If you’re learning about inheritance in Java, you’re learning about one of the most important aspects of Object-Oriented Programming (OOP). Whether you’re preparing for interviews, developing apps that can scale, or just getting started with Java, understanding inheritance can save you countless hours of coding and debugging.
💡 Fun fact! About 80% of the Java interview questions that have been asked involve some concept of OOP — whether it be inheritance, polymorphism, or abstraction (You can check out GeeksforGeeks interview trend for more details). So if you’re looking to pursue a career in development, it is something you want to pay attention to.
In this article, you will learn:
- What inheritance in Java is
- Why it is important
- The syntax
- Types of inheritance with examples
- The challenging concept of multiple inheritance
✅ When you are done, you will not only have an understanding of the theory, but you will also know how developers utilize inheritance to build actual applications.
🔑 Key Highlights
- Inheritance in Java allows one class to acquire properties and methods of another.
- Improves code reusability and reduces redundancy.
- Java supports Single, Multilevel, Hierarchical, Hybrid inheritance.
- Multiple inheritance is not directly supported (because of the “Diamond Problem”).
- Use of the super keyword is critical in constructor chaining and method access.
- Real-world examples: Android framework classes, Java Collections hierarchy.
🔹 What is Inheritance in Java? 🤔
Think of inheritance in Java in real life. For example:
- A Car is a type of Vehicle
- A Truck is also a type of Vehicle
Instead of having to write out the “engine, wheels, fuel” properties for every class, you just define these in Vehicle, and both Car and Truck inherit those definitions — and can add their own.
In Java, inheritance means that one class (called the child class or sub-class) can obtain the fields and methods of another class (called the parent class or super-class).
✨ Why is this useful?
- Inheritance helps us avoid code duplication
- It makes it easier for developers to add functionality
- It supports reusability and scalability in applications
👉 In simple terms:
Inheritance in Java is the process of inheriting the properties and behaviours of a parent class into a child class using the extends keyword.
Example:
class Vehicle {
void start() {
System.out.println("Vehicle starts...");
}
}
class Car extends Vehicle {
void drive() {
System.out.println("Car is driving...");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Car c = new Car();
c.start(); // inherited from Vehicle
c.drive(); // defined in Car
}
}
✔ Output:
Vehicle starts...
Car is driving...
This is single inheritance in Java, the simplest form.
Syntax of Inheritance in Java 📜
Inheritance in Java is written using the extends keyword:
class ChildClass extends ParentClass {
// child’s fields and methods
}
Quick facts to note:
- Java doesn’t support multiple inheritance with classes (only with interfaces).
- The child class can access public and protected members of the parent class.
- Private members of a parent class are not inherited.
Many beginners miss this: when you create an object of the child class, the constructor of the parent class is called first. This ensures the base setup is done before the child adds its own properties.
Types of Inheritance in Java
Now, let’s break down the types of inheritance in Java. These often come up in interviews, and each one has real-world applications.
1. Single Inheritance in Java
This is the most straightforward form: one class inherits from another.
Example:
class Parent {
void display() {
System.out.println("This is the parent class");
}
}
class Child extends Parent {
void show() {
System.out.println("This is the child class");
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Child c = new Child();
c.display(); // parent method
c.show(); // child method
}
}
Real-world use case:
- JDBC classes in Java often extend core utility classes to add specific database operations.

2. Multilevel Inheritance in Java
When a class inherits from a parent, and another class inherits from that child, it’s called multilevel inheritance.
Example:
class Grandparent {
void grandMethod() {
System.out.println("Grandparent method");
}
}
class Parent extends Grandparent {
void parentMethod() {
System.out.println("Parent method");
}
}
class Child extends Parent {
void childMethod() {
System.out.println("Child method");
}
}
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Child c = new Child();
c.grandMethod();
c.parentMethod();
c.childMethod();
}
}
✔ Output:
Grandparent method
Parent method
Child method
Real-world insight:
- The Swing GUI library in Java uses multilevel inheritance heavily. For example,
JFrameinherits fromFrame, which in turn inherits fromWindow.
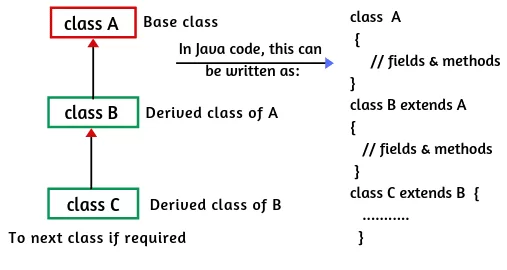
3. Hierarchical Inheritance in Java
Here, multiple classes inherit from a single parent.
Example:
class Animal {
void eat() {
System.out.println("Eating...");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
void bark() {
System.out.println("Barking...");
}
}
class Cat extends Animal {
void meow() {
System.out.println("Meowing...");
}
}
public class TestHierarchical {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog d = new Dog();
d.eat();
d.bark();
Cat c = new Cat();
c.eat();
c.meow();
}
}
✔ Output:
Eating...
Barking...
Eating...
Meowing...
Real-world use case:
- In Android development, many UI components like
Button,TextView, andEditTextextend from the same base classView. This is a textbook example of hierarchical inheritance.

4. Hybrid Inheritance in Java
Here’s the tricky one. Hybrid inheritance is basically a mix of two or more inheritance types. Technically, Java doesn’t support hybrid inheritance directly with classes because it could lead to conflicts. But you can achieve it using interfaces.
Example:
interface A {
void showA();
}
interface B {
void showB();
}
class C implements A, B {
public void showA() {
System.out.println("From A");
}
public void showB() {
System.out.println("From B");
}
}
public class HybridExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
C obj = new C();
obj.showA();
obj.showB();
}
}
✔ Output:
From A
From B
Real-world example:
- In Java’s Collections Framework, classes like
HashMapimplement multiple interfaces (Map,Cloneable,Serializable), achieving hybrid inheritance.

5. Multiple Inheritance in Java
This is one of the most asked interview questions. And here’s the truth: Java does not support multiple inheritance with classes. Why? Because of the Diamond Problem.
Imagine:
- Class A has a method
display(). - Class B also has
display(). - If Class C extends both A and B, which
display()should it inherit?
That ambiguity is the diamond problem.
But here’s the catch: Java allows multiple inheritance using interfaces.
Example:
interface Printer {
void print();
}
interface Scanner {
void scan();
}
class MultiFunctionDevice implements Printer, Scanner {
public void print() {
System.out.println("Printing document...");
}
public void scan() {
System.out.println("Scanning document...");
}
}
public class TestMultipleInheritance {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MultiFunctionDevice mfd = new MultiFunctionDevice();
mfd.print();
mfd.scan();
}
}
Real-world example:
- In Java 8 and above, interfaces can have
defaultmethods. If two interfaces have the same default method, the implementing class must override it. This is Java’s way of letting developers resolve conflicts explicitly.
super Keyword in Inheritance 🔑
The super keyword is the hidden gem of inheritance. It does two important things:
- Calls the parent class constructor.
- Accesses parent class methods/fields when overridden.
Example (constructor chaining):
class Parent {
Parent() {
System.out.println("Parent constructor");
}
}
class Child extends Parent {
Child() {
super(); // calls Parent constructor
System.out.println("Child constructor");
}
}
public class SuperDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Child c = new Child();
}
}
✔ Output:
Parent constructor
Child constructor
In multilevel inheritance, super climbs up the chain step by step. Developers rely on it to avoid accidental overrides and keep behavior consistent.
Method Overriding and Polymorphism in Inheritance
Inheritance without overriding is like coffee without caffeine ☕. Overriding lets a child class redefine a parent’s method. Combined with polymorphism, it allows dynamic method dispatch.
Example:
class Animal {
void sound() {
System.out.println("Animal makes a sound");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
@Override
void sound() {
System.out.println("Dog barks");
}
}
public class OverrideDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal a = new Dog(); // parent reference, child object
a.sound(); // calls Dog's method
}
}
✔ Output:
Dog barks
This is polymorphism in action — the program decides at runtime which method to call.
Access Modifiers and Inheritance
When using inheritance, access levels matter:
public: accessible everywhere.protected: accessible in child classes (even in different packages).- default (no modifier): accessible within the same package.
private: not inherited.
Best practice: Keep sensitive fields private and expose them through getters/setters. This balances security with flexibility.
final Keyword and Inheritance
- A
finalclass (likeString) cannot be extended. - A
finalmethod cannot be overridden.
Why? To prevent misuse or modification of critical code. Imagine if you could extend String and break its immutability — chaos.
Java Abstract Class Inheritance
Abstract classes act as blueprints. You can’t instantiate them, but child classes inherit their methods and must implement the abstract ones.
Example:
abstract class Shape {
abstract void draw();
}
class Circle extends Shape {
void draw() {
System.out.println("Drawing a Circle");
}
}
Real-world:
- Java’s
AbstractListis extended byArrayList,LinkedList, etc. This lets developers provide partial implementations and force subclasses to complete the rest.
Advantages of Inheritance in Java ✅
- Code reusability: Write once, use many times.
- Cleaner architecture: Avoids duplication.
- Flexibility: Update parent logic, and children get it automatically.
- Polymorphism support: Enhances dynamic behavior in applications.
Real-Life Examples of Inheritance in Java
- Android development:
Activityis the parent class, whileMainActivityorLoginActivityextend it. - Collections Framework:
HashSetextendsAbstractSet, which extendsAbstractCollection. - Spring Framework: Uses hierarchical beans where one configuration inherits from another.
Common Interview Questions on Inheritance in Java 🎯
- Why is multiple inheritance not supported in Java?
- How many types of inheritance are there in Java?
- Difference between inheritance and composition?
- How can you achieve multiple inheritance in Java?
- What is constructor chaining in inheritance?
👉 Pro tip: Interviewers often ask for real-world use cases, not just definitions.
FAQs on Inheritance in Java
Q1. What is inheritance and its types in Java?
Inheritance is acquiring fields and methods of one class into another. Types: Single, Multilevel, Hierarchical, Hybrid (through interfaces).
Q2. Which inheritance is not supported in Java?
Multiple inheritance with classes.
Q3. How to achieve multiple inheritance in Java?
By using interfaces.
Q4. Why multiple inheritance is not in Java?
To avoid ambiguity caused by the Diamond Problem.
🎉 Conclusion
So, there you have it — a complete guide to inheritance in Java.
That covers:
- Simple inheritance examples
- The not-so-simple, tricky multiple inheritance case
- Practical information like the super keyword and abstract classes
Now you know how inheritance powers real-world Java applications.
💡 Interview tip:
If you’re preparing for interviews, be ready to explain why Java uses interfaces for multiple inheritance, avoiding the common pitfalls.
🛠️ Developer tip:
If you’re writing code, use inheritance appropriately — not everything requires extending something else. Sometimes composition can be a more elegant solution.
👉 What’s the next step?
- Try writing small programs
- Read the official Oracle Java docs
- Explore related concepts like polymorphism and encapsulation
Each step will strengthen your Java foundation 🚀
📚 Related Reads
To deepen your understanding of Java and OOP concepts, here are some resources you’ll find useful:
- Java Language Basics & Advanced Guide (2025)
A comprehensive guide covering Java fundamentals and advanced topics, ideal for both beginners and experienced developers. - Multithreading in Java (2025)
Explore the latest advancements in Java multithreading, including best practices and performance optimization techniques. - Access Modifiers in Java (2025)
Understand the nuances of Java access modifiers and how they impact class design and encapsulation. - Java Data Types Guide (2025)
A detailed overview of Java’s data types, helping you choose the right type for your variables and enhance code efficiency. - Java Tutorials
A collection of tutorials covering various Java topics, from basics to advanced concepts, with practical examples. - What is Java?
An introductory article explaining what Java is, its features, and why it’s a popular choice for developers. - Java Hello World Example
A step-by-step guide to writing and running your first Java program, the classic “Hello World”. - Java Course
Enroll in a structured Java course to build a solid foundation in Java programming. - Java Internship Opportunities
Gain practical experience through Java internships, enhancing your skills and employability.
👉 These reads will complement your knowledge of inheritance in Java and give you a stronger grip on core OOP principles that every developer needs.