The Hidden Shield Behind Every Secure Login
Every time you log into your bank app, shop online, or even message your friend on WhatsApp — there’s one silent hero working behind the scenes: the RSA algorithm.
It’s not new.
In fact, it’s over 45 years old, yet still guards billions of digital interactions every single day. According to a Statista 2024 cybersecurity report, over 85% of secure websites use public-key encryption methods — with RSA being the oldest and most trusted of them all.
But here’s what makes RSA special — it’s the foundation of digital trust. The internet would simply collapse without it. Your passwords, transactions, and data privacy depend on it.
If you’re a developer, data scientist, or cybersecurity learner — understanding RSA is not just about cryptography.
It’s about career currency. Employers want professionals who know how encryption works, not just those who can code.
So, if you’ve ever wondered “How does encryption really keep my data safe?” or “Why do companies still use RSA in 2025?” — you’re about to get all the answers.
⚡ Key Highlights
- 🧠 RSA Full Form: Rivest–Shamir–Adleman — the trio from MIT who invented modern encryption in 1977.
- 🔐 Type: Asymmetric encryption (uses two keys — one public, one private).
- 💡 Why It Matters: Powers everything from SSL/TLS (web security) to digital signatures, VPNs, and blockchain.
- 📊 Real Stat: Over 90% of enterprises rely on RSA-based encryption for at least one core system (Gartner, 2024).
- 👨💻 Career Insight: Knowing RSA gives you a competitive edge in cybersecurity, cloud computing, and network engineering.
- ⚙️ We’ll Cover: How RSA works, where it’s used, real-world examples, limitations, and how it’s evolving in the quantum era.
💬 What Is RSA Algorithm?
Let’s start with the basics.
RSA Algorithm (Rivest–Shamir–Adleman) is a public-key cryptographic system that secures data using two keys — a public key (for encryption) and a private key (for decryption).
Developed at MIT in 1977, it changed the game. Before RSA, encryption systems were “symmetric” — meaning both sender and receiver used the same secret key. The problem? If someone intercepted that key, your entire communication was compromised.
RSA solved that problem brilliantly. It introduced asymmetric encryption, where one key locks (encrypts) and another key unlocks (decrypts).
Imagine this 🔓:
You give everyone access to your mailbox (public key), but only you hold the key to open it (private key).
People can drop messages safely, but no one else can open them.
That’s RSA in a nutshell — secure, elegant, and almost impossible to break (at least with today’s computers).

⚙️ How It Works (In Simple Words)
RSA’s strength comes from prime numbers. Two large prime numbers are multiplied to create a composite number that forms the key. Breaking RSA means factoring that number — something even supercomputers struggle with.
To put that into perspective:
A 2048-bit RSA key would take billions of years to break using brute force.
That’s why companies still trust RSA to secure everything — from financial transactions to digital signatures.
👨💻 Why Developers Should Care
Here’s the thing — understanding RSA isn’t just about security theory. It’s about being a better problem solver.
- Cybersecurity engineers use RSA to protect APIs, SSL certificates, and VPN tunnels.
- Blockchain developers use it for signing transactions.
- Data engineers use RSA to encrypt stored data in cloud servers.
If you’re stepping into tech in 2025, knowing RSA puts you one step ahead — because you understand why encryption matters, not just how to use it.
🔑 RSA Full Form — A Tribute to the Innovators
The RSA algorithm gets its name from its inventors:
- R – Ron Rivest
- S – Adi Shamir
- A – Leonard Adleman

All three were professors at MIT, and their 1977 invention introduced the concept of public-key cryptography — the foundation of today’s digital security infrastructure.
And yes, it’s still relevant. RSA has stood the test of time because of one thing: mathematical resilience.
The entire algorithm relies on the difficulty of factoring very large numbers — a challenge even AI and modern computing haven’t conquered yet.
⚙️ How RSA Algorithm Works Step-by-Step
So, how does the RSA algorithm actually turn your private message into unreadable gibberish that only the receiver can unlock? Let’s decode that — one step at a time.
Step 1: Key Generation 🔢
RSA begins with math — beautiful, complex, and powerful math.
Two large prime numbers are chosen (call them p and q).
These are multiplied to produce a number n, which becomes part of both the public and private keys.
Then, a second value called φ(n) (phi) is calculated — it’s based on the prime numbers you just chose.
Finally, two keys are generated:
- Public Key (n, e): Shared with the world for encryption.
- Private Key (n, d): Kept secret by the receiver for decryption.
🔐 Think of it as generating a padlock (public) and a key (private). Everyone can use the padlock, but only one person owns the key.
Step 2: Encryption — The Sender Locks the Message 📨
The sender takes the plaintext message (say, M) and encrypts it using the recipient’s public key.
The formula looks like this:
C = Mᵉ mod n
This transforms the readable text into ciphertext — random numbers that make zero sense to anyone snooping around. Even if hackers capture it, all they see is scrambled math.
Step 3: Transmission — The Message Travels Securely 🌐
The ciphertext is sent over the network.
Even if it’s intercepted, it’s useless without the private key.
Fun fact 💡:
Every second, over 4.6 billion RSA-secured data packets travel across the internet — from emails to payment requests.
That’s RSA silently protecting global communication, 24/7.

Step 4: Decryption — The Receiver Unlocks It 🔓
The recipient uses their private key to decrypt the message:
M = Cᵈ mod n
Once decrypted, the ciphertext turns back into readable text — exactly what the sender originally wrote.
This dual-key structure (public + private) is what makes RSA asymmetric, and also what makes it so secure.
🧮 RSA Algorithm Example (Simple Numeric Demo)
Let’s take a quick, simplified example to see RSA in action.
Imagine:
- p = 3
- q = 11
- n = p × q = 33
- φ(n) = (p − 1)(q − 1) = 20
Choose e = 3 (a small number that’s coprime with φ(n)).
Now, find d such that (d × e) mod φ(n) = 1.
Here, d = 7.
Your keys are:
- Public Key: (n=33, e=3)
- Private Key: (n=33, d=7)
If you want to send the number M = 4, encrypt it using:
C = Mᵉ mod n = 4³ mod 33 = 64 mod 33 = 31
Ciphertext = 31
To decrypt it:
M = Cᵈ mod n = 31⁷ mod 33 = 4
🎯 Message decrypted successfully — 4 is back!
Even with small numbers, you can see how RSA’s math works.
Now imagine those primes being hundreds of digits long — that’s what real RSA encryption looks like.
Breaking it?
Not happening anytime soon (unless you own a time-traveling quantum computer).
🌍 Applications of RSA Algorithm in Real Life
RSA isn’t just a theory you study in cryptography class. It’s everywhere. Let’s look at how it powers the modern internet.
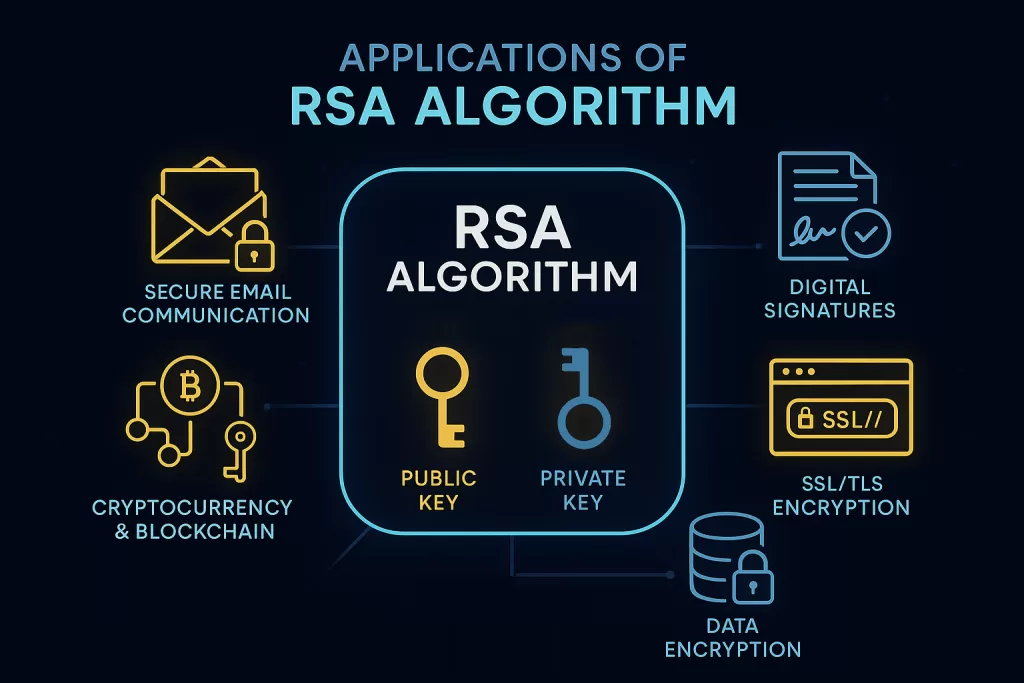
1️⃣ Secure Web Communication (SSL/TLS)
Every time you see that tiny 🔒 lock icon in your browser, you’re seeing RSA at work.
During an SSL handshake, RSA encrypts the exchange of symmetric keys between your browser and the website server. Once the key is exchanged safely, the rest of your data — passwords, transactions, personal info — gets encrypted using that key.
📊 Stat Insight: According to W3Techs, 93.2% of websites now use HTTPS powered by RSA or its hybrid versions (like ECDSA).
Best Practice:
Always check the padlock symbol before entering sensitive data — it means RSA (or a similar algorithm) is guarding your connection.
2️⃣ Email Encryption (PGP and S/MIME)
Tools like Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) and S/MIME use RSA encryption to keep your emails private.
Here’s how it works:
- The sender encrypts the email using the receiver’s public key.
- Only the receiver’s private key can decrypt it.
- RSA also adds a digital signature, ensuring authenticity.
Real-World Example:
Companies like Google and Microsoft use RSA-backed certificates for verifying sender identity in enterprise email systems.
3️⃣ Digital Signatures 🖋️
This is where RSA really shines.
By signing a document with a private key, you’re proving that the data came from you and hasn’t been tampered with. The receiver can verify it using your public key.
It’s the digital equivalent of a fingerprint, used in:
- Software license validation
- Blockchain smart contracts
- Government e-signature platforms
Developer Tip:
Always use RSA digital signatures for integrity checks in APIs — they prevent data tampering and build trust in your systems.
4️⃣ Cloud Data Protection ☁️
Cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud use RSA for key management systems (KMS).
RSA encrypts the symmetric keys used to protect user files — meaning, even if someone gets hold of the encrypted file, it’s unreadable without the correct private key.
Career Insight:
If you’re learning cloud or DevOps, understanding RSA-based key management is a must. Employers love it when you can explain encryption logic instead of just deploying it.
5️⃣ Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
RSA is used to securely exchange keys during VPN session setup.
Once the secure tunnel is formed, other encryption methods (like AES) take over for speed — but RSA does the heavy lifting first.
That’s why your VPN connection stays private and anonymous — RSA is literally setting up the digital handshake between your device and the server.
6️⃣ Cryptocurrency & Blockchain ₿
In the crypto world, RSA ensures transaction authenticity.
When you send crypto, your private key signs the transaction, and others use your public key to verify it. It’s what prevents fraud and guarantees that only you can authorize movement of your funds.
Example:
In blockchain-based voting systems, RSA signatures verify that votes are genuine and haven’t been altered — a powerful real-world use case of encryption ethics in action.
✨ In Short:
RSA powers trust. Whether it’s your bank login, your blockchain wallet, or your Zoom call — this algorithm is quietly ensuring that only the right people see the right data.
⚠️ Limitations of RSA Algorithm
RSA may be a legend in cryptography, but even legends have limits. Let’s be honest about where RSA struggles.
🧮 1️⃣ Computationally Heavy
RSA relies on large prime numbers — often 2048 or 4096 bits long.
That means encryption and decryption take thousands of times longer than symmetric algorithms like AES.
According to Cloudflare, RSA-2048 decryption is 10,000× slower than AES-128.
That’s why RSA is used to exchange keys, not to encrypt full data streams.
Developer Insight:
Use RSA for initial authentication and AES for the actual data transfer. It’s the best of both worlds — security + speed.
🔐 2️⃣ Key Size vs Security Dilemma
The longer the key, the safer RSA gets — but also slower.
Modern systems need at least 2048-bit keys to be secure, but future quantum computers could break even those.
That’s why researchers are already exploring post-quantum cryptography (PQC) — encryption designed to resist quantum attacks.
📉 3️⃣ Not Ideal for Big Data
Encrypting large chunks of data with RSA? Bad idea.
RSA can only handle data smaller than its key size (like a few hundred bytes).
So for encrypting files, streaming data, or databases, RSA hands over the job to faster symmetric algorithms.
🧑💻 4️⃣ Implementation Complexity
RSA looks simple in textbooks — but in real systems, one small coding mistake can ruin everything.
Poor random number generation, incorrect padding, or leaked private keys can make even the strongest RSA setup vulnerable.
Real Example:
In 2017, researchers found over 750,000 weak RSA keys due to reused prime numbers. That’s not a math flaw — it’s human error.
⚔️ RSA vs Other Encryption Algorithms
How does RSA stack up against modern encryption giants? Let’s break it down 👇
| Feature | RSA | AES | ECC (Elliptic Curve) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Asymmetric | Symmetric | Asymmetric |
| Key Length (bits) | 2048–4096 | 128–256 | 256 |
| Speed | Slow | Very Fast | Fast |
| Security Level | High | High | Very High |
| Use Case | Key exchange, signatures | Bulk data encryption | Mobile & IoT devices |
| Future Ready? | Moderate (Quantum risk) | Moderate | High (Smaller key, same strength) |
Summary:
- AES is faster.
- ECC is more efficient.
- RSA is still the backbone — but slowly being replaced in systems where speed and space matter.
Best Practice:
Use RSA when compatibility and trust are key (like SSL/TLS).
Use ECC or hybrid RSA-AES models for modern applications like IoT, APIs, and mobile apps.
🧭 The Future of RSA — and Your Career
Encryption is evolving — and so should you.
By 2030, the global cybersecurity market will hit $425 billion (Statista). And encryption experts? They’re already in short supply.
Knowing RSA isn’t just theory — it’s a career skill.
Here’s where understanding RSA gives you an edge:
- 🛡️ Cybersecurity Analyst: Explaining and configuring RSA-based SSL/TLS certificates.
- 🧠 Data Scientist: Protecting ML pipelines and sensitive datasets.
- ☁️ Cloud Engineer: Managing RSA key pairs in AWS, Azure, or GCP KMS.
- 🔑 Blockchain Developer: Handling RSA-based signatures and wallet security.
Pro Tip:
Add RSA + AES + ECC to your resume — recruiters love seeing practical cryptography knowledge. It shows you’re not just coding, you understand why data stays safe.
🏁 Conclusion: RSA — Still the Guardian of Digital Trust
Even after 40+ years, RSA remains a symbol of digital trust.
It built the foundation of modern cybersecurity and still protects billions of transactions daily.
But the future belongs to hybrid cryptography — systems where RSA works with newer, quantum-resistant methods.
So, if you’re building your tech career, learning RSA isn’t optional — it’s essential.
It’s your first step toward understanding how the invisible walls of digital security actually work.
🔑 Master RSA today, and you won’t just protect data — you’ll protect the digital world itself.
🔗 Related Reads
If you’re diving deep into the world of algorithms, these handpicked reads will take your understanding to the next level:
- 🧠 Algorithms Explained: Essential Reasons to Learn in 2025 and Main Algorithm Types – Discover why algorithms matter and explore their main types that power every modern tech system.
- 🤖 Machine Learning Algorithms: A Complete Guide for Beginners – Understand how algorithms drive machine learning models and real-world AI applications.
- 🔍 What is Linear Search and Binary Search (2025 Guide): Search Algorithms Explained, Code in Python & Java, and More – A hands-on breakdown of search algorithms with code samples and practical insights.
- ⚙️ Design and Analysis of Algorithms – A Complete Guide – Learn how to design efficient algorithms and analyze their complexity for optimal performance.
- 💻 Data Structures and Algorithms: From Basics to Advanced – A comprehensive roadmap from beginner to pro-level understanding of DS & Algo.



![Merge Sort Algorithm [2025]](https://www.wikitechy.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Merge-Sort-Algorithm-2025-380x220.webp)