If you’ve ever had to sort a messy pile of anything, you know the struggle. Now imagine doing it step by step — always picking the smallest item left and moving it into place. That’s selection sort Algorithm in its simplest form.
The selection sort algorithm has been around forever. It’s not the fastest, but it’s one of the easiest to grasp. Computer science professors love it. Interviewers still ask about it. And in 2025, it’s still worth knowing — not because you’ll use it in production, but because it teaches the fundamentals of sorting.
✨ Key Highlights
- 🔑 Selection Sort is one of the simplest sorting methods — but also one of the least efficient.
- ⚡ It repeatedly selects the smallest (or largest) element and puts it in place.
- 🖥️ Selection Sort Algorithm works in O(n²) time — slow for big data, but useful in teaching and small datasets.
- 📊 Requires just O(1) space — perfect when memory writes are costly.
- ❌ Not stable — it may change the order of equal elements.
- ✅ Still used in embedded systems, teaching, and interview prep.
- 🚀 Best suited for small arrays, low-memory situations, and explaining sorting fundamentals.
What is Selection Sort? (Definition & Why It Matters)
At its core, selection sort is a comparison-based sorting algorithm. Instead of juggling adjacent elements like bubble sort, it takes a more “decisive” approach:
- Find the smallest (or largest) element in the unsorted portion.
- Swap it with the first unsorted element.
- Repeat until the entire array is sorted.
Think of it like picking teams in school. You call out the “smallest” or “best” player, put them in the lineup, and keep doing it until everyone’s placed where they belong. Simple, but a little slow when the team is huge.
👉 Why it matters: Even though it runs in O(n²) time, selection sort Algorithm lays the foundation for understanding more advanced algorithms like heap sort. In fact, heap sort is basically a more optimized version of it.

How the Selection Sort Algorithm Works (Step by Step)
Here’s the step-by-step working of the selection sort algorithm:
- Start with the first element.
- Look through the rest of the list to find the smallest.
- Swap the smallest with the current element.
- Move to the next index and repeat.
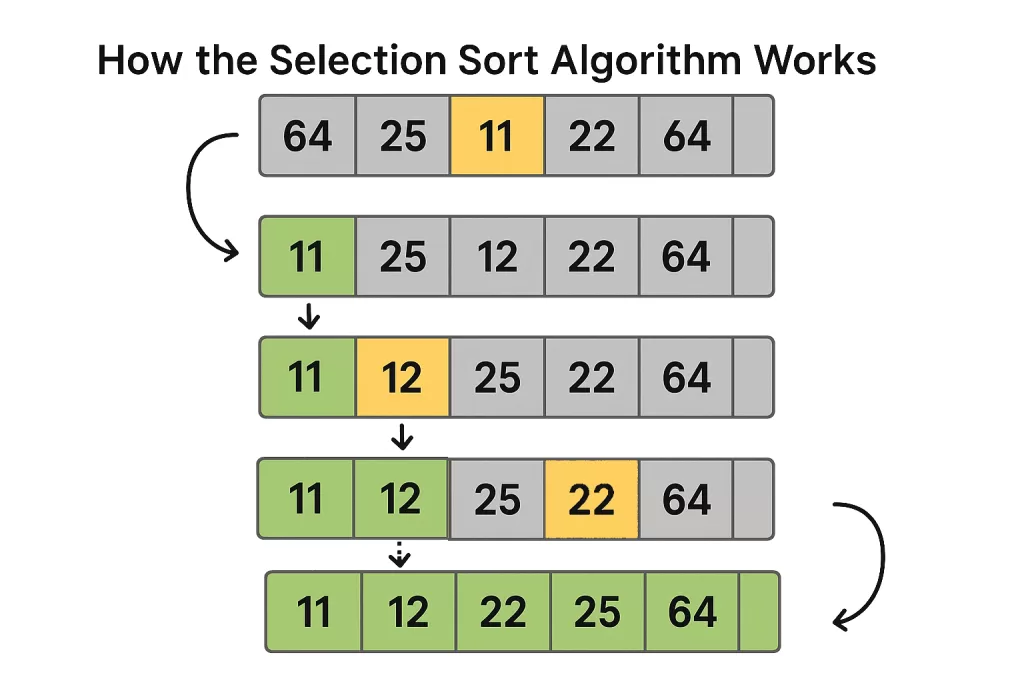
Example: Sorting [64, 25, 12, 22, 11]
- Pass 1 → Smallest = 11 → Swap with 64 →
[11, 25, 12, 22, 64] - Pass 2 → Smallest = 12 → Swap with 25 →
[11, 12, 25, 22, 64] - Pass 3 → Smallest = 22 → Swap with 25 →
[11, 12, 22, 25, 64] - Pass 4 → Smallest = 25 → Already in place →
[11, 12, 22, 25, 64]
🔍 Notice something? By the end of each pass, at least one element is locked in its correct spot.
Selection Sort Algorithm in C, C++, Java, and Python
Here’s the fun part: implementing selection sort Algorithm in different programming languages. If you’re prepping for an interview, you never know which language they’ll throw at you.
C++ Code
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void selectionSort(vector<int>& arr) {
int n = arr.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++) {
int min_idx = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; j++) {
if (arr[j] < arr[min_idx]) {
min_idx = j;
}
}
swap(arr[i], arr[min_idx]);
}
}
int main() {
vector<int> arr = {64, 25, 12, 22, 11};
selectionSort(arr);
for (int x : arr) cout << x << " ";
return 0;
}
Java Code
class SelectionSort {
void sort(int arr[]) {
int n = arr.length;
for (int i = 0; i < n-1; i++) {
int min_idx = i;
for (int j = i+1; j < n; j++) {
if (arr[j] < arr[min_idx]) {
min_idx = j;
}
}
int temp = arr[min_idx];
arr[min_idx] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int arr[] = {64, 25, 12, 22, 11};
new SelectionSort().sort(arr);
for (int x : arr) System.out.print(x + " ");
}
}
Python Code
def selection_sort(arr):
n = len(arr)
for i in range(n):
min_idx = i
for j in range(i+1, n):
if arr[j] < arr[min_idx]:
min_idx = j
arr[i], arr[min_idx] = arr[min_idx], arr[i]
arr = [64, 25, 12, 22, 11]
selection_sort(arr)
print(arr)
💡 Developer Insight: In Python, swapping is neat because of tuple unpacking (arr[i], arr[min_idx] = arr[min_idx], arr[i]). Cleaner than writing a temp variable like in C/Java.
Time Complexity of Selection Sort (Best, Average, Worst Case)
Selection sort Algorithm doesn’t try to be clever — it always scans the unsorted part of the array, no matter what. That’s why its time complexity stays the same across cases.
| Case | Comparisons | Time Complexity |
|---|---|---|
| Best | n² | O(n²) |
| Average | n² | O(n²) |
| Worst | n² | O(n²) |
- Space Complexity: O(1) (in-place sorting).
- Swaps: At most n-1 (fewer than bubble sort).
📊 Fun fact: For an array of 10,000 elements, selection sort can take ~50 million comparisons. That’s why you’ll never see it used for big datasets in production.
Is Selection Sort Algorithm Stable?
Short answer: ❌ No.
Why? Because when you swap the minimum element with the first unsorted element, you might push equal elements out of order.
Example:
Array = [4a, 4b, 3]
- After one pass, it becomes
[3, 4b, 4a]→ the order of4aand4bflipped.
That’s why selection sort is not a stable sorting algorithm.
👉 If stability matters (like sorting student names along with scores), developers prefer algorithms like merge sort or insertion sort.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Selection Sort
Every algorithm has its strengths and weaknesses. Selection sort is no exception.
✅ Advantages
- Easy to understand → New programmers can grasp it without breaking a sweat.
- Low memory footprint → Needs only O(1) extra space, unlike merge sort which requires extra arrays.
- Fewer swaps than bubble sort → If writing to memory is expensive (think flash memory in embedded devices), selection sort reduces wear-and-tear.
- Deterministic → Always makes the same number of comparisons, so it’s predictable.
❌ Disadvantages
- O(n²) complexity → Becomes painfully slow as data grows. Sorting a million elements with selection sort is practically impossible in real-world applications.
- Not stable → Equal values might lose their original order.
- Outclassed in practice → For almost every real dataset, algorithms like quicksort, mergesort, or even insertion sort perform better.
👉 In short: it’s great for teaching, not so great for production.
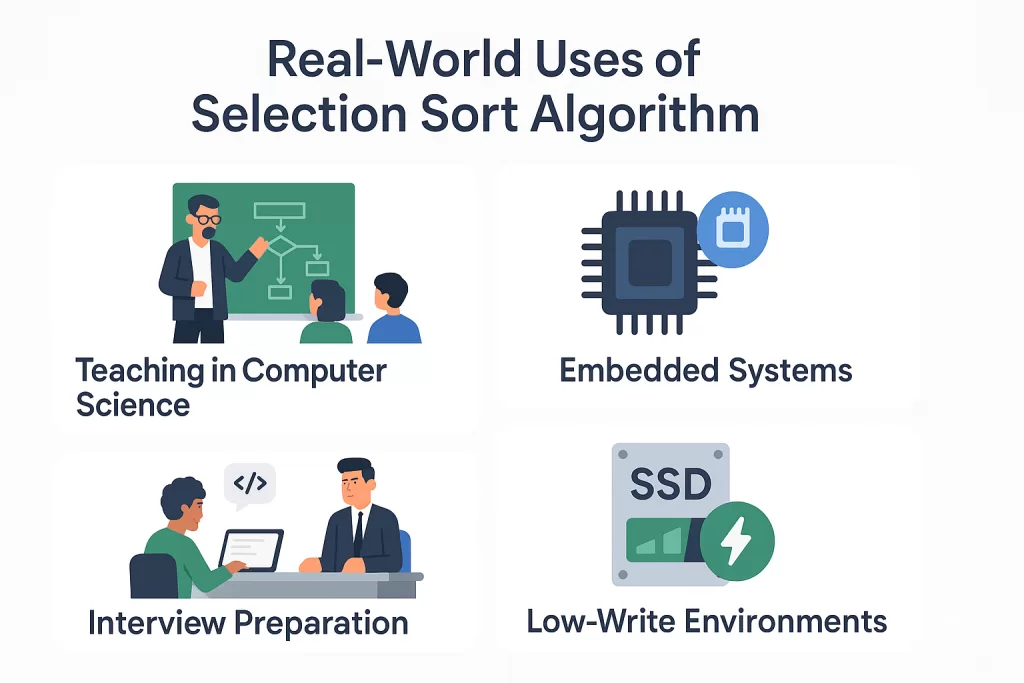
Real-World Use Cases of Selection Sort
So where would you actually see selection sort being used in 2025? Surprisingly, it still has its place.
- Teaching in computer science classes → Professors love it because it’s simple to demonstrate and explains sorting fundamentals.
- Embedded systems → In microcontrollers where memory is super limited, fewer swaps matter more than speed.
- Interview preparation → Recruiters often ask candidates to implement the selection sort algorithm as a warm-up.
- Low-write environments → Flash memory has limited write cycles. Since selection sort minimizes writes, it can sometimes be chosen in very specialized hardware scenarios.
📌 Developer insight: A few chip design companies still use selection sort in firmware testing environments, but you won’t find it in your favorite search engine’s codebase.
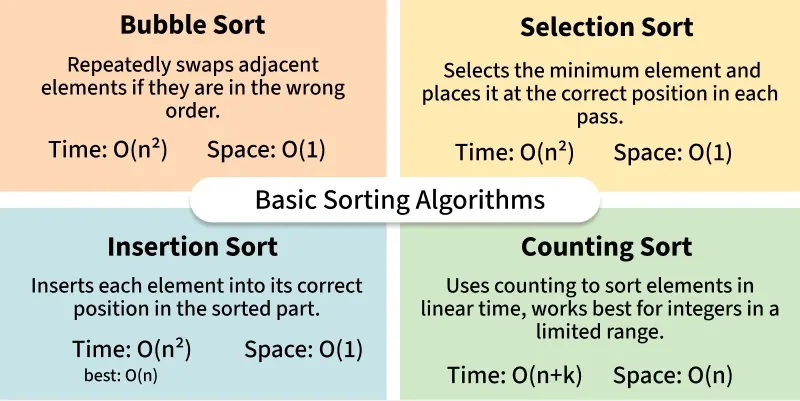
Selection Sort vs Bubble Sort (and Other Sorting Algorithms)
Students often confuse selection sort with bubble sort. Both are O(n²), but the way they work is different:
| Algorithm | Key Idea | Swaps | Stability | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Selection Sort | Find minimum & place it | Few | ❌ Not stable | Teaching, low memory writes |
| Bubble Sort | Repeatedly swap adjacent elements | Many | ✅ Stable | Teaching, very small arrays |
| Insertion Sort | Insert each element in its right place | Few (on sorted data) | ✅ Stable | Small or nearly sorted arrays |
| Merge Sort | Divide and conquer | More memory | ✅ Stable | Large datasets |
| Quick Sort | Partitioning | O(n log n) average | ❌ Not stable | Fast in practice |
👉 Takeaway: selection sort does fewer swaps than bubble sort, but insertion sort often outperforms both in practical scenarios.
Interview Questions on Selection Sort
If you’re preparing for coding interviews, you’ll likely face questions on selection sort. Here are some common ones:
- Is selection sort stable or not?
- No, it’s not stable.
- What’s the time complexity of selection sort?
- O(n²) in all cases.
- How many swaps does selection sort perform?
- At most n-1.
- When would you prefer selection sort over other algorithms?
- In memory-constrained environments or when teaching.
- Can you write a program for selection sort in C/Java/Python?
- Yes → that’s why we showed examples earlier.
Pro tip for interviews: If asked to optimize, talk about heap sort, which improves on selection sort by using a heap data structure.
❓ FAQ
1. What is Selection Sort Algorithm ?
Selection sort is a comparison-based sorting algorithm that repeatedly finds the smallest (or largest) element from the unsorted portion and moves it to its correct position. It’s simple to understand, requires only O(1) extra space, but runs in O(n²) time complexity.
2. What is Selection Sort in Data Structure?
In data structures, selection sort is one of the fundamental sorting algorithms. It helps beginners understand how arrays can be rearranged using comparisons and swaps. It’s often taught alongside bubble sort and insertion sort.
3. How Selection Sort Algorithm Works?
The algorithm works step by step:
- Find the smallest element from the unsorted part.
- Swap it with the first unsorted element.
- Move the boundary between sorted and unsorted one step ahead.
- Repeat until the entire list is sorted.
Example: Sorting [64, 25, 12, 22, 11] → [11, 12, 22, 25, 64].
4. What is the Selection Sort Algorithm in C, C++, Java, and Python?
Selection sort can be implemented in any programming language:
- Selection Sort in C → Uses arrays and a simple loop structure.
- Selection Sort in C++ → Often implemented with
vector<int>andswap(). - Selection Sort in Java → Implemented inside a class with nested
forloops. - Selection Sort in Python → Easy to write thanks to tuple unpacking for swaps.
Each language has its own syntax, but the logic remains the same.
5. What is the Time Complexity of Selection Sort Algorithm?
Selection sort always takes the same number of comparisons:
- Best Case: O(n²)
- Average Case: O(n²)
- Worst Case: O(n²)
👉 That means even if the array is already sorted, selection sort will still scan the entire unsorted part.
6. What is the Space Complexity of Selection Sort Algorithm ?
The space complexity is O(1) because it sorts the array in-place and does not require extra memory.
7. Is Selection Sort Algorithm Stable?
No ❌. Selection sort is not stable. If two equal elements exist, their order can change after a swap.
Example: [4a, 4b, 3] → [3, 4b, 4a]. The order of 4a and 4b is lost.
8. What is the Difference Between Bubble Sort and Selection Sort?
- Bubble Sort → Keeps swapping adjacent elements, stable, but makes many swaps.
- Selection Sort → Finds the minimum element and swaps only once per pass, fewer swaps but not stable.
👉 Both have O(n²) time complexity, but selection sort is better when swap cost is high.
9. How Many Passes Are Required in Selection Sort?
For n elements, selection sort requires n-1 passes.
Example: For 5 elements, 4 passes are enough to place all elements in order.
10. What is the Best Case Complexity of Selection Sort?
Even in the best case (when the array is already sorted), selection sort performs O(n²) comparisons, because it doesn’t check if the array is already sorted.
11. What is the Worst Case Complexity of Selection Sort Algorithm ?
The worst case is also O(n²), which happens when the array is sorted in reverse order. The algorithm still scans and swaps elements until everything is placed correctly.
12. Where is Selection Sort Used in Real Life?
- Teaching: Professors use it in computer science classes.
- Embedded Systems: Works well in devices with limited memory (O(1) space).
- Interview Questions: A favorite question in coding interviews.
- Low-write environments: Useful where minimizing memory writes is more important than speed (like flash memory).
13. What are the Advantages of Selection Sort?
✅ Easy to understand and implement.
✅ Requires no extra space.
✅ Performs fewer swaps compared to bubble sort.
✅ Deterministic — same number of comparisons every time.
14. What are the Disadvantages of Selection Sort?
❌ Slow (O(n²)) for large datasets.
❌ Not stable.
❌ Outperformed by quicksort, mergesort, and insertion sort in practice.
15. What is the Algorithm for Selection Sort?
Pseudo-code for selection sort:
for i = 0 to n-1:
min_idx = i
for j = i+1 to n:
if arr[j] < arr[min_idx]:
min_idx = j
swap(arr[i], arr[min_idx])
16. What is Selection Sort Algorithm in DSA (Data Structures & Algorithms)?
In DSA, selection sort is often the first sorting algorithm taught. It helps students understand loops, comparisons, and swap operations before moving to advanced algorithms like quicksort.
17. What is Selection Sort in C Programming?
In C programming, selection sort is usually written using arrays and simple loops. It’s a favorite exercise in college assignments and interviews.
18. What is Selection Sort in Python?
In Python, selection sort can be written in just a few lines thanks to tuple unpacking:
arr[i], arr[min_idx] = arr[min_idx], arr[i]
This makes the code cleaner compared to C or Java.
19. Why Learn Selection Sort in 2025?
Even though it’s not used in production, learning selection sort helps you:
Appreciate optimized versions like heap sort.
Build a foundation for understanding sorting algorithms.
Practice writing clean, structured code.
Prepare for coding interviews.
Conclusion: Why Learn Selection Sort in 2025?
Sure, selection sort Algorithm won’t power Google’s search ranking or Netflix’s recommendations. But that’s not the point. The real value lies in understanding. Once you’ve wrapped your head around the selection sort algorithm, you’ve built the intuition needed to tackle insertion sort, heap sort, and beyond.
In 2025, you don’t learn selection sort because it’s practical — you learn it because it’s foundational. It teaches you how algorithms think, how to break problems down, and how to write clean, step-by-step logic.
And here’s the truth: if you can explain selection sort clearly to someone else, you’re already ahead in your coding journey. 🚀
📚 Related Reads
- 🔹 Insertion Sort Algorithm in 2025 – Must-Know Facts, Examples in C, Java, Python & More
- 🔹 Merge Sort Algorithm [2025] – Step by Step Explanation, Example, Code in C, C++, Java, Python, and Complexity 🚀
- 🔹 🚀 Bubble Sort Algorithm: A Complete Guide with Examples in Java and C
- 🔹 Python Sort Lists – The Ultimate Guide to Sorting in Python
- 🔹 Insertion Sort Time Complexity: Complete Guide for Beginners & Pros
- 🔹 SQL ORDER BY Clause Explained (Ascending & Descending Order Examples)