🧭 Introduction: The AI Era and Python’s Machine Learning Revolution
Machine learning isn’t a futuristic concept anymore — it’s the present. From Netflix recommending what you should watch next to ChatGPT generating text that feels human, AI runs the modern digital world.
But behind this AI revolution lies one powerful tool that made machine learning accessible to everyone — Scikit learn in Python.
If NumPy made Python handle numbers efficiently and Pandas helped manage data beautifully, Scikit-learn gave Python the power to learn from data. It became the friendly face of machine learning — fast, open-source, and easy to use even for beginners.
By the end of this guide, you’ll not only understand what Scikit-learn is, but also how to install it, use it, and build your first ML model confidently — no PhD required.

🧠 What Is Scikit learn in Python? (Simple Definition + Why It Matters)
So, what exactly is Scikit learn?
In plain English — Scikit learn is an open-source Python library that makes machine learning simple, fast, and practical.
It’s built on top of Python’s core data libraries — NumPy, Pandas, and Matplotlib — and provides everything you need to:
- Train machine learning models
- Classify and predict outcomes
- Cluster similar data points
- Scale and preprocess datasets
- Evaluate and tune performance
Think of it as a Swiss Army knife for machine learning — compact, reliable, and designed for both beginners and pros.
It’s the go-to toolkit used by researchers, startups, and tech giants alike. Whether you’re building a spam detector, predicting housing prices, or clustering customers — Scikit-learn gives you a clean, consistent API to make it happen.
⚙️ How to Install Scikit learn
Setting up Scikit-learn is refreshingly simple. You can install it directly using Python’s package manager, pip:
pip install scikit-learn
Once installed, confirm everything works:
import sklearn
print(sklearn.__version__)
If you see a version number (like 1.5.0 or newer), you’re good to go!
✅ Requirements:
- Python 3.8 or higher
- NumPy and SciPy installed (pip usually handles these automatically)
💡 Pro Tip: If you’re working in Jupyter Notebook or VS Code, restart your environment after installation to ensure Python detects the new library.
🚀 Why Scikit learn Became the Heart of Machine Learning in Python
Scikit-learn’s story started in 2007, when David Cournapeau built it as part of the Google Summer of Code program under the SciPy ecosystem.
What made it revolutionary wasn’t just its algorithms — it was its simplicity.
While most machine learning tools required tons of math or complex setup, Scikit-learn introduced a clean and unified pattern that anyone could learn:
fit() → predict() → evaluate()
That’s the essence of every ML model in Scikit learn — train, test, and measure.
Over the years, the project grew with support from institutions like INRIA, Google, and Intel, evolving into one of the most widely used ML libraries in the world.
It’s now part of almost every data science course, ML bootcamp, and Kaggle project.
No matter what you’re building — classification, regression, or clustering — chances are, Scikit-learn already has the algorithm ready.
🔍 How Scikit learn Works Under the Hood
At its heart, Scikit learn in Python follows one simple philosophy — learn once, apply everywhere.
Everything you do in Scikit-learn revolves around four core building blocks 👇
1️⃣ Estimators (Models)
Estimators are the brains of Scikit learn — they learn from your data.
Think of them as machine learning models like:
LinearRegression()— predicts continuous values (e.g., house prices)DecisionTreeClassifier()— classifies data into categoriesKMeans()— groups similar data points together
You train them with .fit() and make predictions with .predict().
2️⃣ Transformers
Transformers prepare your data before training.
They handle scaling, encoding, or dimensionality reduction using tools like:
StandardScaler()— normalizes numerical featuresOneHotEncoder()— converts categorical dataPCA()— simplifies large datasets into fewer components
Think of them as “data cleaners and compressors.”
3️⃣ Pipelines
Real-world projects combine preprocessing + modeling.
Pipelines let you connect multiple steps in one clean workflow:
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
This ensures consistent transformations and saves tons of debugging time.
4️⃣ Model Evaluation
You can’t trust a model unless you test it.
Scikit-learn makes this easy with tools like:
train_test_split()— splits data into training/testing setscross_val_score()— validates model consistencyaccuracy_score(),confusion_matrix(),classification_report()— evaluate results

💡 Flow to remember:
Data → Preprocessing → Model → Evaluation → Prediction
This pipeline-driven design is what makes Scikit learn both powerful and predictable.
💡 Example: Building a Simple Machine Learning Model in Scikit learn
Let’s make things real.
Here’s how you can train a classifier in just 10 lines of code using Scikit learn.
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
# Load dataset
data = load_iris()
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
data.data, data.target, test_size=0.2, random_state=42
)
# Train model
model = LogisticRegression(max_iter=200)
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Predict and evaluate
predictions = model.predict(X_test)
print("Accuracy:", accuracy_score(y_test, predictions))
🎯 Result: You’ve just built a flower classifier with around 95% accuracy — without touching advanced math or neural networks.
That’s the beauty of Scikit learn in Python — it brings machine learning to everyone, not just data scientists.
⚡ Why Scikit learn Is a Game Changer
Why is everyone — from students to senior data engineers — obsessed with Scikit-learn? Because it makes complex things simple.
Here’s what sets it apart 👇
✅ Unified API across algorithms – Once you learn .fit() and .predict(), you can switch from Linear Regression to Random Forests instantly.
✅ Lightning-fast experimentation – You can try dozens of models quickly without rewriting your codebase.
✅ Seamless integration – Works beautifully with NumPy, Pandas, Matplotlib, and even TensorFlow.
✅ Ideal for small to mid-sized datasets – Perfect for learning and prototyping before moving to deep learning frameworks.
✅ Massive community support – Tutorials, Stack Overflow help, Kaggle notebooks — it’s everywhere.
Scikit learn doesn’t just teach machine learning — it teaches the mindset behind it.

🌐 Real-World Applications of Scikit learn
Scikit-learn isn’t just for tutorials — it powers real-world innovations across industries.
| 🏢 Domain | 💡 Real-World Use Case |
|---|---|
| 🎬 Entertainment | Netflix and Spotify use Scikit-learn for recommendation prototyping and audience clustering. |
| 🏥 Healthcare | Hospitals use it for disease prediction and early readmission risk analysis. |
| 💰 Finance | Banks rely on it for fraud detection, credit scoring, and risk modeling. |
| 🚗 Automotive | Early self-driving systems used Scikit-learn for behavioral data analysis and model testing. |
| 📊 Business & Marketing | Companies use it for customer segmentation, A/B testing, and churn prediction. |
Whether it’s predicting customer churn or analyzing patient health patterns, Scikit learn is the bridge between data and decision-making.
🧩 Relationship with NumPy, Pandas, and Matplotlib
To truly understand Scikit learn in Python, you must see it as part of a bigger ecosystem — the Python Data Science Stack.
Each library plays a vital role:
- 🧮 NumPy: Handles numerical arrays and matrix operations. It’s the foundation Scikit-learn builds upon.
- 📊 Pandas: Manages data efficiently with DataFrames. Most datasets you train with Scikit-learn come from Pandas.
- 📈 Matplotlib: Used to visualize model performance — confusion matrices, ROC curves, accuracy trends, and more.
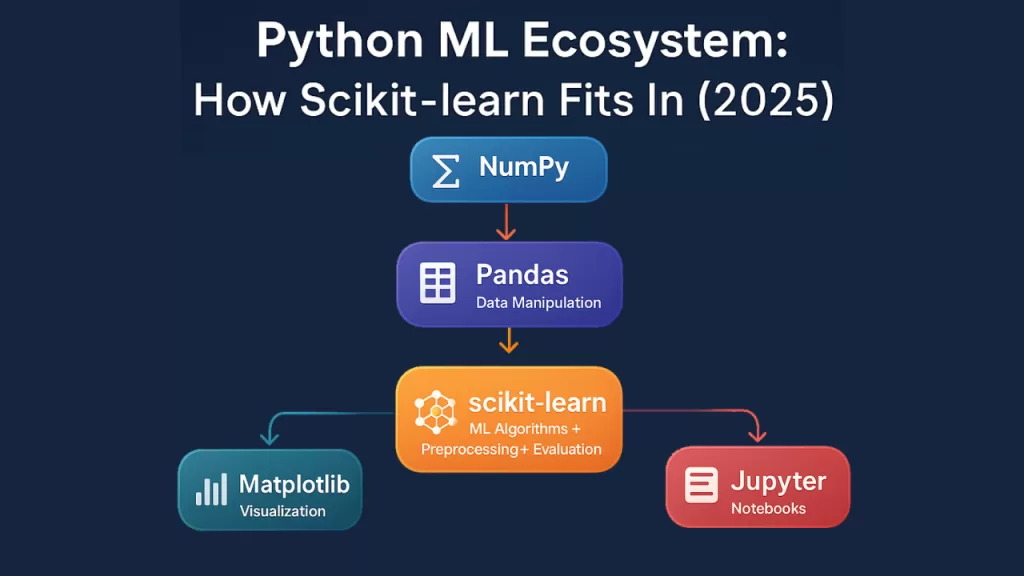
Here’s how they connect in a typical workflow:
Pandas loads and cleans your data → NumPy transforms it into arrays → Scikit-learn trains models → Matplotlib visualizes results.
Together, they make Python the most beginner-friendly and industry-ready environment for machine learning.
💡 Pro Insight: This synergy is why Scikit learn integrates so naturally with Jupyter Notebooks, Colab, and VS Code — your entire ML toolkit lives inside one ecosystem.
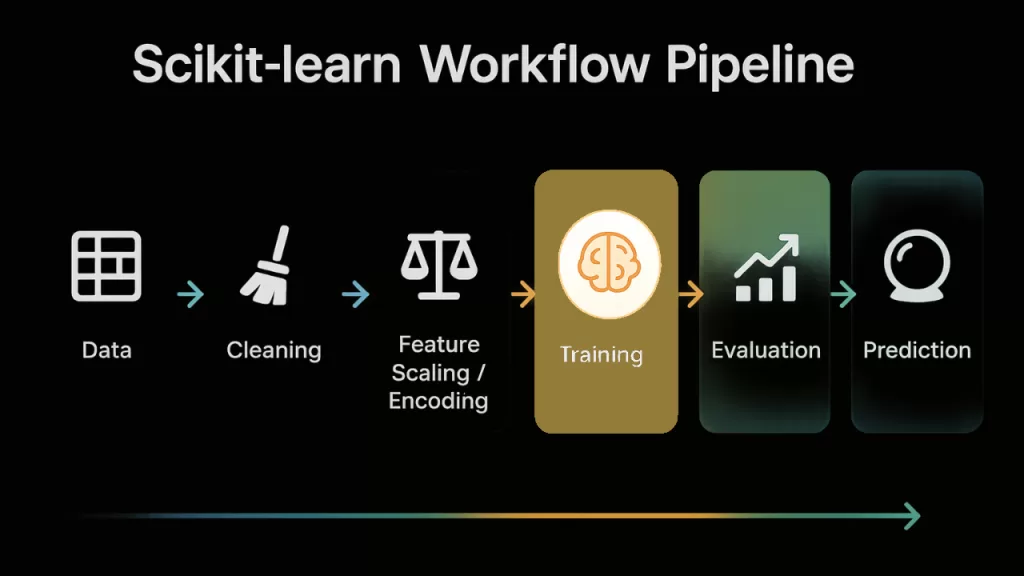
📈 Scikit learn Workflow (Step-by-Step Overview)
Let’s break down a standard machine learning workflow using Scikit-learn. This process works for nearly every project, from predicting house prices to classifying images.
Step 1: Import and Explore Your Dataset
Use Pandas or NumPy to load your data.
import pandas as pd
data = pd.read_csv("data.csv")
data.head()
Step 2: Split Data (Training vs Testing)
Train your model on 80% of the data, and test it on 20% to avoid overfitting.
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
Step 3: Preprocess Data
Use transformers to scale and encode data.
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
scaler = StandardScaler()
X_train = scaler.fit_transform(X_train)
X_test = scaler.transform(X_test)
Step 4: Train the Model
Choose an algorithm (e.g., Logistic Regression, Decision Tree).
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
model = LogisticRegression()
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
Step 5: Evaluate Performance
Test how well your model performs.
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
predictions = model.predict(X_test)
print("Accuracy:", accuracy_score(y_test, predictions))
Step 6: Tune Hyperparameters
Use GridSearchCV or RandomizedSearchCV to find the best parameters automatically.
Step 7: Predict New Data
Feed new input data and get real-time predictions.
💬 Shortcut Tip: This entire process can be automated using Pipelines — a best practice for scaling projects.
🔬 Advanced Topics
Once you’ve built your first few models, Scikit learn offers more advanced techniques to boost performance and automate your workflows.
🧠 Feature Selection
Remove irrelevant or redundant features to make models faster and more accurate.
- Tools:
SelectKBest(),RFE()
🔗 Model Pipelines
Combine preprocessing + modeling into a single reproducible pipeline.
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
🌲 Ensemble Learning
Boost accuracy by combining multiple algorithms.
- Examples:
RandomForestClassifier(),GradientBoostingRegressor()
⚙️ Hyperparameter Tuning
Optimize model settings with:
GridSearchCV()– exhaustive searchRandomizedSearchCV()– faster randomized search
💾 Model Persistence
Save trained models using joblib for reuse:
import joblib
joblib.dump(model, "model.pkl")
These features make Scikit learn suitable not just for students — but for production-ready ML systems in business environments.
💼 Career Tip: Why Learning Scikit learn Pays Off
Here’s a fact: Over 70% of data science and machine learning job interviews include Scikit-learn questions.
According to the 2025 Kaggle State of Data Science Survey, Scikit learn remains the #1 ML library used by data professionals globally — surpassing TensorFlow and PyTorch for everyday tasks.
Here’s why it matters for your career 👇
- 🚀 Resume gold: Listing Scikit learn on your resume signals practical ML skills.
- 🧠 Transferable knowledge: Once you master it, learning advanced frameworks like TensorFlow or PyTorch becomes 2x easier.
- 🧩 Industry relevance: Every company using data — from fintech startups to healthcare giants — relies on Scikit-learn for experimentation and prototyping.
- 💼 Project-ready: It’s a great library to showcase real projects on GitHub or Kaggle portfolios.
Pro Tip: Build one project — like a movie recommender or spam detector — and include it in your LinkedIn portfolio. Recruiters love real results, not just theory.
🧭 Conclusion: The Gateway to Intelligent Python
NumPy gave Python speed.
Pandas gave it structure.
Scikit-learn gave it intelligence.
It’s the reason Python became the world’s favorite language for machine learning.
By learning Scikit-learn in Python, you’re not just understanding a library — you’re unlocking the foundation of modern AI.
Start small. Train a model. Make a prediction.
That’s how every data scientist — from Kaggle champion to Google engineer — began their journey.
So, fire up your IDE, install Scikit-learn, and let your first model learn something new today.
🔗 Related Reads You’ll Love
⚡ What Is Flask in Python? Discover the Game-Changing Framework Behind Fast Web Apps (2025)
📊 What Is a DataFrame in Python? Pandas Power Explained with Real-World Examples (2025 Guide)
🔢 NumPy and Pandas in Python: The 2025 Beginner’s Guide to Unstoppable Data Power
⚙️ Vectorization with NumPy: Game-Changing Loop Optimization Tricks for Amazing Python Speed in 2025
🧩 What is Set in Python? 7 Essential Insights That Boost Your Code
💡 Object Oriented Programming in Python: 7 Powerful Ways Your Code Works Smarter
🚀 Insertion Sort Algorithm in 2025 – Must-Know Facts, Examples in C, Java, Python & More