What is a SQL Query?
A SQL Query is simply a question you ask your database.
That’s it. No drama. No giant academic definition.
When I say:
SELECT * FROM employees;
…I’m basically asking the database:
“Hey, show me all the employees you’ve got.”
When people overcomplicate SQL Query writing with heavy words like relational algebra and query optimization strategies, I smile.
Because 90% of interviews just check whether you can write clean queries and solve real problems.
And that’s exactly what we’re going to prepare for

Why SQL Query Knowledge Is So Important in Interviews?
Let me tell you something many candidates don’t realize:
💥 SQL Query skills don’t belong to one domain.
- Data analysts use them
- Backend developers use them
- Testers use them
- Data scientists (yes, even them!) use them
Whenever you work with data—even a bit—you’ll touch SQL Query writing.
Every time I interview a candidate, one thing I look for is clarity.
Not complexity.
Not fancy words.
Just clarity.
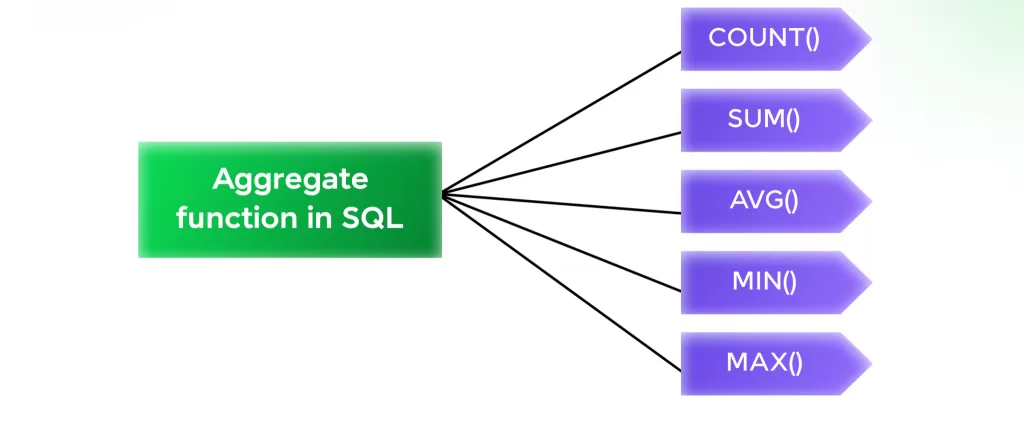
Let’s Dive Into The Top SQL Query Interview Questions
To make this simple, I divided them into levels.
Just like how I learned SQL myself—slowly, with lots of mistakes and a little curiosity.
Basic SQL Query Interview Questions -Beginners Level
1. What is a SQL Query?
I know, I know… you already know this.
But interviewers love to start simple.
A SQL Query is a command used to interact with databases—fetching, updating, deleting, and manipulating data.
2. Difference between WHERE and HAVING?
I always explain it like this:
- WHERE filters rows before grouping
- HAVING filters groups after grouping
Simple and clean.
3. Write a SQL Query to fetch the second-highest salary.
SELECT MAX(salary)
FROM employees
WHERE salary < (SELECT MAX(salary) FROM employees);
This one shows up in almost every interview.
Fun fact—I got this question in my first SQL round and froze .
You don’t have to.
4. What’s the difference between DELETE, TRUNCATE, and DROP?
I remember this using a house analogy:
- DELETE → removes items inside the room
- TRUNCATE → empties the room completely
- DROP → demolishes the entire room

5. Write a SQL Query to find names starting with ‘A’.
SELECT name FROM employees WHERE name LIKE 'A%';
Intermediate SQL Query Interview Questions
This is where the interviews start becoming interesting.
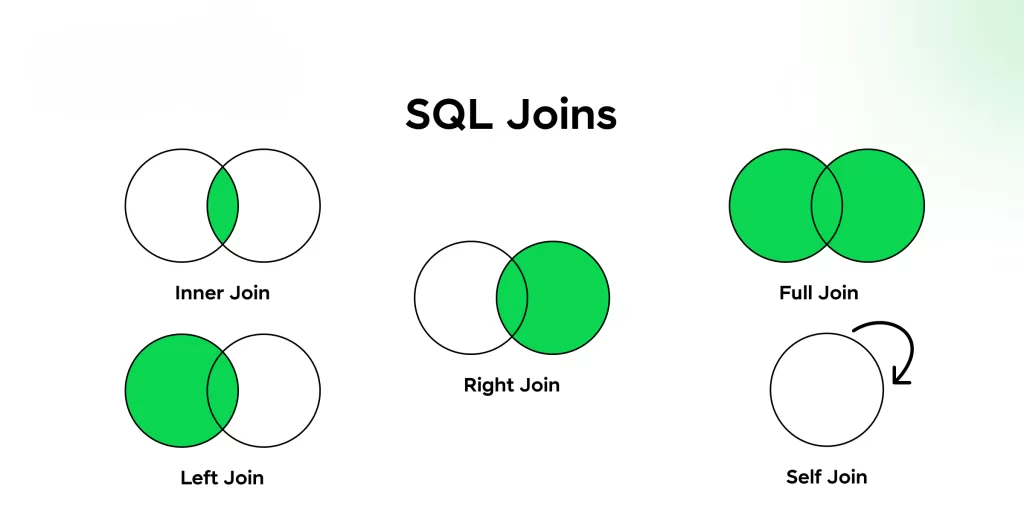
6. What is a JOIN? Name types of JOINs.
A JOIN lets you combine rows from different tables.
Types include:
- INNER JOIN
- LEFT JOIN
- RIGHT JOIN
- FULL JOIN
Whenever I explain this, I imagine connecting two spreadsheets—makes life easier.
7. Write a SQL Query to get the highest salary per department.
SELECT department, MAX(salary)
FROM employees
GROUP BY department;
8. What is a Subquery?
A SQL Query inside another SQL Query.
Just like a story inside another story .
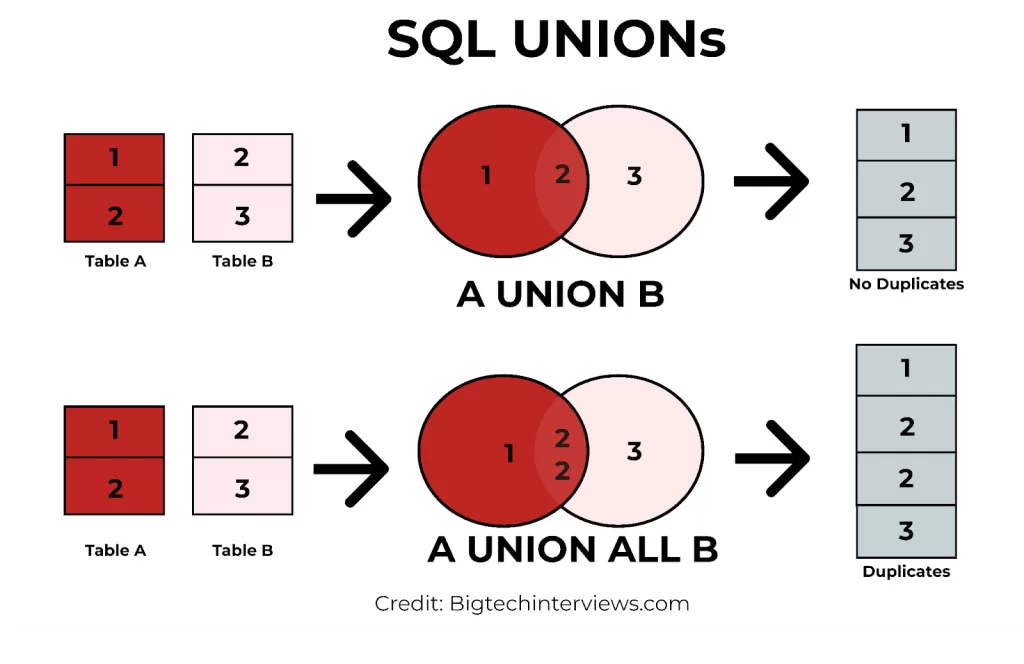
9. Difference between UNION and UNION ALL?
- UNION → removes duplicates
- UNION ALL → keeps duplicates
A surprisingly common question.
10. What are constraints in SQL?
Primary key, foreign key, unique, check, not null.
Advanced SQL Query Interview Questions
If you’re applying for data engineering, backend development, or analytics roles—expect these.
11. What are Window Functions?
Functions like:
- ROW_NUMBER
- RANK
- DENSE_RANK
- LEAD
- LAG

Used when you want running totals, rankings, or comparison between rows.
Here’s a SQL Query example:
SELECT
name, salary,
RANK() OVER (ORDER BY salary DESC) AS salary_rank
FROM employees;
12. What is a CTE? – WITH Clause
A Common Table Expression helps you write cleaner SQL Query structures.
WITH dept_salary AS (
SELECT department, MAX(salary) AS max_salary
FROM employees
GROUP BY department
)
SELECT * FROM dept_salary;
13. Write a SQL Query to find duplicate records.
SELECT name, COUNT(*)
FROM employees
GROUP BY name
HAVING COUNT(*) > 1;
14. How do you optimize a SQL Query?
My usual checklist:
- Add proper indexing
- Avoid SELECT *
- Use WHERE clauses
- Reduce nested subqueries
- Use LIMIT when needed
15. Write a SQL Query to fetch top 3 salaries per department.
SELECT *
FROM (
SELECT name, department, salary,
DENSE_RANK() OVER (PARTITION BY department ORDER BY salary DESC) AS rnk
FROM employees
) t
WHERE rnk <= 3;
Real-Life SQL Query Scenarios
I’ve seen hiring managers throw these questions just to check how practical you are.
Scenario 1: Find employees who never received a bonus
SELECT e.*
FROM employees e
LEFT JOIN bonus b ON e.id = b.emp_id
WHERE b.emp_id IS NULL;
Scenario 2: Find customers who ordered more than 3 times
SELECT customer_id, COUNT(order_id)
FROM orders
GROUP BY customer_id
HAVING COUNT(order_id) > 3;
Scenario 3: Detect gaps in ID sequences
SELECT id + 1 AS missing_id
FROM employees
WHERE (id + 1) NOT IN (SELECT id FROM employees);
My Personal Tips to Crack SQL Query Interviews
Let me share real advice I give my juniors:
✔ Be calm
SQL is logical. If you panic, you lose clarity.
✔ Think out loud
Interviewers love hearing your thought process.
✔ Use real examples
Say things like:
“Let’s say we have an employees table…”
Makes you sound confident.
✔ Ask clarifying questions
It shows maturity.
Final Thoughts — SQL Query Interviews Aren’t Hard
Honestly, SQL Query interviews seem tough only when you don’t practice real questions.
But once you understand the why behind each SQL Query, everything clicks into place.
And trust me—everyone learns SQL at their own pace.
Even I messed up simple JOINs when I first started.
So don’t worry, you’ll get there .
want to learn more?, kaashiv infotech offers, SQL Course , data science course, data analytics and more visit their website www.kaashivinfotech.com







