Hearing tech words like “byte and bit” can be really confusing initially. However, these two small words underlie everything that is digital from the files on your phone to your internet speed.
I’ll demystify bit or byte differences in human language, provide real world examples, and then answer the most common questions about byte and bits. You will leave with a really good grasp on these basic concepts.
What is a Bit?

- The bit (binary digit) is the smallest unit of data in computing.
- It can take only two values: 0 or 1.
- Consider it like a light switch — it’s either OFF (0) or ON (1).
- All digital data (no matter how complex) is ultimately made up of billions of bits.
For example:
- A letter such as “A” in binary is stored as bits (in ASCII, it is 01000001).
- Images, videos, and music, etc. are all just arrangements of bits.
What is a Byte?
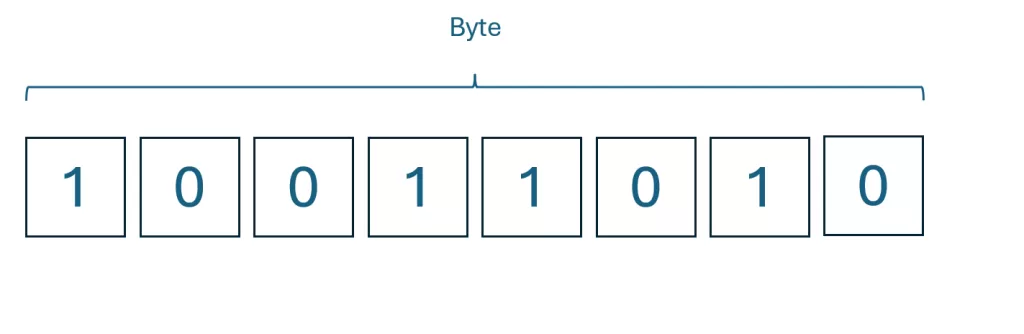
- A byte is a group of 8 bits.
- This is easier for humans to manage because, 8 bits can represent 256 different values (from 0 -255).
- Bytes are the de facto number when talking about file sizes or computer memory.
Examples:
- A single text character (like “A” or “b”) typically is 1 byte.
- A short email can be a few kilobytes.
- A high-definition movie may be a few gigabytes.
Difference Between Byte and Bit
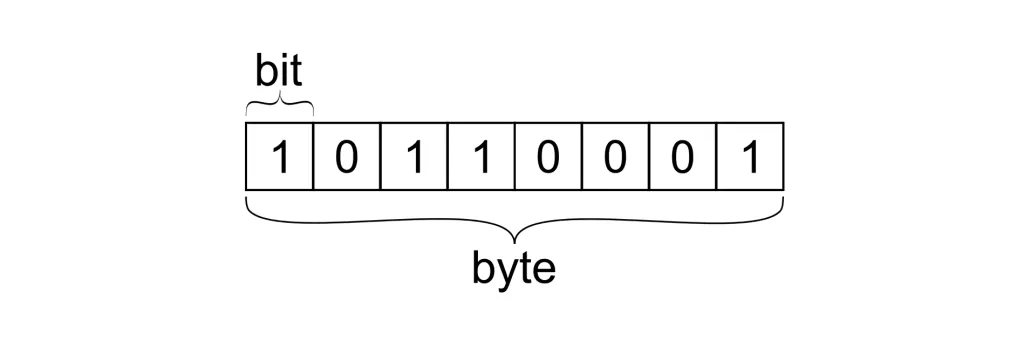
Here’s a simple comparison table to make sense of bit or byte differences:
| Feature | Bit | Byte |
| Size | Smallest unit (1) | 8 bits = 1 byte |
| Symbol | b (lowercase) | B (uppercase) |
| Represents | 0 or 1 | A number, character, or symbol |
| Usage | Internet speeds (Mbps) | File sizes (MB, GB) |
| Example | 100 Mbps speed | 700 MB movie file |
👉 Pro tip: Always pay attention to b (bit) vs B (byte) when reading internet plans or file storage.
Real-World Examples of Byte and Bits
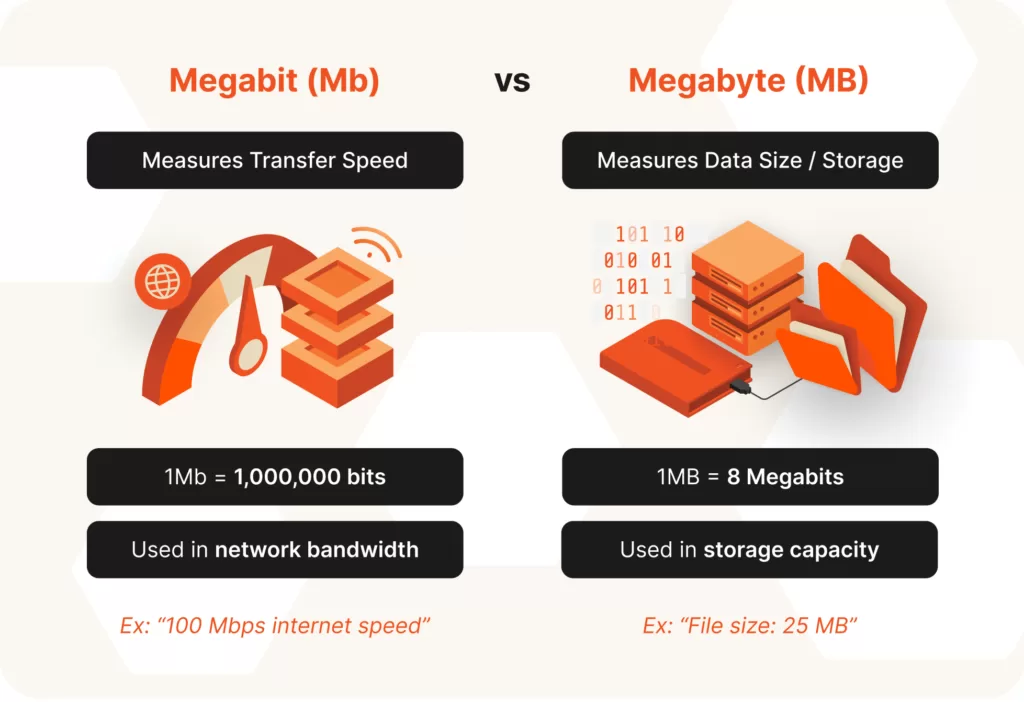
Internet Speed (Mbps vs MBps):
- Internet providers advertise speeds in Mbps (megabits per second).
- But when you download, your system shows MB/s (megabytes per second).
- Since 1 byte = 8 bits, a 100 Mbps connection = about 12.5 MB/s download speed.
File Sizes:
- A Word document = ~50 KB (kilobytes).
- An MP3 song = ~5 MB (megabytes).
- A 4K movie = ~10 GB (gigabytes).
Text Storage:
- “Hi” = 2 bytes.
- A novel like Harry Potter (~1M words) = a few MBs.
History of Bits and Bytes
- The bit property was given to information by Claude Shannon in 1948, who new information is a binary, make a choice property.
- A byte was introduced in the 1950s as a standard unit of data storage with IBM computers.
- After years of using bits and bytes, bytes became the standard way to measure storage, while bits become the standard for measuring communications speed.
Common Misconceptions: Bit or Byte?
- Mbps vs MBps confusion
Many people think a 100 Mbps internet plan = 100 MB/s download speed. Wrong! Divide by 8. - Capitalization matters
- b = bit
- B = byte
A small mistake can lead to huge misunderstandings.
- “Byte and bits” are interchangeable
Nope. They’re related but very different.
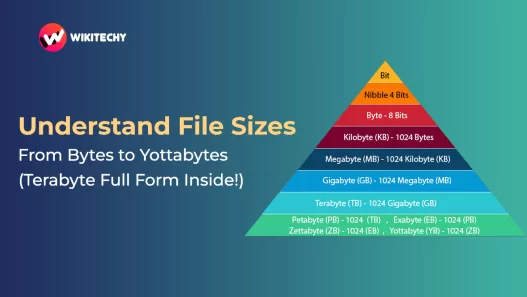
Related Units of Digital Storage
To understand byte and bits fully, you also need to know about digital storage units:
- 1 Kilobyte (KB) = 1,024 bytes
- 1 Megabyte (MB) = 1,024 KB
- 1 Gigabyte (GB) = 1,024 MB
- 1 Terabyte (TB) = 1,024 GB
This exponential scaling explains why your 256 GB phone can hold thousands of songs, videos, and apps.
FAQs about Byte and Bit
Q1: How many bits are in a byte?
👉 8 bits = 1 byte.
Q2: Which is bigger, bit or byte?
👉 A byte. It’s made of 8 bits.
Q3: Why is internet speed measured in bits, not bytes?
👉 Because communication systems deal with raw data transfer (bits). Storage systems use bytes.
Q4: How many bytes are in 1 KB?
👉 1,024 bytes (not 1,000 — that’s marketing trickery).
Final Thoughts on Byte and Bit
The world of computing wouldn’t exist without bits and bytes. Whether you’re looking at internet speed, saving a photo or streaming @Netflix, you need a bit and byte to dance invisibly
So, the next time you are asked about bit or byte, you will have all the knowledge to express it like a pro.