If you’ve ever dreamt about building your own AI chatbot, one that remembers, reasons, and responds like a real human — I’ve got news for you. The tool that made me rethink everything I knew about conversational design is called LangGraph.
Yes, LangGraph — a powerful framework that takes Python-based conversational AI to a whole new level. When I first heard about it, I thought, “Okay, just another library.” But when I actually used it? It felt like unlocking a secret layer of intelligence behind AI agents.
In this blog, I’ll share what I learned, how I built a working LangGraph chatbot, and why I think it’s one of the most exciting technologies for anyone working in AI, machine learning, or automation.
What Exactly is LangGraph?

To put it simply, It is a framework designed to make conversational AI development easier, more structured, and deeply customizable.
Think of LangGraph as the “brain wiring” of your AI — it connects multiple reasoning steps, memory states, and tools to help your chatbot think, act, and adapt in real time.
Here’s what blew my mind 👇
- You can build stateful conversational agents (they remember your past chats!).
- You can combine reasoning steps with custom tools like APIs or databases.
- It integrates beautifully with LangChain — another popular framework for LLM-based applications.
In short, LangGraph lets your AI behave more like a person, not just a parrot that repeats facts.
👉 You can check out the official LangGraph documentation here if you want to dive deeper.
My First Encounter with LangGraph
When I started experimenting with LangGraph, I was building a simple Python chatbot for an educational project. I wanted it to remember previous questions, not just answer them.
Most libraries struggled with state management — the AI would “forget” context easily. But when I switched to LangGraph, something clicked.
LangGraph allowed me to:
- Define graphs of logical steps (like “analyze input → check memory → respond”).
- Manage conversations as states, not just text responses.
- Plug in memory, tools, and APIs seamlessly.
I remember running my first test, asking the bot:
“Hey, what did I ask you earlier?”
And it replied, perfectly recalling my previous message. That’s when I knew I was onto something real.
How It Works:
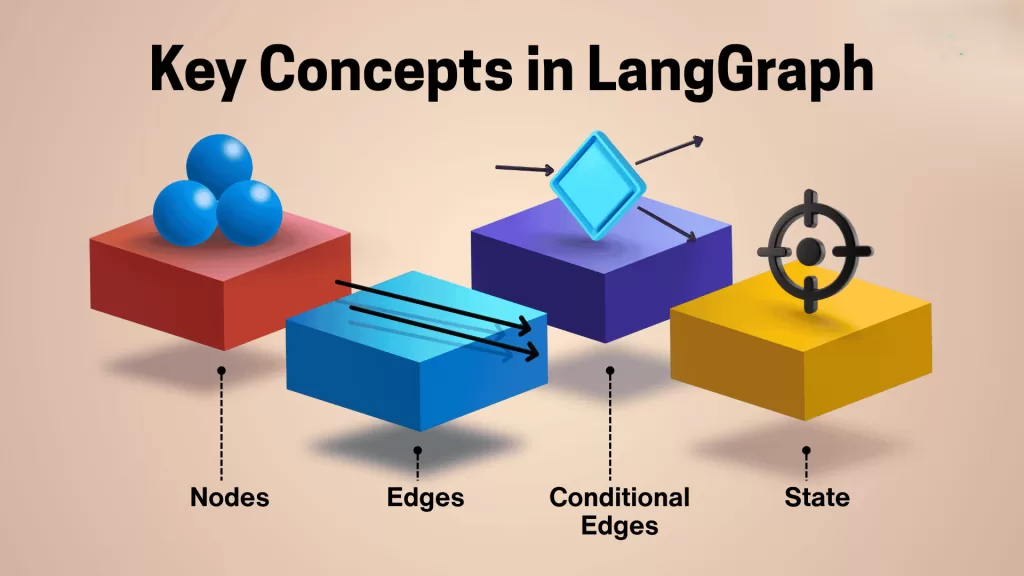
At its core, LangGraph uses a graph-based architecture — where each node represents a task or reasoning step, and the edges define how data flows between them.
Let me break it down in a human way 👇
Imagine you’re building a chatbot named “Aiden.”
Here’s how It helps you design Aiden’s mind:
- Nodes = Steps like “Understand message”, “Fetch info”, “Generate reply”.
- Edges = The flow between steps (who talks to whom).
- Memory = The AI’s brain that stores chat history.
- Tools = Optional APIs or functions (like a weather checker or calculator).
You connect these pieces like LEGO blocks using Python — and suddenly, Aiden starts thinking more like a human than a script.
Setting Up LangGraph with Python
Here’s a simplified way to start using It in Python 👇
Step 1: Install Dependencies
Step 2: Create a Simple Graph
This simple snippet creates a LangGraph chatbot that greets users — but trust me, this can scale into a full-fledged assistant.
Importance Of LangGraph for Conversational AI
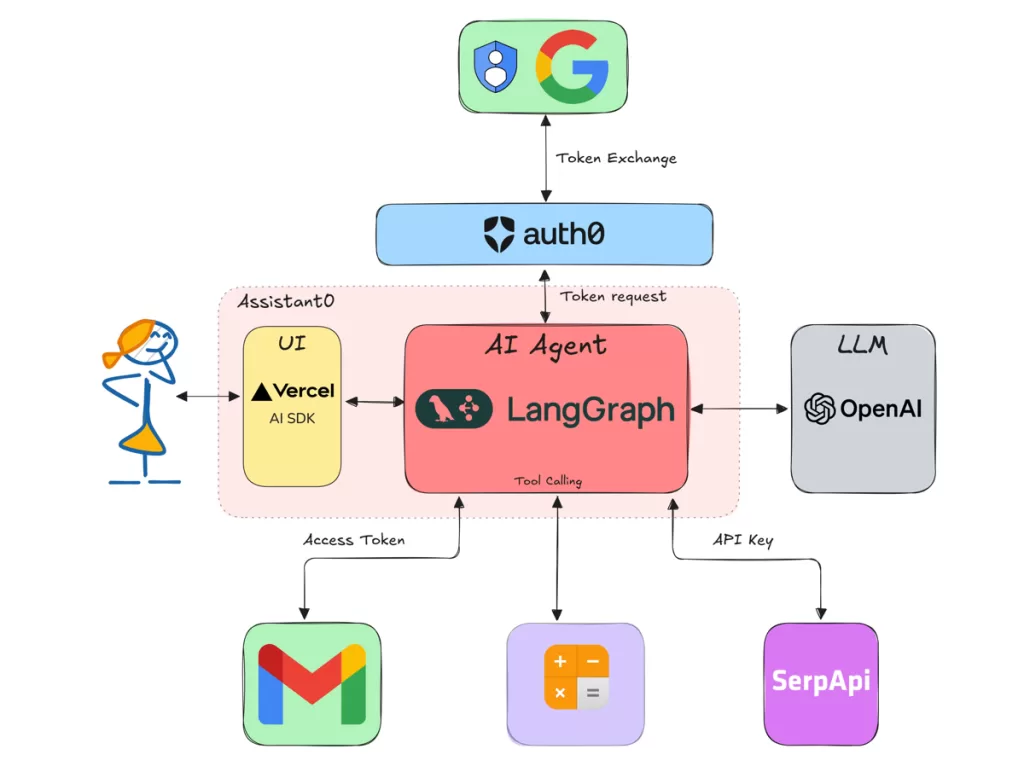
What makes It so special? For me, it’s the control it gives developers.
When building chatbots, I often struggled to balance context retention and response logic. But It solved that elegantly.
Here’s why I swear by it now:
- It’s modular — you can tweak parts without breaking the whole.
- It’s memory-aware — conversations flow naturally.
- It’s integrated with LangChain — meaning you can use all your favorite tools (OpenAI, Anthropic, Hugging Face, etc.).
- It’s open-source, so you can explore and customize everything.
If you’ve ever worked with Rasa, Dialogflow, or ChatterBot, you’ll immediately notice how much cleaner and developer-friendly It feels.
Real-World Use Cases of LangGraph

- 🧑💻 Customer Support Bots – Smart agents that handle context-heavy conversations.
- 🎓 Learning Assistants – Educational tutors that remember what students previously asked.
- 💬 Therapy or Mental Health Bots – Conversations that adapt emotionally and contextually.
- 🧾 Automation Agents – AIs that combine data fetching, reasoning, and output generation in one flow.
For me, I used It in a college project where I built a career counseling chatbot that remembered user preferences
LangGraph vs LangChain

| Feature | LangChain | LangGraph |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Framework for LLM apps | Framework for stateful conversational AI |
| Focus | Tool integration | Logical flow & memory management |
| State Handling | Limited | Built-in |
| Visualization | Minimal | Graph-based (clear flow) |
In short:
LangChain gives your bot tools,
LangGraph gives your bot brains.
Together, they make your Python conversational AI unstoppable.
Final Thoughts:
If there’s one takeaway from my experience, it’s this — It is not just another tool. It’s the future blueprint for how we’ll design AI conversations in the next decade.
It gives developers like us power, clarity, and control — the three things every AI system desperately needs.
So, if you love Python and have ever wanted to create your own AI assistant, LangGraph is where you should start.
Want to Learn More About Python & Artificial Intelligence ???, Kaashiv Infotech Offers Full Stack Python Course, Artificial Intelligence Course, Data Science Course & More Visit Their Website www.kaashivinfotech.com.