Here’s a wild fact: over 80% of modern programming languages — including Python, Java, and Go — borrow their syntax and structure from C. That’s why understanding what is the structure of a C program isn’t just for beginners — it’s the foundation of programming logic itself.
So if you’re learning C, you’re not just learning an old-school language. You’re learning the foundation of programming logic itself.
Whether you’re preparing for a technical interview, writing your first embedded system code, or brushing up for a coding test, understanding what is the structure of a C program is non-negotiable. It’s the first step to writing clean, readable, and bug-free code.
🔑 Key Highlights
- 🧠 Learn the 6 essential sections that every C program must have.
- 🧩 Understand how compilation works — from creation to output.
- ⚙️ See a real working C program example explained line-by-line.
- 💡 Discover best practices developers still use in 2025.
- 🧭 Bonus: Career tip on why C is still the go-to for system programming and IoT.
🧱 What Is the Structure of a C Program?
The structure of a C program defines how your code is organized so the compiler can read, compile, and execute it successfully.
Think of it like building a house: the foundation, walls, wiring, and finishing all need to be in the right order — or the whole thing collapses.
A typical C program is divided into six core sections:
- Documentation
- Preprocessor Section
- Definition
- Global Declaration
main()Function- Subprograms (User-Defined Functions)
Let’s break each part down like a developer would.

🧾 1. Documentation Section in c— The Program’s Cover Page
This is the part most beginners skip — and that’s a mistake.
The documentation section in c is where you describe what your code does and who wrote it. In large projects, this helps teams maintain and update code quickly.
// Program: sum.c
// Author: KD
// Date: 22 September 2025
// Description: Program to find the sum of two numbers.
👉 Pro Tip: Always document your file, especially in collaborative environments or open-source repositories. Recruiters notice developers who write readable, well-commented code.
⚙️ 2. Preprocessor in c — Borrowing the Best Code
The preprocessor in c is where you include header files — reusable chunks of code that save time and reduce errors.
#include <stdio.h> // For standard input-output
#include <math.h> // For mathematical operations
When you write #include, the compiler literally pastes the content of that file before compilation.
In 2025, most embedded C and firmware projects still rely heavily on preprocessors for performance optimization.
🔠 3. Definition Section in c — Setting Constants (and Rules)
Ever seen #define PI 3.14? That’s what happens here.
The definition section lets you define constants or macros used throughout the program.
#define X 20
This ensures you don’t hard-code magic numbers everywhere in your program. If a constant changes, you update it once — not in 20 places.
👉 Best Practice (2025): Use descriptive macro names like #define MAX_USERS 1000 instead of generic ones like #define X 20. It improves readability and reduces debugging pain.
🌍 4. Global Declaration Section in c — Variables That Live Everywhere
Global Declaration Section in c , you declare variables and functions that can be used anywhere in your code.
int num = 18;
int sum(int y);
Global declarations Section in c are powerful — but dangerous. Use them wisely.
A 2025 Stack Overflow survey showed that nearly 35% of debugging issues in C projects come from improperly managed global variables.
👉 Pro Tip: Prefer local variables when possible. Use globals only for constants or configurations that truly need to be shared.
🧩 5. main() Function — The Heartbeat of Every C Program
Every C program starts and ends with the main() function.
It’s where execution begins. You can think of it as the entry point of your program.
int main(void)
{
int y = 55;
printf("Sum: %d", sum(y));
return 0;
}
The return 0; statement means your program ran successfully.
Use int main() instead of void main() — it’s the modern standard accepted by all compilers.

🔁 6. Subprograms — Breaking Code Into Smaller Brains
Subprograms (or user-defined functions) make your code modular and reusable.
int sum(int y)
{
return y + X;
}
When sum(y) is called from the main() function, the control temporarily jumps here, executes the logic, and returns the result.

👉 Developer Insight:
Top tech companies prefer candidates who can break large problems into smaller, testable functions. Learning to use subprograms efficiently is a skill that directly improves your debugging and design ability.
💻 Full Example: Structure of a C Program with Example
Here’s the complete example in one place 👇
// Documentation
/**
* file: sum.c
* author: KD
* description: Program to find sum.
*/
// Preprocessor Section
#include <stdio.h>
// Definition Section
#define X 20
// Global Declaration
int sum(int y);
// main() Function
int main(void)
{
int y = 55;
printf("Sum: %d", sum(y));
return 0;
}
// Subprogram
int sum(int y)
{
return y + X;
}
Output:
Sum: 75
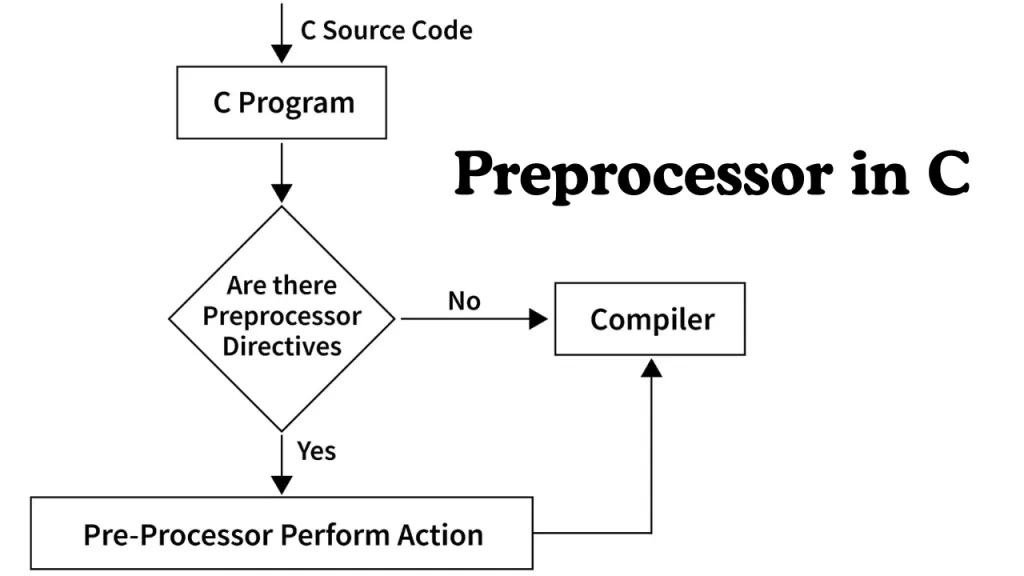
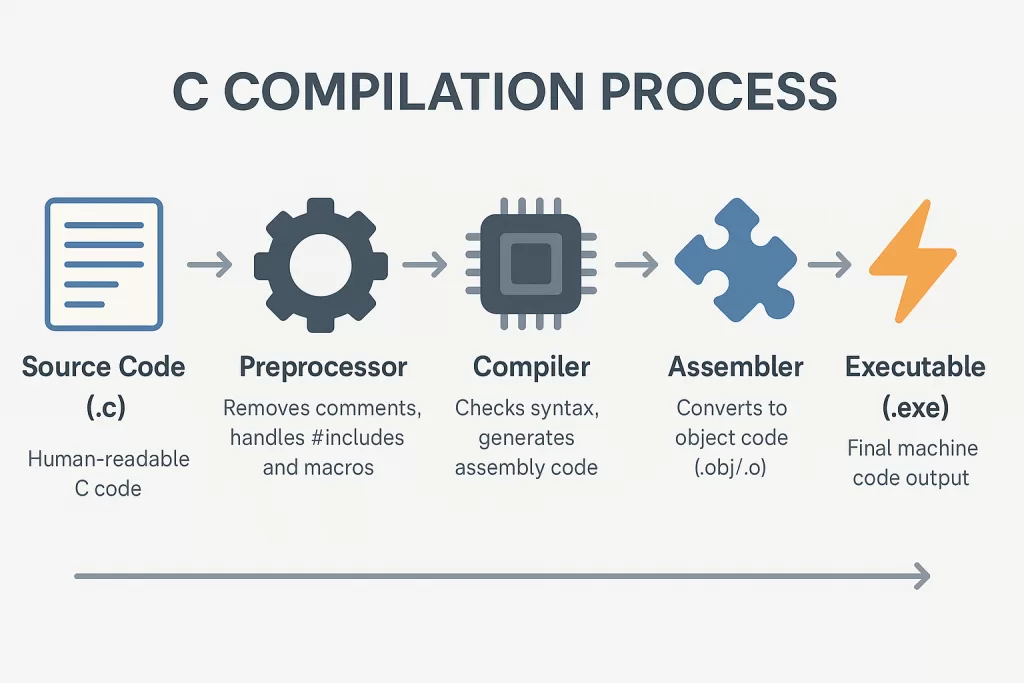
🧠 Behind the Scenes: What Happens During Compilation
Understanding structure is only half the story. Here’s what happens when you hit Compile → Run:
- Program Creation — You write and save your code.
- Compilation — The preprocessor inserts headers, checks syntax, and generates object
- Assembler – converts assembly language code into machine code, which is stored in an object file.
- Linking — The linker combines your code with external libraries.
- Execution — Your final executable runs, producing output.
This process hasn’t changed much in decades — but compilers today are faster, smarter, and can even auto-optimize redundant lines.
🌐 Real-World Use Case: Why It Still Matters in 2025
Even in 2025, C remains the backbone of operating systems, device drivers, microcontrollers, and IoT firmware.
If you’re aiming for a career in embedded systems, robotics, or OS development, a deep understanding of C structure is essential.

“C is like Latin for programmers — even if you don’t speak it every day, it makes you better at every other language.”
— Linus Torvalds (Creator of Linux)
🧭 Best Practices for Writing Structured C Programs
- 🧾 Always document your program with purpose and date.
- 🧠 Keep your
main()function small — delegate logic to subprograms. - ⚙️ Use meaningful names for macros and functions.
- 🚫 Avoid too many global variables — prefer modular code.
- 🧩 Test each function independently before linking.
- 📊 Use compiler warnings (
-Wallflag in GCC) — they catch 90% of logic issues early.
🧩 Conclusion
🧩 Conclusion
If you’ve made it this far, you now clearly understand what is the structure of C program — not just the syntax, but the thinking behind it.
And that understanding matters more today than ever.
According to the 2025 Stack Overflow Developer Survey, over 39% of professional developers still use C or C++ in some form — powering everything from AI-driven devices to automotive systems and IoT microcontrollers. Mastering the structure of a C program isn’t just an academic exercise; it’s the foundation that prepares you for real engineering challenges.
Think of it like this — if you can structure C code properly, you can structure any language logically. That’s why top recruiters at companies like Intel, NVIDIA, and Bosch still test candidates on C fundamentals before hiring for embedded or systems roles.
So, don’t stop here.
✅ Build a few small projects (like a mini calculator, file parser, or sensor monitor).
✅ Practice writing structured C code every day.
✅ Explore how this structure connects to languages like C++, Python, and Rust.
Remember: mastering the structure of a C program isn’t about memorizing sections.
It’s about thinking like a developer who can build systems that last.
📚 Related Reads You’ll Love
If you enjoyed learning about what is the structure of a C program, here are some other guides that’ll help you level up your C and programming fundamentals:
- 🔥 Logical Operators in C (AND, OR, NOT) with Real Examples You’ll Actually Use
→ Master how logic works in C — from condition checks to complex boolean expressions. - 🧩 Format Specifiers in C – List, Examples & printf/scanf Guide [2025]
→ Understand how C interprets data types when printing or scanning values. - 💻 What is C Program? A Beginner-Friendly Guide to the C Language in 2025 (With Real Examples!)
→ Start from scratch and get comfortable with the C language basics. - 🏗️ Design Patterns in C# & Java (2025 Guide) – With Code Examples, UML & Best Practices
→ Learn how professional developers structure large-scale projects with reusable patterns. - 🚀 Linked List in C: The Complete Beginner-to-Pro Guide (with Real Use Cases in 2025)
→ Move beyond arrays — understand memory management and dynamic data structures in C. - 🔥 Pointers in C Explained (2025 Guide with Real Examples & Best Practices)
→ Finally demystify pointers with visuals, use cases, and coding tips every C developer needs.