🟢 Introduction: Why Java Operators Matter
When I Started learning Java, I thought the concept of operators was basic—until I realized how fundamentally important they were for everything from very basic math to very complex logic. This article will give you everything you need to know about operators in Java, including what they do, how operators work with examples that illustrate the concepts. Whether you’re a Java beginner or you’re preparing for interviews, you will get clarity and substance.
🟢 What Are Operators in Java?
Operators in Java are special symbols that act on variables & values. Java Programming Operators are what connect your logic, data, and control flow!
You could think of operators as the tools of a programmer’s trade: you’ll be using them every day you write code.
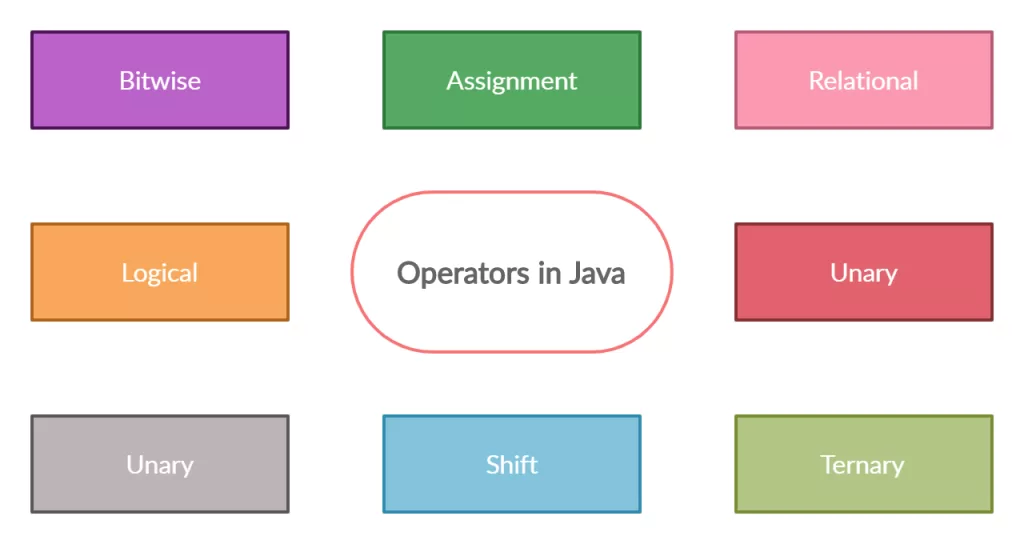
🧠 Types of Operators in Java
Java supports a wide variety of operators. Let’s break them down:
These are your basic math operators.
🔸 1. Arithmetic Operators
| Operator | Description | Example | Output |
| + | Addition | 5 + 3 | 8 |
| – | Subtraction | 10 – 4 | 6 |
| * | Multiplication | 7 * 6 | 42 |
| / | Division | 20 / 5 | 4 |
| % | Modulus (Remainder) | 9 % 2 | 1 |
Use case: Calculating totals, averages, and performing simple math operations in applications.
🔸 2. Relational (Comparison) Operators
These check relationships between two values.
| Operator | Meaning | Example | Result |
| == | Equal to | 5 == 5 | true |
| != | Not equal to | 3 != 2 | true |
| > | Greater than | 7 > 3 | true |
| < | Less than | 4 < 10 | true |
| >= | Greater than or equal | 5 >= 5 | true |
| <= | Less than or equal | 3 <= 5 | true |
Use case: Conditional statements like if-else, loops, and validations.
🔸 3. Logical Operators
Used to combine multiple conditions.
| Operator | Description | Example | Result |
| && | Logical AND | true && false | false |
| ` | ` | Logical OR | |
| ! | Logical NOT | !true | false |
Use case: Validating form input, multiple condition checks in decision-making.
🔸 4. Assignment Operators
Used to assign values to variables.
| Operator | Description | Example |
| = | Assigns value | a = 5 |
| += | Adds then assigns | a += 3 (a = a + 3) |
| -= | Subtracts then assigns | a -= 2 |
| *= | Multiplies then assigns | a *= 4 |
| /= | Divides then assigns | a /= 2 |
| %= | Modulus then assigns | a %= 3 |
Use case: Updating counters, financial calculations, loop accumulators.
🔸 5. Unary Operators
Operate on a single operand.
| Operator | Description | Example | Output |
| + | Unary plus | +a | Same as a |
| – | Unary minus | -a | Negates a |
| ++ | Increment | a++ or ++a | Increases by 1 |
| — | Decrement | a– or –a | Decreases by 1 |
| ! | Logical complement | !true | false |
Use case: Loop counters, toggling boolean flags.
🔸 6. Bitwise Operators
Perform operations at the bit level.
| Operator | Description | Example |
| & | Bitwise AND | a & b |
| | | Bitwise OR | a | b |
| ^ | Bitwise XOR | a ^ b |
| ~ | Bitwise Complement | ~a |
| << | Left Shift | a << 2 |
| >> | Right Shift | a >> 2 |
Use case: Efficient math, encryption, networking, low-level programming.
🔸 7. Ternary Operator
A compact version of an if-else.
int result = (a > b) ? a : b;Reads as: If a > b, then result = a; else result = b.
Use case: Short decision-making statements.
🔸 8. Instanceof Operator
Checks whether an object is an instance of a specific class.
if (obj instanceof String) {
System.out.println("It's a String!");
}Use case: Type checking in polymorphism, runtime decisions.
🧪 Real-Life Example with Multiple Operators
public class OperatorExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 10;
int y = 5;
int result = (x > y) ? x + y : x - y;
if (result % 2 == 0 && result != 0) {
System.out.println("Even and non-zero: " + result);
} else {
System.out.println("Odd or zero");
}
}
}🎯 Why Understanding Java Operators Is Critical
Mastering operators in Java helps you:
- Write efficient, clean code
- Pass technical interviews
- Debug with confidence
- Build real-world logic for apps and systems
Every Java program—no matter how complex—relies on operators. That’s why they’re often one of the first things taught in any Java course or Java certification program.
📚 Bonus Tips
✅ Avoid these common mistakes:
- Confusing == with = (comparison vs assignment)
- Using a++ when ++a is needed (pre vs post increment)
- Overusing nested ternary operators (hurts readability)
✅ Pro Interview Questions:
- What’s the difference between == and .equals()?
- How does bitwise shift affect performance?
- Where would you use the instanceof operator in polymorphism?
🧾 Final Thoughts – Java Operators Power Everything

To learn java programming, you have to learn java programming operators. The reason it is important to learn java programming operators is because they are the building blocks that will allow your code to manipulate data, make decisions, do calculations and so much more. Operators give your code capabilities like simply adding or subtracting and with it to the more complex conditional logic where operators give your code the ability to think, behave, and act intelligently. 👉 To promote your improvement, you can increase your skills with Java exercises or try an in-depth complete Java Programming Course to help you learn faster.
Related Links
- Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) In Java
- How does Java handle exceptions ?
- 100+ Essential Coding Interview Questions
FAQs
1. What are operators in Java and how many types of operators in Java are there?
Operators in Java are special symbols or keywords used to perform operations on variables and values. There are 8 main types of operators in Java, including arithmetic, relational, logical, bitwise, assignment, unary, ternary, and instanceof operators.
2. What is the use of Java operators and can you give a Java operators list with examples?
Java operators are used to perform operations like arithmetic calculations, comparisons, and logical decisions. Here’s a quick list:
- +, -, *, /, % – Arithmetic
- ==, !=, <, > – Relational
- &&, ||, ! – Logical
- =, +=, -= – Assignment
- ++, — – Unary
Each operator helps Java programs behave logically and efficiently.
3. What is logical operators in Java and how are they used in Java programs?
Logical operators in Java allow you to combine multiple conditions and control flow. Common logical operators are:
- && (AND)
- || (OR)
- ! (NOT)
They are frequently used in Java if-else statements, loops, and boolean expressions.
4. Which of these operators is used to allocate memory to array variable in Java?
In Java, the new operator is used to allocate memory to an array variable.
Example:
int[] numbers = new int[5];
5. How many types of assignment operators in Java and how are they used?
Java has several assignment operators used to assign values to variables. Common types include:
- = (Simple assignment)
- +=, -=, *=, /=, %= (Compound assignments)
These are used to perform an operation and assign the result in a single step.

![Agile Model in Software Engineering [2025]](https://www.wikitechy.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Agile-Model-in-Software-Engineering-2025-380x220.webp)


