In modern software development, ensuring application stability is no longer limited to validating expected user flows. Real users behave unpredictably—they click randomly, enter invalid inputs, navigate abruptly, and push applications beyond their comfort zone. Traditional test cases often fail to capture these chaotic interactions. This is where Monkey-Testing plays a vital role.
When combined with Robot Framework, Monkey-Testing becomes a powerful automated approach to uncover hidden defects, improve application robustness, and enhance overall user experience. This article explores Monkey Testing in depth, explains how it works with Robot Framework, and provides practical implementation strategies.
Understanding Monkey Testing
Monkey-Testing is a software testing technique where random inputs, actions, or events are applied to an application to observe its behavior. The purpose is not to verify correctness against predefined expectations, but to identify crashes, freezes, memory leaks, or unexpected behavior under random usage conditions.

The name originates from the idea that a monkey randomly pressing keys or clicking UI elements could potentially break an application.
Key Characteristics of Monkey Testing
- No predefined test scripts
- Randomized actions and inputs
- Focus on stability rather than correctness
- Minimal assumptions about user behavior
Monkey-Testing is especially effective in detecting issues that structured testing often overlooks.
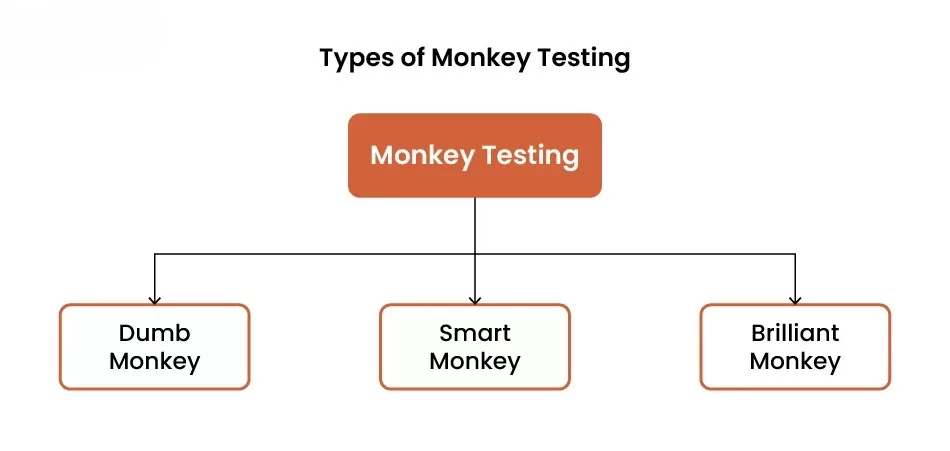
Types of Monkey Testing
Monkey-Testing can be categorized based on the level of intelligence applied during testing:
1. Dumb Monkey Testing
This involves completely random inputs with no understanding of the system. Actions are executed blindly, making it useful for stress testing but difficult to reproduce failures.
2. Smart Monkey Testing
The tester has knowledge of the application’s structure, workflows, and valid inputs. While actions are still random, they are contextually relevant.
3. Brilliant Monkey Testing
This approach understands both valid and invalid states of the system. It intentionally navigates the application into problematic areas to uncover logical defects.
Robot Framework is most commonly used for Smart Monkey Testing, where randomness is controlled programmatically.
Why Monkey Testing Is Important in Real-World Applications
Modern applications must handle:
- Unexpected user behavior
- Invalid data inputs
- Sudden navigation changes
- Concurrent operations
Monkey Testing helps identify:
- Application crashes
- Unhandled exceptions
- Performance degradation
- UI freezes or deadlocks
- Memory and resource leaks
By introducing randomness, testers gain confidence that the application will remain stable under unpredictable conditions.
Introduction to Robot Framework

Robot Framework is an open-source automation framework built on Python, widely used for test automation and robotic process automation (RPA). It follows a keyword-driven approach, making test cases easy to read, write, and maintain.
Core Features of Robot Framework
- Plain-text test syntax
- Extensive library support
- Cross-platform compatibility
- Detailed test reports and logs
- Easy integration with CI/CD pipelines
These features make Robot Framework an excellent choice for implementing Monkey Testing in an organized manner.
Why Use Robot Framework for Monkey Testing?

Robot Framework adds structure to randomness. Instead of chaotic testing without visibility, Robot Framework enables:
- Controlled random action generation
- Detailed execution logs
- Repeatability using random seeds
- Easy debugging and reporting
- Scalability across browsers and platforms
With external libraries like SeleniumLibrary, Robot Framework can perform Monkey Testing on web applications efficiently.
Environment Setup for Monkey Testing
Step 1: Install Python
Ensure Python 3.8 or above is installed.
Step 2: Install Robot Framework
pip install robotframeworkStep 3: Install Selenium Library
pip install robotframework-seleniumlibraryStep 4: Install WebDriver
Download the appropriate WebDriver (ChromeDriver, GeckoDriver) compatible with your browser version.
Designing a Monkey Testing Strategy

Monkey Testing should be planned, even though the execution is random.
1. Define Test Scope
Decide which parts of the application should be tested randomly:
- Navigation menus
- Forms
- Buttons
- Links
- Input fields
2. Identify Random Actions
Examples include:
- Random clicking
- Random text input
- Random navigation
- Random scrolling
- Random delays
3. Set Execution Limits
Define:
- Maximum test duration
- Maximum number of actions
- Failure thresholds
This prevents endless execution.
Implementing Monkey Testing Using Robot Framework
Below is an extended example demonstrating random navigation and interactions.
Sample Monkey Testing Script
*** Settings ***
Library SeleniumLibrary
Library Collections
Library BuiltIn
Suite Setup Open Browser And Prepare
Suite Teardown Close Browser
*** Variables ***
${BASE_URL} https://example.com
${BUTTONS} xpath://button
${INPUTS} xpath://input
${LINKS} xpath://a
${ITERATIONS} 20
*** Test Cases ***
Monkey Testing Web Application
[Documentation] Randomly interact with UI elements to test stability
:FOR ${index} IN RANGE ${ITERATIONS}
\ Perform Random Action
\ Sleep ${random.uniform(0.5, 2.0)}
*** Keywords ***
Open Browser And Prepare
Open Browser ${BASE_URL} Chrome
Maximize Browser Window
Wait Until Page Contains Element ${LINKS}
Perform Random Action
${choice}= Evaluate random.randint(1, 3) modules=random
Run Keyword If ${choice} == 1 Click Random Button
Run Keyword If ${choice} == 2 Enter Random Text
Run Keyword If ${choice} == 3 Click Random Link
Click Random Button
${elements}= Get WebElements ${BUTTONS}
Run Keyword If '${elements}' == '[]' Return From Keyword
${count}= Get Length ${elements}
${index}= Evaluate random.randint(0, ${count}-1) modules=random
Click Element ${elements}[${index}]
Log Clicked a random button
Enter Random Text
${inputs}= Get WebElements ${INPUTS}
Run Keyword If '${inputs}' == '[]' Return From Keyword
${count}= Get Length ${inputs}
${index}= Evaluate random.randint(0, ${count}-1) modules=random
Input Text ${inputs}[${index}] RandomText${index}
Log Entered random text
Click Random Link
${links}= Get WebElements ${LINKS}
${count}= Get Length ${links}
${index}= Evaluate random.randint(0, ${count}-1) modules=random
Click Element ${links}[${index}]
Log Clicked a random link
How This Script Works
- Randomly selects an action during each iteration
- Interacts with buttons, inputs, or links
- Logs every action for traceability
- Introduces random delays to mimic human behavior
This approach ensures broader coverage without rigid scripting.
Best Practices for Monkey Testing
1. Enable Detailed Logging
Always capture logs, screenshots, and timestamps.
2. Control Randomness
Use random seeds for reproducibility when debugging failures.
3. Combine with Other Testing Types
Monkey Testing complements unit, integration, and regression testing—it should not replace them.
4. Monitor System Resources
Track memory usage, CPU spikes, and response time during execution.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its advantages, Monkey Testing has some drawbacks:
- Difficult to reproduce failures without logs
- May miss specific business logic issues
- Requires careful monitoring
Understanding these limitations helps in applying Monkey Testing effectively.
Use Cases Where Monkey Testing Excels

- UI-heavy applications
- Consumer-facing web apps
- Early-stage application stability checks
- Regression stability testing
Conclusion
The art of Monkey Testing lies in embracing chaos while maintaining control. When implemented using Robot Framework, Monkey Testing becomes structured, traceable, and scalable. It empowers QA teams to simulate real-world user unpredictability and uncover hidden vulnerabilities before users encounter them.
By integrating Monkey Testing into your automation strategy, you significantly improve application resilience, reliability, and user confidence.
If You Want to study more about testing, kaashiv Infotech Offers, Software Testing Course, or any other course & Internship visit www.kaashivinfotech.com.







