🟢 Key Highlights
- What network networking actually means
- A personal take on why networking isn’t as boring as it sounds
- Real-life analogies to make this topic easy to digest
- Basics of computer networking you wish someone had explained earlier
- Tips for beginners stepping into IT or tech courses
- Internal & external resources to help you go deeper
- Simple, relatable, and human-style explanation with real examples
👋 Let’s Get Real About Networking
I still remember the first time I heard the term “network networking.” I thought, “Is that like making friends with computers or something?” 😅 Sounds silly, right? But trust me, that was my honest first thought.
Fast forward to today—after tinkering with routers, troubleshooting LAN parties gone wrong, and diving into my tech course—I finally get it. And now, I’m here to share everything I wish someone had told me when I first got into networking.
So, let’s break it down like we’re just two friends chatting over coffee ☕.
🧠 What Is Computer Networking (Without the Tech )?
Okay, picture this.
You’ve got a laptop, your friend’s got a phone, and your sibling’s playing online games on a PC—all connected to the same Wi-Fi. Now, imagine this setup, but bigger… like thousands of devices connected globally. That’s what computer networking is all about: connecting devices to share information.

But there’s more. Let’s unpack the core fundamentals you absolutely need to know.
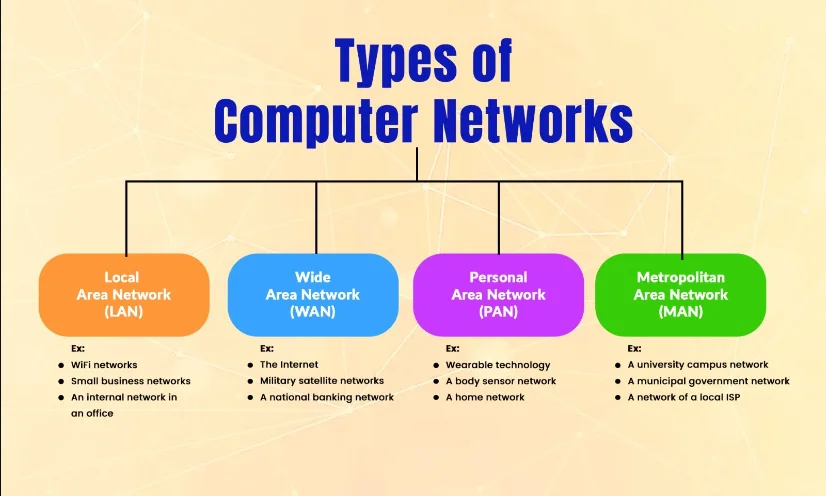
🔑 1. Types of Computer Networks – It’s Not Just Wi-Fi
When people say networking, they often think Wi-Fi is the whole deal. Nope. There’s a variety:
- LAN (Local Area Network): Think home, schools, or small offices.
- WAN (Wide Area Network): The Internet itself is a WAN! It connects devices across countries.
- MAN (Metropolitan Area Network): Like a city-wide network—used by large corporations or municipal systems.
- PAN (Personal Area Network): Your Bluetooth headset and your phone chatting—yep, that’s PAN.
🧩 Mini story: I once connected two laptops with just an Ethernet cable during a power cut. No Internet, but we still shared files. That’s a tiny LAN in action!
💡 2. IP Addressing and Subnetting – Sounds Scary, Isn’t Really
IP addresses are like your device’s home address. Without one, your data wouldn’t know where to go.
But what about subnetting?
Here’s how I understood it: imagine a huge apartment building (that’s your network). Subnetting splits it into smaller flats or sections. Each room still gets mail, but it’s now more organized and faster to deliver.
When you learn networking, you’ll come across this early—and often. But don’t worry. It’ll start making sense once you see it in action.
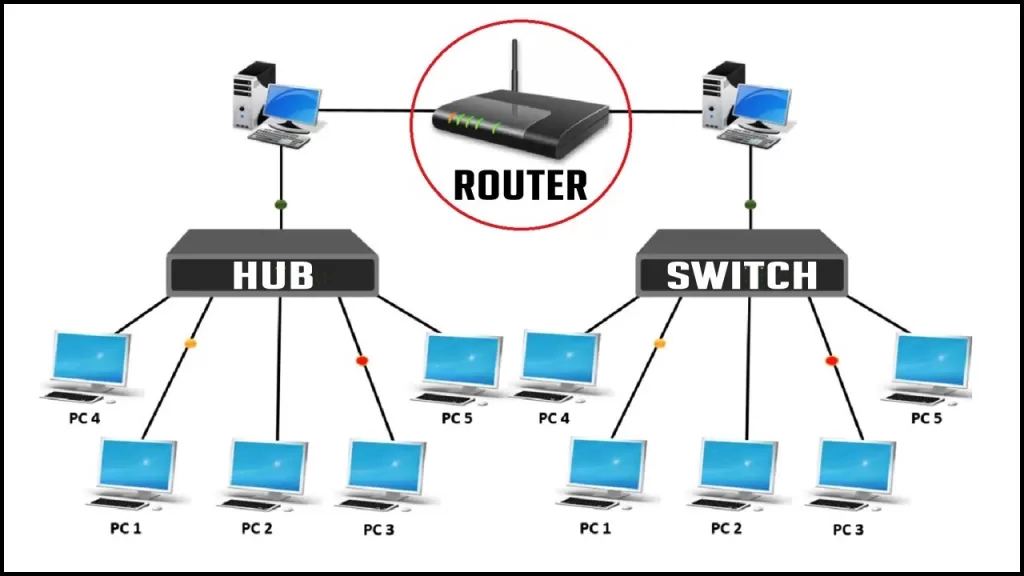
⚙️ 3. Switches, Routers, and Hubs – The Middlemen of Networking
- Routers connect different networks together. Think of them as airport hubs redirecting flights.
- Switches work within one network, sending data to the right device. Like a hotel receptionist handing your parcel directly to you.
- Hubs just broadcast data to everyone, whether they asked for it or not. Not efficient, but simple.
🎯 Pro tip: If you’re into IT certifications or tech courses, understanding routers and switches is non-negotiable.
👉 If you’re curious, Cisco’s Networking Academy has a solid free course on this.
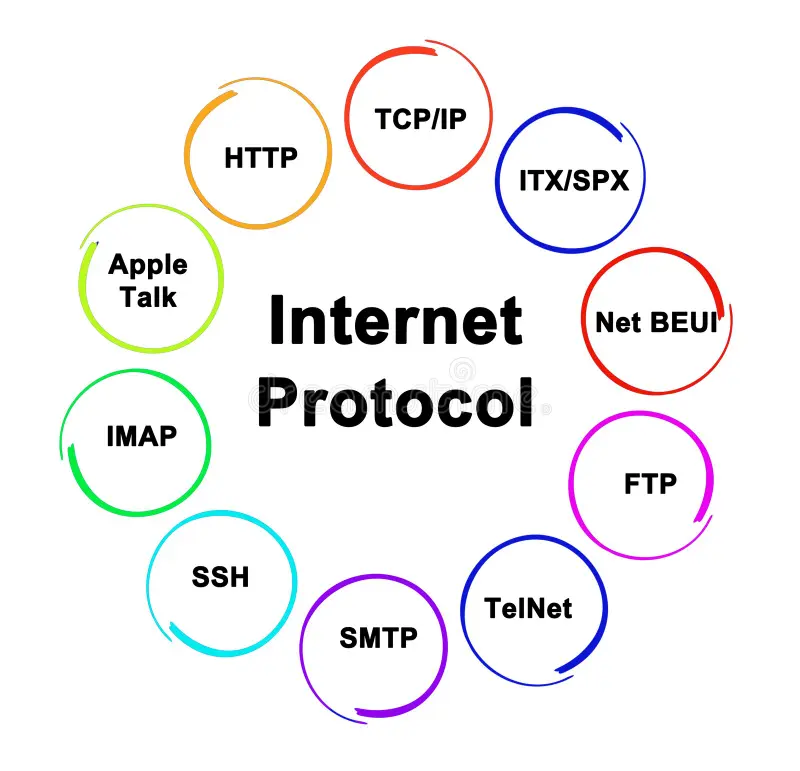
🧰 4. Protocols – The Rules of the Game
A protocol is just a set of rules. Just like we follow grammar while speaking, devices follow protocols while sharing data.
A few you’ll hear all the time:
- HTTP/HTTPS – Browsing websites
- FTP – File transfers
- TCP/IP – The backbone of the internet
- DNS – Like the contacts app for websites (turns google.com into an IP address)
🎙️ Real-world example: Ever tried sending a file via WhatsApp and it just fails halfway? That’s usually a protocol timeout. Understanding networking helped me know why that happens!
📡 5. Wireless Networking – The Invisible Magic
Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, 4G, 5G—this is wireless networking. No cables, just pure electromagnetic wizardry.
But did you know there’s a downside too?
Wireless networks are more vulnerable to attacks. That’s why you keep hearing about “secure your Wi-Fi password.” It’s not just paranoia—it’s cybersecurity 101!
This is where network networking collides with cybersecurity. 🔐 If you’re into ethical hacking or want to build a career in cybersecurity, you need a strong grip on wireless protocols.
🔒 6. Network Security – Because Not Everyone Online Is Nice
We lock our homes at night. Why should our data be any different?
Network security involves:
- Firewalls – Your bouncer at the gate.
- Antivirus software
- Encryption – Making data unreadable to outsiders.
- VPNs – Like a private tunnel through the open internet.
⚠️ Personal story: I once logged into public Wi-Fi at a café. Within an hour, my email was acting weird. A friendly techie told me I probably got hit by a “Man-in-the-Middle” attack. 😨 Never again.
🧠 7. Networking Models – The OSI and TCP/IP Stack
Here’s the honest truth: I ignored this part when I first studied network networking. And I regretted it during interviews.
The OSI model has 7 layers—each layer doing a specific job. Think of it like layers of a cake: you need them all for the whole thing to work.
- Physical
- Data Link
- Network
- Transport
- Session
- Presentation
- Application

💥 Remember: “Please Do Not Throw Sausage Pizza Away”—that’s how I memorized the OSI layers. You’re welcome. 😉
💬 Why Should You Even Care About Networking?
If you’re planning to:
- Get into IT
- Pursue tech courses like cybersecurity, cloud computing, or data science
- Become a network engineer or ethical hacker
- Or just finally understand what your router actually does…
📝 Final Thoughts
I used to think networking was this boring, ultra-technical thing buried in thick textbooks. But once I got it, everything in tech started to click.
Now, every time my Wi-Fi slows down or someone asks, “Why does the internet work like that?”—I have answers. And you will too.
So take your first step. Learn networking not because it’s in the syllabus, but because it’s how the digital world speaks.





