Selenium is one of the most widely used tools for web automation testing. While working with Selenium, testers often face unexpected errors during execution. These errors are known as exceptions. If not handled properly, exceptions can cause test failures, flaky automation scripts, and wasted debugging time.
Exception handling in Selenium helps you manage runtime errors gracefully, improve test stability, and build reliable automation frameworks. In this article, we will explore the most common Selenium exceptions, why they occur, and how to solve them with best practices and examples.
What Is Exception Handling in Selenium?

An exception is an unwanted or unexpected event that occurs during program execution and disrupts the normal flow of a test script.
In Selenium:
- Exceptions occur mainly due to timing issues
- Incorrect locators
- Changes in DOM
- Browser or environment problems
Exception handling allows:
- Graceful failure handling
- Better debugging
- Reduced test flakiness
- More reliable test execution
Types of Exceptions in Selenium
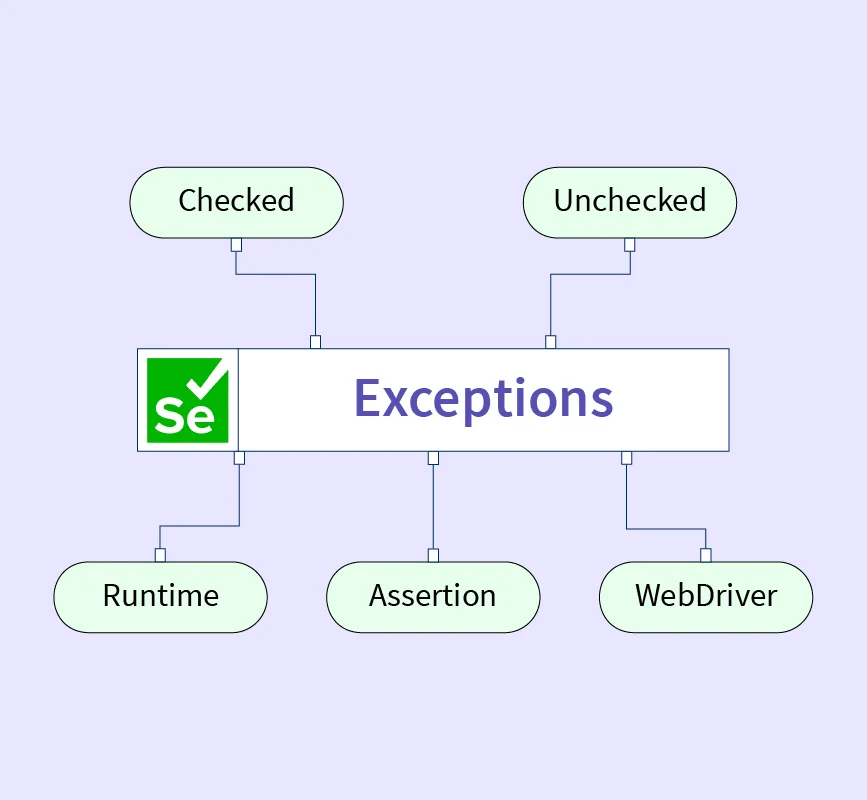
Selenium exceptions are mainly:
- Checked Exceptions – Occur at compile time (rare in Selenium)
- Unchecked Exceptions – Occur at runtime (most Selenium errors)
Selenium commonly throws runtime exceptions.
1. NoSuchElementException

Cause
Occurs when Selenium cannot find a web element using the given locator.
Common Reasons
- Incorrect XPath or CSS selector
- Element not loaded yet
- Element inside iframe or shadow DOM
- Typo in locator
Example
driver.findElement(By.id("loginBtn")).click();
Solution
- Verify locator using browser DevTools
- Use explicit waits
- Switch to iframe if required
WebDriverWait wait = new WebDriverWait(driver, Duration.ofSeconds(10));
wait.until(ExpectedConditions.visibilityOfElementLocated(By.id("loginBtn")));
2. StaleElementReferenceException

Cause
Occurs when the referenced element is no longer attached to the DOM.
Common Reasons
- Page refresh
- DOM update after AJAX call
- Navigation to another page
Solution
- Re-locate the element before using it
- Avoid storing WebElements for long time
WebElement button = driver.findElement(By.id("submit"));
button.click(); // re-locate before using
3. ElementNotInteractableException

Cause
Occurs when an element exists but cannot be interacted with.
Common Reasons
- Element hidden
- Element disabled
- Overlay blocking the element
Solution
- Use explicit waits
- Scroll into view
JavascriptExecutor js = (JavascriptExecutor) driver;
js.executeScript("arguments[0].scrollIntoView(true);", element);
4. ElementClickInterceptedException

Cause
Another element is blocking the target element.
Common Reasons
- Popups
- Ads
- Loader overlays
Solution
- Close popup
- Wait until overlay disappears
- Use JavaScript click
js.executeScript("arguments[0].click();", element);
5. TimeoutException
Cause
Occurs when a condition is not met within the specified time.
Common Reasons
- Slow application
- Wrong expected condition
- Network latency
Solution
- Increase wait time
- Use correct wait condition
wait.until(ExpectedConditions.elementToBeClickable(element));
6. InvalidSelectorException

Cause
Occurs when XPath or CSS selector syntax is incorrect.
Example of Wrong XPath
//div[@id='login'
Solution
- Validate XPath in browser
- Use simpler locators
7. WebDriverException
Cause
Occurs due to browser or driver issues.
Common Reasons
- Browser crash
- Version mismatch
- Driver not compatible
Solution
- Update browser and WebDriver
- Use WebDriverManager
WebDriverManager.chromedriver().setup();
8. SessionNotCreatedException

Cause
Occurs when Selenium cannot create a new browser session.
Common Reasons
- Browser version mismatch
- Incorrect driver path
Solution
- Match browser and driver versions
- Use WebDriverManager
9. NoSuchFrameException
Cause
Occurs when Selenium fails to switch to a frame.
Solution
- Verify frame name or index
- Switch correctly
driver.switchTo().frame("frameName");
10. NoAlertPresentException

Cause
Occurs when Selenium tries to handle an alert that does not exist.
Solution
- Check alert presence before switching
try {
driver.switchTo().alert().accept();
} catch (NoAlertPresentException e) {
System.out.println("No alert present");
}
Using Try-Catch for Exception Handling
Basic Example
try {
driver.findElement(By.id("login")).click();
} catch (NoSuchElementException e) {
System.out.println("Element not found");
}
Best Practices for Exception Handling in Selenium
- Always use explicit waits
- Avoid
Thread.sleep() - Handle dynamic elements carefully
- Use proper locator strategies
- Implement retry logic for flaky elements
- Log exceptions properly
- Capture screenshots on failure
- Use Page Object Model (POM)
Advanced Exception Handling Techniques
Custom Wait Utility
Create reusable wait methods for stability.
Global Exception Handling
Handle exceptions at framework level using listeners.
TestNG Listeners
Capture screenshots on failures automatically.
Why Exception Handling Is Critical in Selenium Automation
- Improves script reliability
- Reduces flaky test failures
- Makes debugging easier
- Saves execution time
- Enhances automation framework quality
Conclusion
Mastering exception handling in Selenium is essential for building robust and maintainable automation scripts. By understanding common Selenium exceptions and applying the right solutions, you can significantly improve your test execution stability. Proper waits, correct locators, and structured exception handling are the backbone of any successful Selenium automation framework.
If You Want to Learn Software Testing Course, or any other course & Internship visit www.kaashivinfotech.com.