Why Knowing the Difference Between RAM and ROM Matters in 2025
Have you ever asked yourself: “What’s the difference between RAM and ROM?” 🤔
you’ve probably wondered why should I need to know the difference between ram or rom.
Does it matters at all. After all, isn’t it just a spec in your phone or laptop?
But here’s the catch: that spec decides how fast your apps run, how smooth multitasking feels, and even whether your system boots up correctly. Ever noticed how a phone with 12GB RAM + 256GB ROM can feel faster than an older laptop with the same processor? The answer lies in understanding RAM and ROM.
These terms confuse students, job seekers, and even working professionals. Yet they appear everywhere — in smartphone ads, laptop comparisons, and especially in technical interviews. And recruiters don’t want textbook definitions. They want to know if you truly understand how memory works.
By the end of this guide, you’ll know:
- What RAM and ROM are (with full forms and types)
- How they work in computers vs mobiles
- The five key differences every beginner must know
- Common confusions (like ROM in smartphones)
- Real-world insights, plus interview-focused Q&As
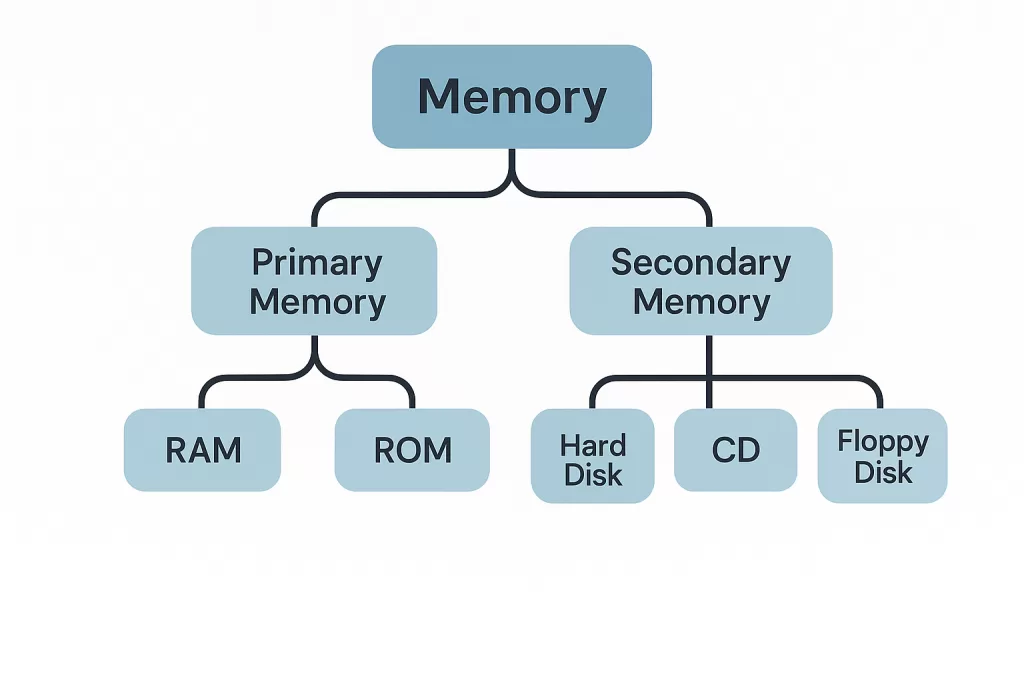
🔑 Key Highlights
- RAM (Random Access Memory): Temporary, volatile, fast. Used by CPU to run apps and processes.
- ROM (Read Only Memory): Permanent, non-volatile, slower. Stores firmware, BIOS, or mobile OS.
- Main difference between RAM and ROM: RAM loses data when power is off; ROM doesn’t.
- RAM in mobiles: Runs apps you open.
- ROM in mobiles: Stores OS, apps, and personal files.
- Simple analogy: RAM = your short-term memory 🧠, ROM = your permanent memory 📚.
What is RAM and ROM? (Full Form + Explanation)
Let’s break it down clearly 👇
What is RAM (Random Access Memory)?
RAM is your device’s short-term working memory. It holds apps, programs, and files while you’re using them. The moment power cuts off — 💨 everything’s gone.
- Full Form: Random Access Memory
- Volatile: Loses data when powered off
- Role: Makes multitasking fast and smooth
👉 Types of RAM:
- Static RAM (SRAM): Super fast, used in CPU cache.
- Dynamic RAM (DRAM): Common system memory in PCs and mobiles.
Best Practices / Real Example:
Developers often suggest at least 8GB RAM for coding or gaming laptops. Why? Because modern IDEs like VS Code or Android Studio eat RAM like snacks 🍪. With just 4GB, your system lags badly when running Docker or emulators.


What is ROM (Read Only Memory)?
ROM is your device’s permanent memory. Unlike RAM, it doesn’t forget. ROM stores instructions that start your computer or mobile when you power it on.
- Full Form: Read Only Memory
- Non-volatile: Retains data even without power
- Role: Stores BIOS, firmware, or mobile OS
👉 Types of ROM:
- PROM: Can be written once after manufacturing
- EPROM: Erased by UV light, then reprogrammed
- EEPROM: Erased electrically (used in modern hardware)
- Mask ROM: Pre-programmed during manufacturing
Real-World Use Case:
When you press the power button, it’s ROM that kicks in before RAM even wakes up. Without ROM, your device wouldn’t know how to start.

Difference Between RAM and ROM (Easy Comparison Table)
Here’s the ram and rom difference in a nutshell:
| Feature | RAM (Random Access Memory) | ROM (Read Only Memory) |
|---|---|---|
| Volatility | Volatile – data lost when power is off | Non-volatile – data retained |
| Speed | Very fast (GHz range) | Slower (MHz range) |
| Read/Write | Read & Write supported | Read-only (with exceptions like EEPROM) |
| Usage | Stores data currently used by CPU | Stores firmware, BIOS, OS |
| Capacity | Large (GBs) | Small (MBs to a few GBs) |
| Cost | More expensive | Cheaper |
| Examples | Apps, multitasking | BIOS, embedded systems |
👉 This table also answers queries like:
- five difference between ram and rom
- differentiate between ram and rom
- what are the difference between ram and rom
RAM vs ROM in Computer and Mobile 📱💻
- In Computers:
- RAM = runs multiple programs at once (browsers, IDEs, games).
- ROM = stores BIOS that checks hardware before booting OS.
- In Mobiles:
- RAM = keeps apps running in background.
- ROM = internal storage (OS, apps, photos, videos).
👉 So next time you see a phone spec “8GB RAM + 128GB ROM”, you’ll know exactly what that means.
FAQs on RAM and ROM
1. What is the difference between RAM and ROM?
RAM is volatile and temporary. ROM is non-volatile and permanent.
2. What is ram and rom full form?
- RAM = Random Access Memory
- ROM = Read Only Memory
3. What is the difference between rom and ram?
ROM stores permanent instructions (like BIOS). RAM only stores temporary active data.
4. What is ram and rom in computer?
In computers, RAM handles multitasking. ROM ensures system startup.
5. What is ram and rom in mobile?
RAM runs apps, ROM stores the OS and files.
6. Explain the difference between ram and rom with examples.
RAM example: Running MS Word. ROM example: BIOS running before Windows starts.
Conclusion (Career + Tech Insight)
So, the difference between RAM and ROM boils down to this:
- RAM = speed and multitasking 🏃
- ROM = permanence and reliability 🛡️
For a career in tech, never memorize definitions blindly. Interviewers love when candidates connect theory with practice. For example, say:
“RAM is like my workspace during coding, while ROM is like the rulebook that tells my laptop how to boot.”
That kind of clarity shows you don’t just study for exams — you understand technology.
And here’s the takeaway for daily life:
- If your laptop hangs, check your RAM.
- If your phone won’t start, ROM might be corrupt.
Now the next time someone asks, “what is the difference between ram and rom?”, you can explain it like a pro.







