What is RAM?
What is RAM? Ever wondered what makes your computer hum when you open Photoshop, stream videos, or crunch code? That magic lies in the tiny chip called Random Access Memory (RAM). It’s like your computer’s desk—fast, temporary, and essential. If you’re curious how it works and want to actually read its contents, you’re in the right place.
🧭 Quick Guide: Why I Wrote This (What You’ll Learn)
This isn’t just theory. I’ll walk you through:
- What RAM/read access memory really is
- Why you might want to read it
- Tools and methods to access it on Windows, Linux, and macOS
- Examples—from personal crashes to debugging sessions
- Plus: safety tips, FAQs, and further reading
1. What is Read Access Memory (RAM)?
Think of RAM as your workspace. It holds:
- Open apps
- Active documents
- Browser tabs
- System files needed right now
When you close an app or turn off your PC, those items are wiped clean. It’s volatile, temporary storage.
👉 Read access memory (RAM) is the technical heart of this system—fast data storage that your CPU reads and writes instantly.
2. Why You’d Want to Read RAM Contents
You might be thinking, “Why peek there?”
Here are real reasons:
- Crash analysis: I once had Photoshop crash mid-design—reading RAM helped me track the faulty plugin.
- Forensic insight: Security pros dump RAM to uncover hidden malware.
- Performance tuning: I saw Chrome gobbling memory and optimized my workflow.
- Curiosity: Yes, sometimes we just want to know what’s running under the hood.
The original article describes this well—inspect your live environment to gather precise moment-in-time data, like passwords in RAM before encryption
3. How to Access RAM: Step-by-Step Guides
A. On Windows
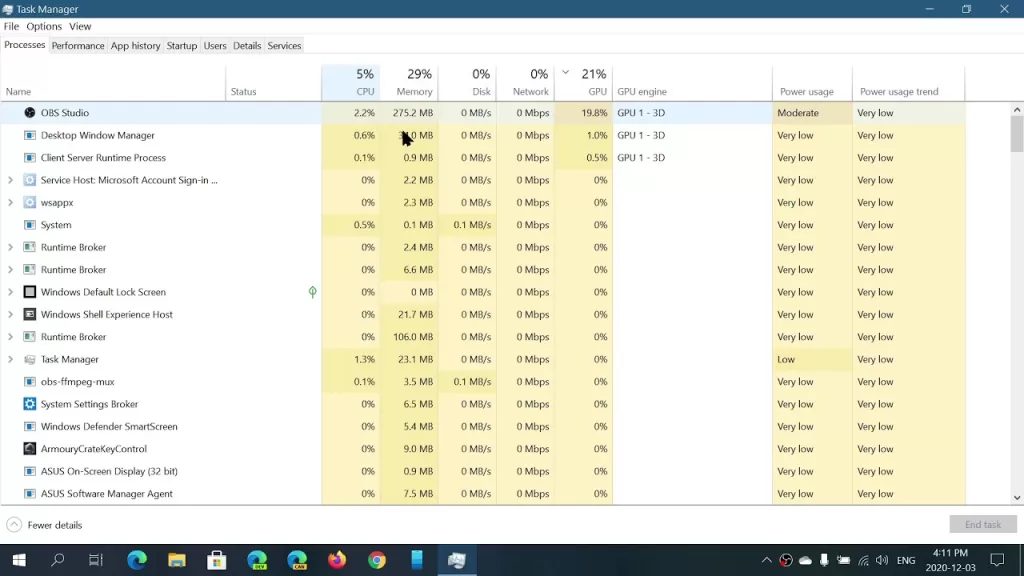
🪟 1. Task Manager
- Press Ctrl + Shift + Esc
- Go to Performance → Memory
Here you get a snapshot of total RAM, used vs free, and speed.
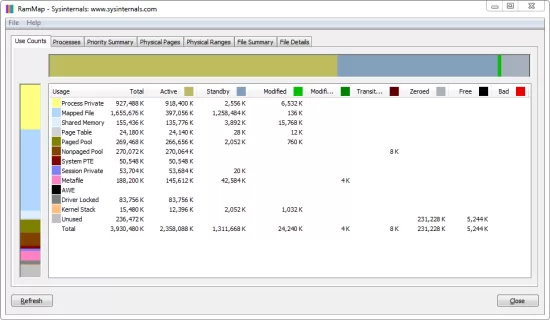
🧰 2. RAMMap (Microsoft Sysinternals)
- Download RAMMap
- Run it (no install needed)
- Explore memory usage by file, process, and usage category
It shows details like standby vs active memory—helped me identify a memory leak in a browser extension.
🐍 3. For the coder crowd: Python + psutil
pythonCopyEditimport psutil
for proc in psutil.process_iter(['pid','name','memory_info']):
print(proc.info)<code>
This lists every running process and its RAM usage. A safe entry into “reading” memory usage.

But to dump actual memory contents, you’d need more advanced tools like WinDbg or a memory dump with Volatility.
B. On Linux
Linux Memory Extractor—to dump RAM Here’s a distilled-but-friendly version:
sudo apt install linux-headers-$(uname -r) build-essential gitgit clone https://github.com/504ensicsLabs/LiME.git- Build with
make - Load the module to dump RAM: luaCopyEdit
sudo insmod lime.ko path=/root/ramdump.raw format=raw - Convert binary dump to readable text: perlCopyEdit
strings ramdump.raw | grep "password"

Yes—you can find your password in RAM before encryption. Freaky, huh?
C. On macOS
I know, Macs are trickier. You can create a memory dump via sudo gcore [pid] to capture a process. Or use lldb:
cssCopyEditlldb -p <pid>
(lldb) memory read --format x --count <num> <address>
Advanced—but feasible. I once did this to debug a stubborn kernel extension!
4. Safety & Ethics 🛡️
- Reading memory = potential security risk
You might expose passwords or personal data if you’re not careful. - Dumping RAM requires root/admin access
Always double-check what you’re dumping and where it goes. - Shared machines or corporate devices?
Make sure you’re allowed—don’t violate privacy or policy.
5. Tools You’ll Love
- Windows: Task Manager, RAMMap, Process Hacker, WinDbg
- Linux: LiME, Volatility, devmem2, dd, GDB
- macOS: gcore, lldb, instruments
Most are free and accessible. Personally, RAMMap and LiME changed the way I think about RAM.
6. Real-World Example
Here’s a personal story:
I was running a Node.js script that randomly crashed. Using /usr/bin/top and psutil, I narrowed high memory usage to a specific function. I dumped memory at crash time, looked for large buffers, and found a misused API—solved in 10 minutes.
🎉 Debugging success, thanks to read access memory.
7. FAQs
Q: Is read access memory the same as RAM?
Yes—it emphasizes both reading and writing temporary data on your computer.
Q: Can I access RAM without admin rights?
No—dumping or low-level access requires elevated permissions.
Q: How much RAM do I need?
- Web browsing: 4 GB
- Gaming/development: 8–16 GB
- Power users/VMs: 32 GB+
8. Wrapping Up
Read access memory isn’t just a buzzword—it’s the vital workspace your computer uses in real-time. Accessing and reading its contents gives you power—over crashes, security, and performance.
If You are a student learn Networking, Linux, Cyber security course online with certification, Visit their website www.kaashivinfotech.com.