The CPU processor is the main brain of your computer. This small but powerful chip does all of the calculations, runs your programs, and ultimately is what makes your device work properly. In this guide, we will discuss what a processor in CPU does, how it works, what types there are, and the best way to decide which one is the best for your needs, whether you are a gamer, programmer or just checking your email.
What is a CPU Processor?
The CPU (Central Processing Unit) is the main piece in your computer that actually runs commands. It executes instructions just like a chef in a chaotic kitchen. The chef interprets the recipe (program code), gathers the ingredients (data) in this case, and serves from the kitchen (output).
What you need to know:
- The CPU processes and executes commands from the software and hardware in the computer
- The CPU works with memory (RAM) and storage (SSD/HDD)
- Speed depends on clock speed, number of cores, and architecture.
CPU Processor Architecture
CPU processor architecture establishes the design, structure, and flow of the chip in your computer. Simply put, it is the architectural drawing that specifies how a CPU processor processes instructions, accesses data, and communicates with other hardware.
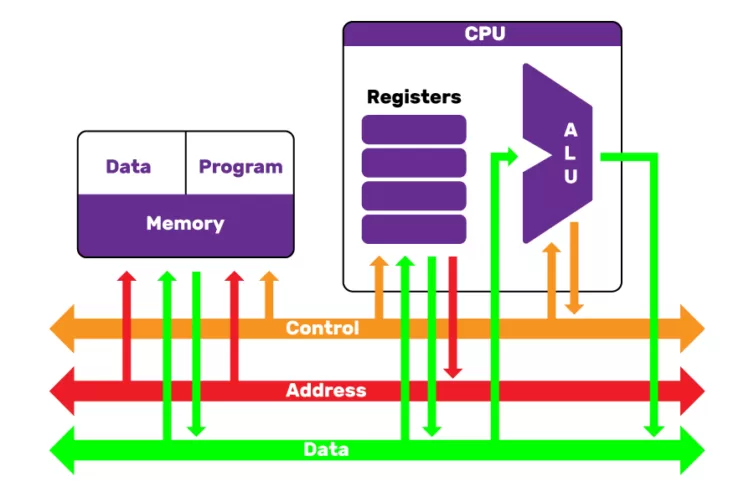
Basic Components of CPU Architecture
A modern cpu processor contains several important units:
- Control Unit (CU) – Coordinates instruction and data movement from unit to unit.
- Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) – Performs all mathematical and logical functions.
- Registers – Very fast storage for very immediate data use.
- Cache Memory – Memory for frequently used instructions, leading to increased CPU processing speed.
- Buses – Pathways to carry data, addresses, and control signals.
Instruction Set Architecture (ISA)
The ISA is the “language” of the processor in the CPU.
- x86/x64 – The architecture common on desktops and laptops, good compatibility, and performance.
- ARM – The architecture used on smartphones, tablets, and some laptops emphasizing efficiency and low power use.
- RISC-V – A new open-source architecture which is getting a lot of attention as a flexible architecture.
CPU Architecture Types
Different CPU designs uses different philosophies:
- Von Neumann Architecture – both the instructions and data utilize the same memory pathways/memory.
- Harvard Architecture – instructions and data have separate storage/memory pathways, allowing potential performance improvements in some systems.
- Hybrid Architectures – Modern CPUs now use many aspects of these arrangements for performance and efficiency.
Modern Enhancements
The cpu processors used today are far more advanced than the early chips:
- Multi-core Design – The more cores, the better the multitasking.
- Hyper-Thread / SMT – Each core can run multiple threads simultaneously.
- Integrated Graphics – The CPU can handle basic graphics without a separate graphics processor.
- AI Acceleration – New CPUs include neural processing units for AI related tasks.
The Role of the Processor in CPU
The CPU processor executes millions, maybe even billions, instructions per second. It follows the fetch-decode-execute cycle:
- Fetch – retrieve an instruction from memory.
- Decode – interpret what the instruction means.
- Execute – carry out the operation, either performing mathematics, moving data anywhere in your devices memory, or controlling other components.
Without your CPU processor, your device will be useless, like a car without an engine.
Types of Processors used in CPU

Not all processors are created equal. Here are the main categories:
1. Single-Core Processors
Older technology — one core to handle tasks. Slow for multitasking.
2. Dual-Core & Quad-Core Processors
Two or four cores that allow multiple tasks to be processed at once.
3. Multi-Core Processors (6-Core, 8-Core, etc.)
Modern CPUs, such as Intel Core i7/i9 or AMD Ryzen series, have many cores for heavy workloads like gaming, video editing, and AI.
Key CPU Processor Specifications You Should Know
Here are the some specifications of processor:
- Clock Speed (GHZ) – Generally higher is better, although how efficient an individual processor is really matters too.
- Cores & Threads – More cores generally means better multitasking.
- Cache Memory – Storing frequently accessed data for quicker access.
- TDP (Thermal Design Power) – amount of power it uses and how much heat it generates.
CPU vs GPU: What’s the Difference?

CPU for general tasks, while a GPU (Graphics Processing Unit) is an internally programmed unit for rendering images internally, plus running parallel calculations. For gaming you need both; for office work, the processing from the CPU is the main consideration.
Intel vs AMD: Which CPU Processor is Better?

- Intel – Known for stability, strong single-core performance, and higher clock speeds.
- AMD – Offers more cores and better multi-threaded performance at competitive prices.
How to Choose the Right Processor
When selecting a CPU take in mind the following:
- For daily tasks: Intel Core i3 or AMD Ryzen 3.
- For gaming: Intel Core i5/i7 or AMD Ryzen 5/7.
- For productivity workloads: Intel Core i9 or AMD Ryzen 9/Threadripper.
Future of CPU Processors in 2025 and Beyond
The CPU processor landscape is changing quickly:
- Transistor sizes are getting smaller (3nm chips).
- AI optimized architectures.
- Hybrid designs of performance and efficiency cores.
Tips to Boost Your Processor Performance
- Make sure your device staying cool with adequate ventilation.
- Make sure the BIOS and drivers are up to date.
- Limit the programs you have running unnecessarily in the background.
Conclusion
The CPU processor is the heart of your computer, and learning about what it does will help you make wise buying decisions and increase the performance of your system. Whether you’re an average user or an extreme gamer, the right CPU processor can make a difference.