When entering the realm of data and IT, you will encounter two terms that are often confused: Database and Database Management System (DBMS). They may be similar, but they serve very different functions in computing. If you have wondered what is database and database management system, or even searched for the difference between database and dbms, this article will help explain it in easy, straightforward language — with real examples.
What is a Database?

A database is simply an organized collection of data that exists in electronic format. You can think of a database as a digital filing cabinet.
Definition: A database is a structured set of data held in a computer that can be easily accessed, managed, and updated.
Examples:
A customer list in Excel
A library catalogue
Contact information in your cell phone
Key Message: A database stores raw data, such as names, numbers, and records, but by itself, it does not manage how that data is accessed and secured.
What is a Database Management System (DBMS)?
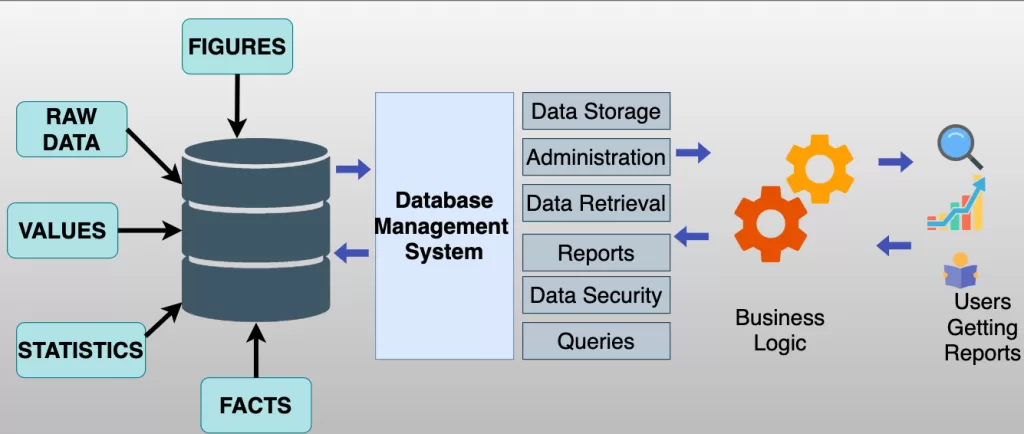
A Database Management System (DBMS) is software for users to create, manage, manipulate and secure databases.
Definition: DBMS is a software application that interacts with the database to ensure consistency, security, and easy access to data.
Examples of DBMS:
- MySQL
- Oracle Database
- Microsoft SQL Server
- PostgreSQL
- Mongo DB
Key Message: A DBMS acts as intermediary between users / applications, and the database.
Difference Between Database and DBMS
Here’s a side-by-side comparison that will make things crystal clear:
| Aspect | Database | Database Management System (DBMS) |
| Definition | Organized collection of data | Software that manages and controls databases |
| Function | Stores data | Provides tools to insert, update, retrieve, and delete data |
| Examples | Excel file, CSV file, phone contacts | MySQL, Oracle, SQL Server, MongoDB |
| Complexity | Simple storage | Complex software with multiple functionalities |
| Security | Limited (depends on file system) | High (user authentication, permissions, encryption) |
| Users | Can be accessed directly by end-user | Accessed via applications, admins, or developers |
Database and Database Management System in Real Life

To illustrate this more clearly, let’s say:
- An example of a database: A spreadsheet with employee records in your company
- An example of database management system: HR software you can use to search employees by department, make reports, and raise salaries, and restrict access to only what authorized users can see.
A database is simply the area for storage while a database management system is what provides the intelligence when managing the storage.
Why Do We Need a DBMS If We Already Have a Database?
At first glance, it may just seem like enough to store data in a database, but without a DBMS:
- Retrieving data in an database can be slow and ineffective.
- Security becomes weak (since anyone can just open the file and view or edit data if authorized)
- You cannot manage large amounts of data manually.
This is why companies use DBMS rather than a database only.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Database vs DBMS
Advantages of a Database:
- Easy to use and set up
- Inexpensive
- Good for storing small data (spreadsheets)
Disadvantages of a Database:
- Not secure
- No backup or recovery
Advantages of a DBMS:
- Provides security to stored data and identity and authentication for users
- Ensures consistency and integrity of stored data
- Multiple users can access data concurrently
- Complex queries can be done using SQL language
Disadvantages of a DBMS:
- Expensive (software license, hardware, and staff competence)
- Takes up more space to use
- Potential complexity of page management depending on the OO PDO application
Types of Databases and DBMS
To understand what is database and database management system, it is useful to have knowledge of the different types:
Types of Databases:
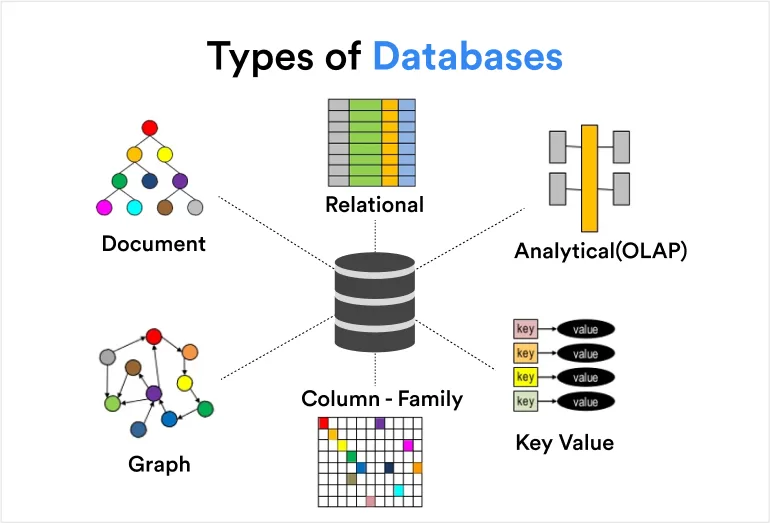
- Relational (consist of arrays whose values are stored in rows and columns)
- Non-relational (consist of documents or key value pairs, etc.)
- Cloud databases
- Distributed databases
Types of DBMS:

- Relational DBMS (RDBMS) – MySQL, Oracle
- NoSQL DBMS – Mongo DB, Cassandra
- In-memory DBMS – Redis
- Object-oriented DBMS
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is the primary difference between a database and a database management system?
A database is used to store, while a DBMS manages how information is stored, retrieved, and, secured.
Q2: It is possible to use a database without a DBMS?
While it is possible to use a database without a database management system, it would only be for small-scale things like spreadsheets. A database management system is needed for material information processing on an enterprise scale.
Q3: Is SQL a database or a DBMS?
SQL is neither a database or a DBMS. It is a language used to communicate with a database using a DBMS.
Conclusion
The difference between database and dbms is simple, but also very important:
- A Database is where data lives.
- A DBMS is the powerful software that makes that data useful, secure and manageable.
So, next time you hear database and database management system, remember this: without a database there is no data, but without a DBMS, that data is just a messy pile, unorganized.
👉 No matter you are a student, developer, or IT professional, understanding the differences between database and DBMS will help you design better databases, secure your data, and manage it more effectively.







