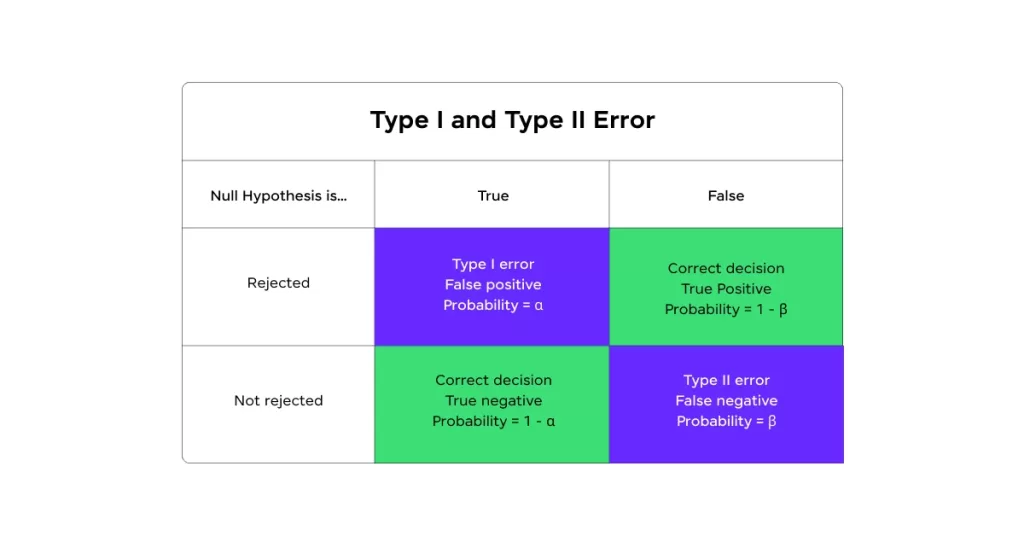
7. Level of Significance (α)
The probability threshold for rejecting the null hypothesis.
8. P-value
The probability of observing the result assuming the null hypothesis is true.
Final Thoughts ❤️
When I look back at my early days in data science, I realize that understanding what is hypothesis testing was a turning point. It transformed how I viewed data — from something I merely explored to something I could truly trust. The importance of hypothesis testing in data science lies in the confidence it gives you to make decisions that matter, not based on intuition or flashy dashboards, but on evidence that stands up to scrutiny. It bridges the gap between curiosity and certainty. If there’s one thing I’d tell anyone learning data science today, it’s this: don’t rush past hypothesis testing. Sit with it. Question it. Practice it. Once it clicks, you’ll stop guessing — and start deciding with clarity and conviction.
Related Reads:
- What is the Data Science Life Cycle? Stages, Frameworks & Workflow Explained
- 7 Powerful Insights Into Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) in Data Science: Types, Tools, Techniques & Best Practices
- Types of Software Testing – Different Types of Testing in Software
- What Is SciPy in Python? A Mind-Blowing Guide for Data Science and Engineers in 2025 for Data Science and Engineers
- Regression Testing of Software – The Unsung Hero of Software Engineering







