What is a Distributed Computing Operating System?
Let’s be honest — when I first heard the term distributed computing operating system, it sounded like something right out of a sci-fi movie. But once I got into software engineering, I realized it’s actually the invisible backbone of modern computing.
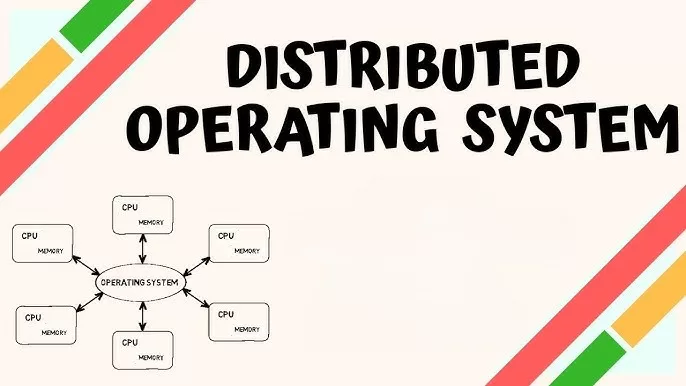
A distributed computing operating system is basically an advanced type of operating system that manages a group of interconnected computers and makes them work as one single system. Think of it as a team of computers collaborating under one “leader” — the OS.

For example, when you use Google Search, it doesn’t rely on a single computer. Instead, hundreds of servers across different locations work together — seamlessly. And guess what helps make that possible? Yep, a distributed computing operating system.
I remember when I first learned about this in my networking class. I was blown away by how multiple machines can share resources and workload like a group of synchronized swimmers. Every machine has its role, but the coordination is so smooth that it feels like one big computer.
Why Do We Even Need a Distributed Operating System?
Let’s say you’re watching Netflix. Behind that experience lies a distributed computing operating system managing countless data centers. Even if one server crashes, others take over instantly — meaning your show doesn’t buffer.

That’s the beauty of distributed computing. It’s built for:
- Fault tolerance – No single point of failure.
- Speed and efficiency – Tasks are split across multiple nodes.
- Scalability – You can add more machines anytime.
- Resource sharing – Memory, data, and processors are shared smartly.
When I worked on my first cloud-based project, I realized the power of this concept. We had three virtual machines handling a massive data load. Without a distributed system, it would’ve taken hours. But with one, it finished in minutes. That’s when it hit me — this is what powers the modern internet.
How Does a Distributed Computing Operating System Work?

Imagine you have four computers. Now, instead of working independently, they all work together like a brain with four lobes. The distributed computing operating system coordinates which task goes where.
Here’s what happens behind the scenes:
- Task allocation: The system breaks a large job into smaller parts.
- Communication: Each computer (or node) talks to others over a network.
- Synchronization: Tasks are aligned in real-time to prevent conflicts.
- Transparency: You don’t even realize multiple systems are involved — it feels like one big OS.
This is how large-scale systems like Facebook, YouTube, or Amazon AWS run millions of requests per second.
If you want to geek out further, check out Google’s Borg system — it’s a distributed OS that inspired Kubernetes. It’s a fantastic real-world example of distributed computing in action.
Types of Distributed Computing Operating Systems

Not all distributed systems are created equal. Here are the main types I’ve worked with (and learned from the hard way ):
1. Client-Server Systems
This one’s simple. A server provides services, and clients (like your laptop) request them. Think of it like how browsers connect to websites hosted on a remote server.
2. Peer-to-Peer Systems
Every node acts as both a client and a server. Remember BitTorrent? That’s a peer-to-peer distributed system in action.
3. Cluster-Based Systems
Used in high-performance computing. Multiple computers are grouped together to solve complex problems — like weather forecasting or AI training.
4. Cloud-Based Systems
This is the present (and future). Services like AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure are all powered by distributed computing operating systems.
Real-World Examples of Distributed Computing Operating Systems
Here are some famous systems you’ve probably heard of (even if you didn’t realize they’re “distributed”):
- Google File System (GFS) – Manages data storage across multiple servers.
- Apache Hadoop – Handles big data analytics.
- Kubernetes – Automates containerized applications (fun fact: it’s open-source!).
- Microsoft Azure Fabric – Manages distributed cloud applications.
- Amoeba Distributed OS – One of the earliest examples used in research.
These examples show how distributed computing operating systems power nearly every large-scale digital service we use daily.
Benefits of a Distributed Computing Operating System
Now, let’s talk about the good stuff. Here’s why engineers (like me) love working with distributed systems:
✅ High Reliability: If one machine fails, others jump in.
✅ Better Performance: Tasks are executed in parallel.
✅ Easy Scalability: You can expand the system without downtime.
✅ Efficient Resource Utilization: Every node contributes its share.
✅ Cost-Effective: You can use cheap machines to build powerful networks.
When I helped deploy a mini distributed setup at my university lab, the performance improvement was unreal. A process that took 30 minutes on one system was done in under five. That’s when I stopped underestimating distributed computing.
Challenges in Distributed Operating Systems
Of course, it’s not all sunshine and speed. Working with a distributed computing operating system can also be tricky.

Some common challenges include:
- Security risks: Multiple nodes = multiple entry points for attackers.
- Complex synchronization: Keeping every system in sync is hard.
- Network dependency: If one link goes down, performance can suffer.
- Debugging issues: Identifying where a problem occurs can take time.
I still remember staying up all night debugging a cluster sync issue — turns out one node had a wrong timestamp. A small detail, but it broke everything. That’s the reality of distributed computing — powerful but fragile.
My Final Thoughts
A distributed computing operating system isn’t just a tech buzzword. It’s the unsung hero of modern computing — from your favorite streaming service to the cloud platforms hosting your apps.
The idea that multiple machines, across different continents, can act as one unified system still fascinates me. Whether you’re a developer, student, or just curious about tech, understanding this concept gives you a glimpse into how the digital world truly works.
If you’re eager to dive deeper, I’d recommend checking out:
- Google Cloud Documentation for real-world distributed examples.
- Kubernetes Official Site to understand orchestration.
Kaashiv Infotech Offers Networking Course, Cyber Security Course, Cloud Computing Course Visit Their Website www.kaashivinfotech.com.