As software systems grow more complex, ensuring quality through manual testing alone has become impractical. Businesses today expect faster releases, higher reliability, and minimal defects, which has led to the widespread adoption of automation testing frameworks. Among the many automation tools available, Robot-Framework has emerged as a powerful and beginner-friendly solution.
Robot Framework is an open-source, keyword-driven automation framework designed to simplify test automation and robotic process automation (RPA). Its human-readable syntax allows testers, developers, and even non-technical stakeholders to collaborate efficiently. Because of its flexibility and extensibility, Robot-Framework is widely used across industries for web, mobile, API, and desktop automation.
This comprehensive article explains Robot-Framework in depth, covering its concepts, architecture, components, libraries, installation, test structure, execution process, advantages, limitations, real-world use cases, and best practices.
What is Robot Framework?

Robot-Framework is a generic automation framework written in Python that supports keyword-driven testing. Instead of writing complex code, users create test cases using simple keywords that describe actions in plain English.
Originally designed for acceptance testing, Robot-Framework has evolved into a full-fledged automation solution supporting:
- Functional testing
- Regression testing
- Acceptance testing
- API testing
- Mobile and desktop automation
- Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Robot-Framework is platform-independent and works seamlessly on Windows, Linux, and macOS.
Why Choose Robot Framework?
Robot-Framework is chosen by organizations and testers because it bridges the gap between technical and non-technical teams. Test cases are readable, maintainable, and reusable, reducing both development time and maintenance costs.
Key reasons to use Robot-Framework include:
- Low learning curve
- Easy collaboration
- Extensive library support
- Open-source and free
- Scalable for large projects
Key Features of Robot Framework
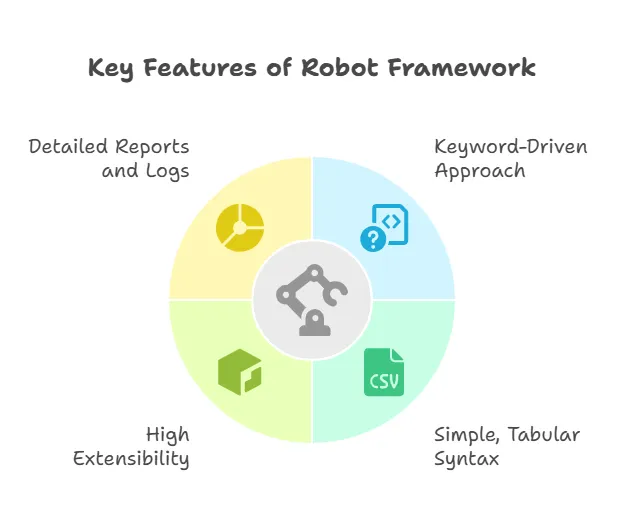
1. Keyword-Driven Approach
Test cases are written using keywords that represent actions, validations, or processes. This improves readability and maintainability.
2. Simple and Readable Syntax
Tests are written in plain text using tabular format, making them easy to understand.
3. Cross-Platform Support
Robot-Framework runs on multiple operating systems without modification.
4. Extensibility
Users can create custom keywords using Python or Java.
5. Rich Library Ecosystem
Supports numerous built-in and external libraries for various testing needs.
6. Automatic Reports and Logs
After execution, Robot-Framework generates detailed HTML reports and logs.
7. CI/CD Integration
Integrates easily with Jenkins, GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, and other DevOps tools.
Robot Framework Architecture Explained
The Robot Framework architecture is designed to separate test logic from implementation.
1. Test Data Layer
Contains test cases, test suites, variables, and keywords written in .robot files.
2. Test Libraries Layer
Includes built-in, external, and custom libraries that provide keyword implementations.
3. Core Framework Engine
Interprets test cases, executes keywords, manages variables, and handles errors.
4. Execution Interface
Supports command-line execution and CI/CD pipeline execution.
5. Reporting and Logging Layer
Generates execution reports and logs in HTML format.
Core Components of Robot Framework
Test Cases
Test cases define the steps to verify application functionality.
Keywords
Keywords are reusable actions such as login, click button, or verify page title.
Variables
Variables store reusable data like URLs, credentials, and test values.
Test Suites
A test suite is a collection of test cases grouped logically.
Resource Files
Resource files store reusable keywords and variables.
Robot Framework File Structure
A typical Robot-Framework project follows this structure:
tests/– Test case filesresources/– Reusable keywords and variableslibraries/– Custom Python librariesresults/– Execution reports and logs
This structure improves scalability and maintainability.
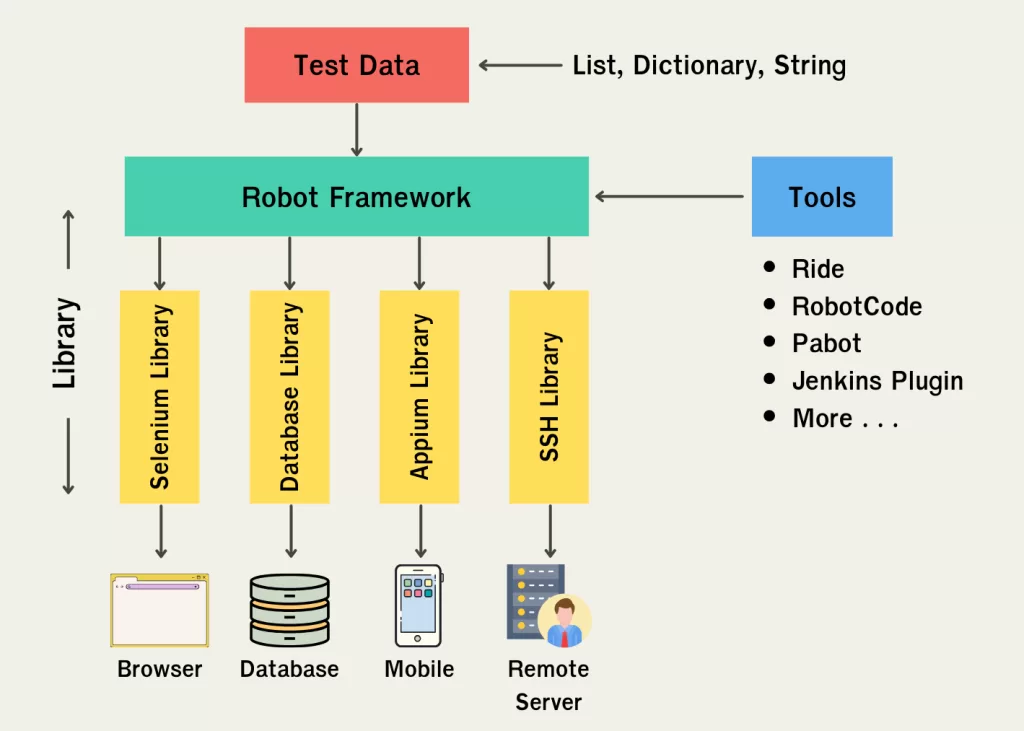
Built-in Libraries in Robot Framework
Robot-Framework provides several built-in libraries:
- BuiltIn – Core functionality
- OperatingSystem – File and OS operations
- Collections – List and dictionary handling
- String – String manipulation
- DateTime – Date and time operations
- Process – Running external processes
These libraries reduce dependency on external tools.
Popular External Libraries
Robot Framework supports many third-party libraries:
- SeleniumLibrary – Web automation
- AppiumLibrary – Mobile automation
- RequestsLibrary – API testing
- DatabaseLibrary – Database validation
- SSHLibrary – Remote server automation
Installing Robot Framework
Prerequisites
- Python 3.x
- pip package manager
Installation Steps
pip install robotframeworkVerify installation:
robot --versionInstall SeleniumLibrary:
pip install robotframework-seleniumlibraryUnderstanding Robot Framework Test File Sections
Settings Section
Defines libraries, resources, and suite setup.
Variables Section
Stores reusable values.
Test Cases Section
Contains test scenarios.
Keywords Section
Defines custom keywords.
Writing Your First Robot Framework Test Case
*** Settings ***
Library SeleniumLibrary
*** Variables ***
${URL} https://example.com
*** Test Cases ***
Open Website
Open Browser ${URL} chrome
Close Browser
Executing Robot Framework Tests
Tests can be executed using:
robot tests/Results include:
report.htmllog.htmloutput.xml
Robot Framework for Different Types of Testing
Web Testing
Automates browser-based applications using Selenium.
API Testing
Validates REST APIs using RequestsLibrary.
Mobile Testing
Automates Android and iOS apps using Appium.
Desktop Testing
Supports Windows-based applications.
RPA Automation
Automates repetitive business processes.
Advantages of Robot Framework
- Beginner-friendly
- Highly readable test cases
- Strong community support
- Excellent reporting
- Flexible and scalable
Limitations of Robot Framework
- Complex logic can reduce readability
- Slower execution than pure code-based tests
- Requires proper keyword design
Best Practices for Robot Framework

- Use meaningful keyword names
- Keep test cases short
- Store reusable logic in resource files
- Follow proper folder structure
- Maintain clear documentation
Career Scope of Robot Framework
Robot Framework skills are valuable for:
- Automation Test Engineers
- QA Engineers
- DevOps Engineers
- RPA Developers
Conclusion
Robot Framework is a robust, flexible, and beginner-friendly automation framework that simplifies testing through its keyword-driven approach. With strong library support, easy integration, and excellent reporting, it is an ideal choice for modern test automation and RPA projects.
Learning Robot Framework builds a solid foundation in automation testing and opens opportunities across QA, DevOps, and enterprise automation roles.
Kaashiv Infotech Offers, Full Stack Python Course, Full Stack Java Course, & More, Visit Their Website course.kaashivinfotech.com.







