Spring Boot has changed the way Java developers create microservices and enterprise applications. At the foundation of its simplicity is a powerful concept: Spring Boot annotations.
In this guide, we will cover nearly all the Spring Boot annotations list, how and when to apply them, and provide you with a helpful Spring Boot annotations directory with code sample snippets.
What Are Spring Boot Annotations?
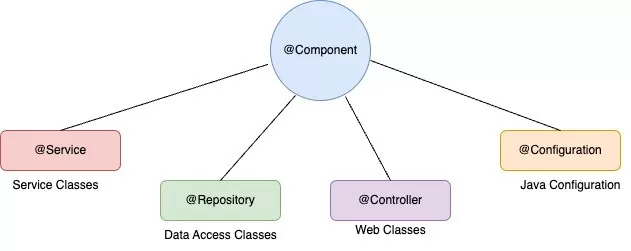
Annotations are metadata in Spring Boot that tell Spring how to behave at runtime. Spring Boot annotations allow you to eliminate cumbersome XML configurations.
With a few lines of code, you can use Spring Boot annotations to configure beans, specify controllers, enable auto-configuration, and much more.
Why Use Annotations in Spring Boot?
- Speedy Development – eliminates boilerplate code.
- Auto-Configuration – allows Spring Boot to automatically ‘wire’ dependencies for you.
- Readable – the code speaks for itself.
- Integration – navigate connections to the Spring ecosystem and your components.
Key Features of Spring Boot Annotations
Reduced Configuration
- Annotations will replace lengthy XML configuration, allowing you to simply configure components in Java classes, for example.
Automatic Configuration
- Spring Boot uses @SpringBootApplication and @EnableAutoConfiguration annotations so that it can automatically create and wire beans if classes are on the classpath.
Component Scanning
- The component scanning feature of Spring Boot, which uses @ComponentScan, allows Spring Boot to automatically discover beans, services, and controllers, without any manual configuration.
Simple Dependency Injection
- Dependency injection can be done simply. It reduces complex constructions. The @Autowired, @Qualifier, and the stereotype (the @Service, @Repository, @Component) annotations allow you to inject and manage dependencies much less formally.
Self-Documenting Code
- The code you write becomes partially self-documenting, when you look at a class and its annotations. For example, you know what a method does, or the purpose of the class, from what annotations are present.
Fine Coarse Control
- With conditional identifiers (@Profile, @ConditionalOnProperty), you can load beans conditionally.
Support for REST and Web Development
- Spring Boot makes writing APIs and web endpoints simpler with @RestController, @GetMapping, and @RequestMapping.
Better Testing
- With the testing specific annotations (@SpringBootTest, @WebMvcTest, @MockBean) it allows you to write a focused unit or integration test, with minimal setup.
Scalability and DRY-ness
- You can create custom annotations to encapsulate common behaviors, this allows you to scale your code appropriately and implement DRY programming.
Uniformity across Java EE feature-set implementation
- The same annotations are employed across the web, data, security, and message modules of Java EE, leading to a “consistent” programming style.
Essential Spring Boot Annotations in Java
Here are some of the most common Spring Boot annotations you’ll use daily:

@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}- @SpringBootApplication
Combines @Configuration, @EnableAutoConfiguration, and @ComponentScan. - @ComponentScan
Scans the package for components, services, and configurations. - @EnableAutoConfiguration
Automatically configures beans based on the classpath.
Configuration & Application Annotations
Spring Boot annotations list wouldn’t be complete without configuration helpers:
- @Configuration – Marks a class as a source of bean definitions.
- @Bean – Declares a bean method inside a configuration class.
- @PropertySource – Loads external properties files.
Example:
@Configuration
@PropertySource("classpath:application.properties")
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
public MyService myService() {
return new MyService();
}
}Web & REST Controller Annotations
For building APIs, these Spring Boot annotations in Java shine:
- @RestController – Combines @Controller and @ResponseBody.
- @RequestMapping – Maps HTTP requests to handler methods.
- @GetMapping, @PostMapping, @PutMapping, @DeleteMapping.
- @PathVariable, @RequestParam, @RequestBody.
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/hello/{name}")
public String hello(@PathVariable String name) {
return "Hello, " + name;
}
}Dependency Injection & Bean Management

Spring Boot excels at dependency injection thanks to these annotations:
- @Component, @Service, @Repository – Stereotypes for beans.
- @Autowired – Injects bean dependencies automatically.
- @Qualifier – Choose between multiple beans of the same type.
- @Value – Inject property values.
Example:
@Service
public class GreetingService {
public String greet(String name) {
return "Hello, " + name;
}
}Testing Annotations
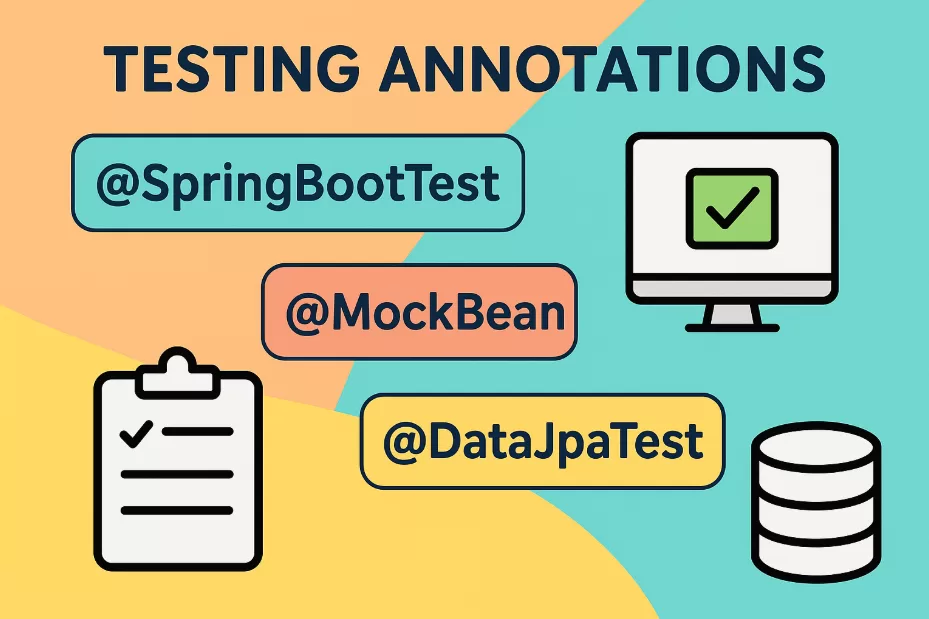
Testing is easier with dedicated Spring Boot annotations:
- @SpringBootTest – Boots the full context for integration tests.
- @MockBean – Creates and injects Mockito mocks.
- @DataJpaTest – Slices out JPA components for testing repositories.
@SpringBootTest
class GreetingServiceTest {
@Autowired
private GreetingService service;
@Test
void greetShouldReturnMessage() {
assertEquals("Hello, John", service.greet("John"));
}
}Complete List of Annotations in Spring Boot (Cheat Sheet)
| Annotation | Description |
| @SpringBootApplication | Core entry point for apps |
| @Configuration | Defines configuration classes |
| @Bean | Declares a bean |
| @RestController | REST endpoints |
| @Service | Business logic component |
| @Repository | DAO component |
| @Autowired | Inject dependencies |
| @Value | Inject property value |
| @EnableAutoConfiguration | Auto-config beans |
| @ComponentScan | Scan for components |
| @RequestMapping | Map URLs |
| @GetMapping | Handle GET |
| @PostMapping | Handle POST |
| @SpringBootTest | Integration testing |
Best Practices & Final Thoughts
- Keep annotations minimal – avoid over-annotating.
- Organize configuration classes in a logical way.
- Use @ConfigurationProperties for complex property binding.
- Document custom annotations for your team.
Now with this guide, you are set to get started with spring boot annotations in java to build cleaner, faster, and maintainable applications.