Machine learning is a main branch of Artificial Intelligence that enables the development of algorithms and systems that are capable of learning patterns from data. Rather than being explicitly programmed for every rule, ML models adjust to identify relationships with the data presented to them.

At a high level,
Machine learning allows computers to learn and improve by themselves like humans learn from experience.
Explore our free, ongoing course: Introduction to Data Science Skillup.
This course includes weekly study plans, notes, quizzes, and even coding challenges.
There are many different fields of machine learning, but the commonly recognized three are Supervised,Unsupervised and Reinforcement
Learning, as well as two newer forms, Semi-Supervised Learning and Self-Supervised Learning.
Module 1:Types of Machine Learning.

1. Supervised Learning
Through trained models, stained data are used to forecast or categorize unknown data.
2. Unsupervised Learning
Determines trends or clusters of data sets that do not have defined labels.
3. Reinforcement Learning
Acquires through the action of exposure to an environment and by getting rewards or punishment.
Additional Learning Types
Self-Supervised Learning
An increasing area that automatically creates labels based on the data itself.
It is an unsupervised learning technique that is however considered a separate category because of its effectiveness in the training of large-scale models.
Semi-Supervised Learning
Uses a small number of labeled samples and a large unlabeled dataset- This is applicable in cases where the labeling is costly or time-consuming.
Module 2: Financing the Pipeline.
The module is devoted to preprocessing, exploratory analysis, and model evaluation in order to guarantee the high-quality and consistent results.
1. Data Preprocessing
ML workflow Data cleaning Preprocessing of data in Python.
- Feature scaling
- Feature extraction
- Feature engineering
- Selection methods of features.
2. Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
- Introduction to EDA
- EDA in Python
- Advanced EDA techniques
- Time series visualization
Model 3: Evaluation.
Regularization techniques
Confusion matrix
Precision, recall, F1-score
AUC-ROC curve
Cross-validation methods
Hyperparameter tuning
Module 2: Supervised Learning.

Supervised algorithms could be divided into two groups:
- Classification – discrete label prediction.
- Regression – the forecasting of continuous values.
- Ordinary Supervised Learning Algorithms.
1. Linear Regression
Applied to forecast numerical results in terms of straight-line correlation.
- The Linear Regression Introduction.
- Gradient Descent Multiple Linear Regression
2. Logistic Regression
Categorizes inputs as pass/fail or spam/ not spam.
- An Appreciation of the Logistic Regression.
- Cost function
3. Decision Trees
The tree-based models divide data by the help of simple questions.
- Decision Trees in ML
- decision tree algorithm types.
- Decision tree regression
- Classification using a decision tree.
4. Support Vector Machines (SVM)
- Determines the best boundary between classes.
- Understanding SVM
- Hyperparameter Optimization (BayesianOptimization)
- Non-linear SVM
5. k-Nearest Neighbors (k-NN)
Makes predictions according to the closest data points.
- Introduction to KNN
- Decision boundaries in KNN
6. Naïve Bayes
Often, probabilistic classifier is used to analyze text.
Introduction to Naïve Bayes
Gaussian NB
Multinomial NB
Bernoulli NB
Complement NB
7. Random Forest (Bagging Method)
Combination of decision trees to be more accurate.
Module 3: Random Forest Current Introduction.
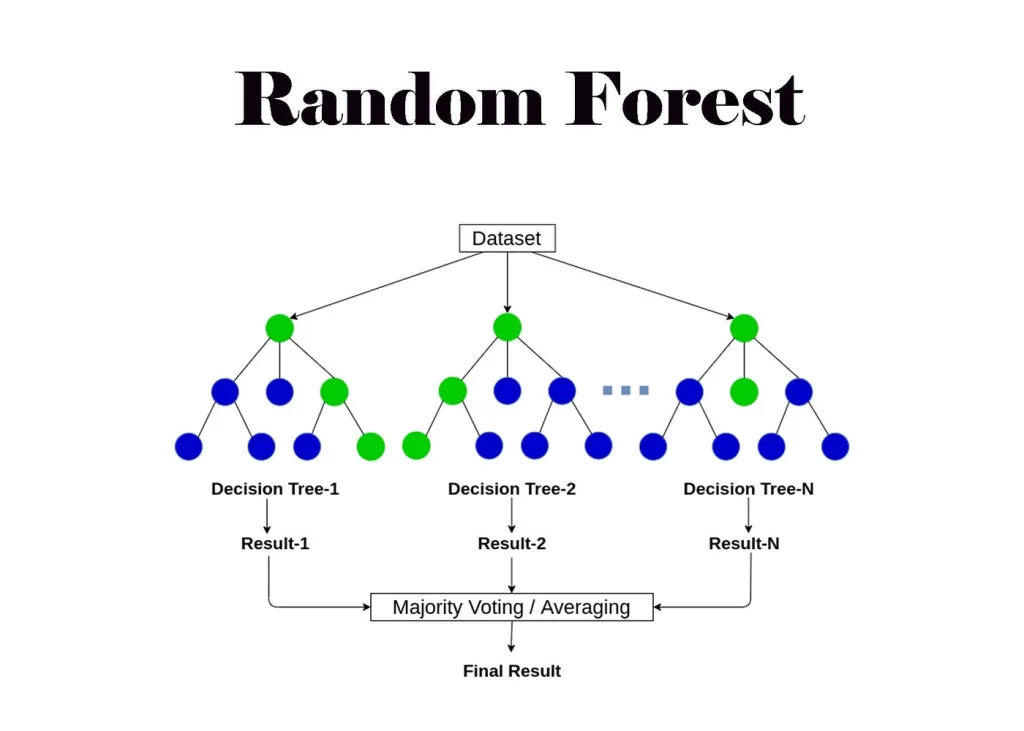
The basic introduction of the random forest is found in the documentation of theR package version 3.1.10. Basic:
This is the simplest introduction of the random forest available in the documentation of the R package
version 3.1.10.
- Random Forest Classifier
- Random Forest Regression
- Hyperparameter tuning
Introduction to Ensemble Learning.
Ensemble Learning Types:
- Bagging
- Boosting
Module 4: Reinforcement.
Unsupervised learning involves the following categories:

- Clustering
- Association Rule Mining
- Dimensionality Reduction
1. Clustering
Algorithms of clustering similar items.
- Centroid-based Methods
- K-Means clustering
- Elbow method
- K-Means++
- K-Modes
- Fuzzy C-Means
- Distribution-based Methods
- Gaussian Mixture Models
- Expectation-Maximization
- Dirichlet Process Mixture Models.
- Connectivity-based Methods
- Hierarchical clustering
- Agglomerative clustering
- Divisive clustering
- Affinity propagation
- Density-based Methods
- DBSCAN
- OPTICS
2. Dimensionality Reduction
Eliminates features and maintains important information.
- PCA
- t-SNE
- NMF
- ICA
- Isomap
- LLE
3. Association Rule Learning
Utilized to find out associations between things (e.g., market basket analysis).
Apriori algorithm
Apriori implementation
FP-Growth
ECLAT
Module 5: on-the-job learning.
The agents of reinforcement learning learn by taking rewards in the environment.
1. Model-Based Approaches
- Markov Decision Processes (MDPs)
- Bellman equation
- Value iteration
- Monte Carlo Tree Search
2. Model-Free Approaches
- Q-Learning
- SARSA
- Monte Carlo methods
- REINFORCE algorithm
- Actor-Critic models
- A3C
Module 6: Generative Adversarial Networks.
Deals with labeled and unlabeled data- best where it is costly to label data.
- Semi-supervised classification
- Self-training
- Few-shot learning
Module 7: Forecasting Models
Applied to forecast the time-dependent trends, e.g. sales or demand.
- ARIMA
- SARIMA
Exponential Smoothing (Holt-Winters).
Module 8: Implementation of ML Models.
Deployment is what makes the model trained applicable in applications.
- Machine Learning model deployment with Streamlit.
- Deploy ML web apps on Heroku
- Code Gradio ML prototypes.
- API-based Deployment
- Flask model deployment
- FastAPI model deployment
- MLOps
- CI/CD in MLOps
- End-to-End MLOps
Related Reads:
Machine Learning Interview Questions and Answers





