Introduction to Bubble Sort Algorithm
The bubble sort algorithm is one of the most simple sorting methods available in computer science and data structures. While bubble sort is not the most efficient sorting algorithm for long lists, it serves as an easy method to learn about sorting and helps us understand sorting.
What is Bubble Sort Algorithm?

Bubble sort is a comparison-based sorting method. Each time we go through a pass, we data fields that are adjacent to one another in the dataset will swap if they are out of order. We continue this process until we have fully sorted the entire dataset.
We have bubble sort because the largest elements of the data fields “bubble up” to the end of the list with every pass.
How Bubble Sort Algorithm Works (Step-by-Step)
Try to think of it like this: You are arranging books on a shelf based on the height of the book. You will compare two books at a time. If the first book is taller than the second book than you will swap the two books as such:

- You will continue to move down the shelf comparing books as pairs while swapping them if necessary.
- Continue until the largest book gets to the right end of the shelf.
- On the next pass go through the shelf again comparing and swapping books as necessary.
- Continue until the books are all sorted.
Example: Sorting [5, 3, 8, 4, 2]
- Pass 1: [3, 5, 4, 2, 8] → largest element (8) moved to the end
- Pass 2: [3, 4, 2, 5, 8]
- Pass 3: [3, 2, 4, 5, 8]
- Pass 4: [2, 3, 4, 5, 8] → sorted
Bubble Sort Algorithm in C
#include <stdio.h>
void bubbleSort(int arr[], int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n-1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n-i-1; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[j+1]) {
// Swap elements
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j+1];
arr[j+1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
int main() {
int arr[] = {5, 3, 8, 4, 2};
int n = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
bubbleSort(arr, n);
printf("Sorted Array: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
return 0;
}This bubble sort algorithm in C demonstrates how nested loops repeatedly compare and swap elements until the array is sorted.
Bubble Sort Algorithm in Java
public class BubbleSort {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {5, 3, 8, 4, 2};
bubbleSort(arr);
System.out.print("Sorted Array: ");
for (int num : arr) {
System.out.print(num + " ");
}
}
public static void bubbleSort(int[] arr) {
int n = arr.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n - i - 1; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
// Swap elements
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
}This bubble sort algorithm in Java follows the same principle but is implemented using Java syntax and array handling.
Bubble Sort Algorithm in Data Structure

In data structures, bubble sort is a:
- Comparison sorting → it is based on comparing data fields.
- In-place sorting → it doesn’t require any extra memory.
- Stable sorting → it does not rearrange equally valued data fields.
Time and Space Complexity of Bubble Sort
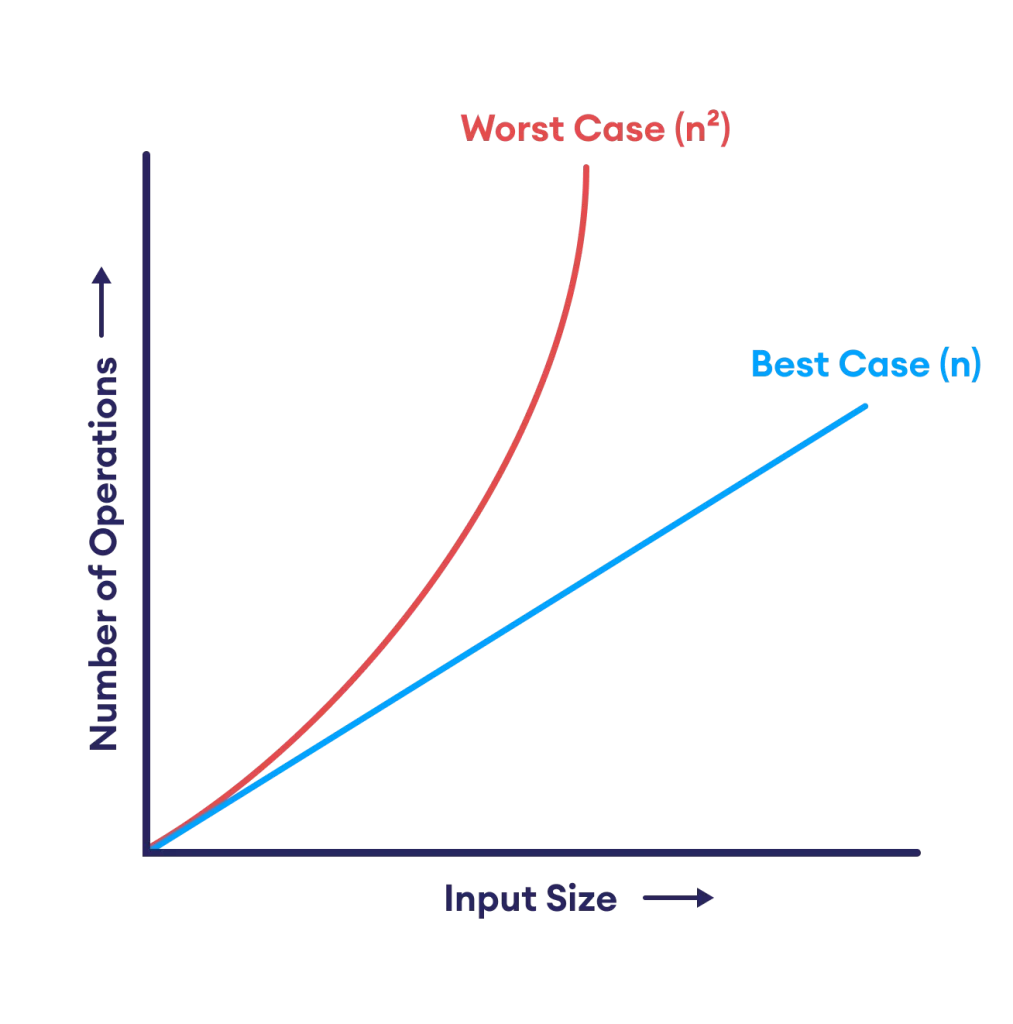
- Best Case (already sorted): O(n)
- Average Case: O(n²)
- Worst Case (reverse sorted): O(n²)
- Space Complexity: O(1) (only a few variables are needed)
Advantages of Bubble Sort Algorithm
✅ Very easy to understand and implement
✅ Useful for teaching sorting basics
✅ Works well with small datasets
Disadvantages of Bubble Sort Algorithm
❌ Very inefficient for large datasets
❌ Requires too many comparisons and swaps
❌ Outperformed by other sorting algorithms like Quick Sort, Merge Sort, or Heap Sort
Bubble Sort vs Other Sorting Algorithms
- Bubble Sort vs Selection Sort: Bubble is stable, selection is not.
- Bubble Sort vs Insertion Sort: Insertion is usually faster.
- Bubble Sort vs Merge/Quick Sort: Merge and Quick are much more efficient for large inputs.
Real-Life Analogy for Bubble Sort
Consider the bubble sort algorithm to be analogous to students organizing themselves by height in a line. Each student is compelled to look at the student next to them and
- If he/she is taller, they swap places.
- After a sufficient number of passes, the tallest student will “bubble” to the end of the line.
Conclusion
The bubble sort algorithm is one of the simplest sorting algorithms available. It is not optimally effective for large data processing. but, it is a fantastic introduction to algorithms and data structures for a beginner.
If you are preparing for interviews or studying sorting, learn bubble sort, then on to insertion sort, then merge sort, then quicksort.







