Introduction: The Brain of Your Computer
Every time you start your laptop computer, play a video game, or read this article, there is a small but mighty hero working behind the scenes inside your machine – the CPU. But, what is CPU? The CPU is usually called the central processing unit or simply the processor, but this little chip is the heart and brain of every computer. Without the CPU, your computer would just be a pile of useless hardware.
In this guide, we will go through everything you need to know about the CPU, including all of the following: the definition of a CPU; the parts of a CPU; how it works; how it works with CPU memory; and why it is essential to modern computers.
What is CPU? (Central Processing Unit Explained)

The CPU, or Central Processing Unit, is the main component in your computer responsible for most of the processing that occurs inside your machine. The CPU retrieves instructions from a program, processes commands, and produces results. In layman’s terms, the CPU is similar to the brain of a human being, telling all the other parts what to do.
Here are some key responsibilities of the CPU:
- Instruction fetching
- Command decoding
- Operation execution
- Storage of results into memory
CPU Components and Architecture
The central processing unit is not one chip doing one thing. It consists of several parts that work together.
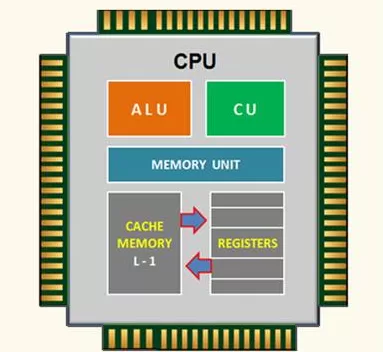
1. Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
The ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit) does not run programs, it performs mathematical calculations (addition, subtraction, multiplication) and logical comparisons (greater than, equal to, less than.)
2. Control Unit (CU)
The control unit controls directions and flow of data and instructions. Think of it as a traffic controller directing data between CPU, memory, and input/output devices.
3. Registers
Registers are super-fast storage space located inside the CPU. They hold temporary data such as instructions, memory addresses, and execution results.
4. Cache Memory
CPU memory (cache) is a very small, but very fast, space, which saves the most often used instructions and data, reducing the amount of times your CPU needs to look in the much slower main memory (RAM).
How Does a CPU Work?
The CPU operates on what’s referred to as the fetch-decode-execute cycle:
- Fetch: grabs the instructions from RAM.
- Decode: breaks instructions down to signals the CPU can understand.
- Execute: executes the instructions, which can be calculate, logical jump, or movement of data.
- Store: result is stored into CPU memory or RAM.
This happens billions of times per second by today’s standards!
Types of CPU

Over the years, CPUs have made remarkable changes. The main types are:
- Single-core CPU: The CPU type that has been around the longest and is only capable of processing one task at a time.
- Dual-core CPU: A CPU consisting of two cores which means better multitasking.
- Quad-core CPU: A CPU with four cores. This type has become pretty standard when it comes to gaming and productivity.
- Octa-core CPU and later: i9, AMD Ryzen 9, Apple M2 Ultra are all considered to be high-performance CPUs.
- Server CPUs: These are built for handling thousands of requests simultaneously.
CPU vs Memory: What’s the Difference?
A common misconception is the confusion between CPU and memory.
- CPU = brain that processes instructions
- Memory (RAM, cache, registers) = where you keep data while it’s being used
Think of it like a chef in the kitchen:
- The CPU is the chef that cooks
- Memory is the countertop where the ingredients (data) are kept temporarily
Even the fastest processor can slow due to poor CPU memory.
Real-World Examples of CPUs

These are popular examples of modern CPUs.
- Intel Core i9 — Powerhouse for gamers and professionals.
- AMD Ryzen 9 — Often referred to as highly effective at multitasking and performance.
- Apple M1/M2 chips — These are low-energy but very powerful.
Why is CPU Important?
- Provides your operating system (Windows, MacOS, Linux).
- Runs applications, games, and browsers.
- Processes whenever you multitask (ie. streaming + browsing + background processes).
- Helps determine how ‘fast’ your computer feels.
Future of CPUs
AI, quantum computing, and GPUs continue to develop and emerge. CPUs are still important, but changes will happen. Hybrid processors, like we see with Apple’s ARM-based chips, prove that power and efficiency can co-exist.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is CPU in simple words?
The CPU is the brain of the computer—it processes instructions and tells other parts what to do.
2. Is CPU the same as memory?
No. CPU processes data, while CPU memory (cache, RAM) stores it temporarily.
3. What are the main parts of a CPU?
ALU, Control Unit, Registers, and Cache Memory.
4. Which is better: more cores or higher speed?
It depends! More cores = better multitasking. Higher speed (GHz) = faster single-task performance.
Conclusion: CPU – The Unsung Hero of Technology
So what is CPU? The CPU – or central processing unit – is the driving force behind every digital operation we perform. CPUs exist from the smallest smartphone to the largest data centre, and represent the foundation of computational sophistication. Acquiring further understanding of the CPU memory, architecture, and overall features truly grounds appreciation for this small was of silicon.
Next time you start your computer, remember that it is powered by the remarkable complexity of your CPU!