Why You Should Care About a² – b² and a² + b² Formulas in 2025
Let’s be honest: most people learn algebra formulas in school, memorize them for exams, and forget them right after. But here’s the thing — the a² – b² formula and the a² + b² formula are not just exam tricks. They’re shortcuts that keep showing up in real-world math, coding, and even data science problems.
Think of a developer optimizing code for graphics. Instead of expanding (x+6)(x-6), the difference of squares formula makes it a one-liner: x² - 36. Clean, efficient, and fast. That’s why this formula has stood the test of time — even in 2025.
Key Highlights ✨
- a² – b² formula = (a+b)(a-b), also known as the difference of squares formula.
- a² + b² formula = (a+b)² – 2ab, widely used in algebra and geometry.
- Both formulas simplify algebraic expressions and save time in factorization.
- Real-world use cases include area calculation, coding optimizations, and trigonometric identities.
- Even in 2025, these formulas remain fundamental for students, developers, and problem-solvers alike.
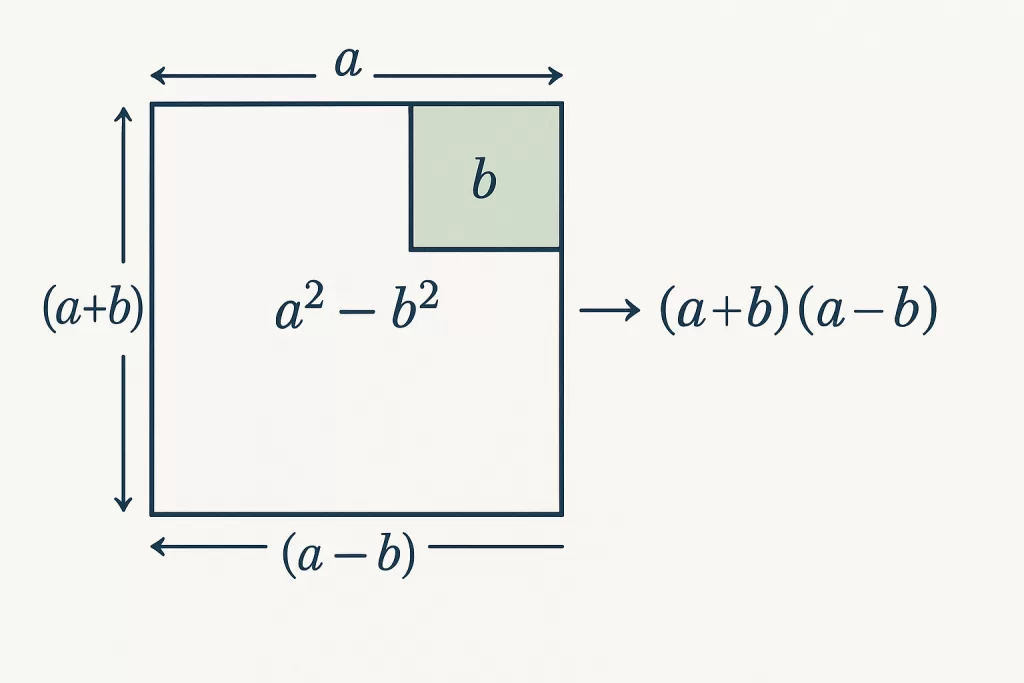
a² – b² Formula (A Square minus B Square)
👉 Formula: a² – b² = (a+b)(a-b)
This means you can find the difference a square minus b square without actually calculating the squares.
Example:
- x² – 49 = (x+7)(x-7)
- 9y2−144=(3y+12)(3y−12)
💡 Real-life analogy: Imagine two square plots of land — one 15m by 15m, another 14m by 14m. Instead of calculating both areas separately, just use a² – b² = (a+b)(a-b). In one step, you know the area difference is 29×1=29 square meters.
a² + b² Formula (The Sum of Squares)
👉 Formula: a² + b² = (a+b)² – 2ab
This one’s a little trickier because unlike a² – b², the sum of squares doesn’t factorize neatly. But it still has plenty of uses in algebra and trigonometry.
Example:
- 5² + 12² = (5+12)² – 2(5)(12)
- =289−120=169
💡 Developer insight: In computer science, when calculating Euclidean distance between two points (x1, y1) and (x2, y2), you use something like: (x1 – x2)² + (y1 – y2)²
Here, the a² + b² structure is literally powering algorithms behind maps, games, and AI models.
Other Important Algebraic Expression Formulas
These often go hand in hand with a² – b² and a² + b²:
- (a+b)² = a² + 2ab + b²
- (a-b)² = a² – 2ab + b²
- a² + b² + c² = (a+b+c)² – 2(ab+bc+ca)
These are the bread and butter of algebraic expressions — and you’ll see them everywhere in math problems, competitive exams, and even developer interviews.
Solved Examples 🔍
- Simplify: x2−16x² – 16×2−16
→ (x+4)(x−4) - Simplify: y² – 100
→ (y+10)(y−10) - Simplify: (3x+2)² – (3x-2)²
→ 24x - Evaluate: (x+6)(x−6)
→x² – 36 - Simplify (coding style):
Instead of computing(n+1)*(n-1), apply a² – b²
→ n² – 1(faster, fewer operations).
Algebra doesn’t have to feel abstract. The a square – b square formula and the a square + b square formula are two of the most powerful algebraic expression formulas you’ll ever use. we saw how they work, why they matter in 2025, and the easiest examples to master them.

More Examples of a Square + b Square Formula in Action
The a square + b square formula isn’t just for textbook problems. You’ll see it pop up in geometry, trigonometry, and even real-world problem solving. Here are a few examples:
1. Geometry Example
Find the length of the diagonal of a square with side 7 units.
Diagonal² = 8² + 15² = a² + b²
=64+225=289
Diagonal ²=289= (17)²
Diagonal = 17
This shows how the a square + b square formula naturally appears in Pythagoras’ theorem.
2. Trigonometry Example
Simplify: cos²θ + sin²θ
Here, the a² + b² structure equals 1, which is one of the most famous trigonometric identities.
3. Real-World Example
Two friends walk north and east from the same point — one walks 3 km, the other 4 km. How far apart are they?
Distance² = 3² + 4² = a² + b² = 9 + 16 = 25
Distance = 5 km
That’s the a square + b square formula giving you the shortest path, or straight-line distance, between two points.
Practice Questions for You (Unsolved)
- Simplify: 15² – 14²
- Simplify: 11² – 7²
- Solve: 23² – 9²
- Solve: 29² – 7²
Real-World Applications in 2025 🌍
- Architecture & Design: Quickly calculate area differences between squares/rectangles.
- Data Science: Distance formulas rely on a² + b² in vector mathematics.
- Competitive Exams: Shortcuts for factorization problems save precious time.
- Programming: Simplifying math-heavy operations in graphics, simulations, and AI models.
Fun fact: According to a 2024 Stack Overflow survey, over 41% of developers said they frequently use math shortcuts like these when optimizing algorithms.
Final Thoughts 💭
The a² – b² formula and a² + b² formula are not just high-school memories. They’re timeless tools — from calculating plots of land to powering AI-driven maps. By 2025, their importance hasn’t faded; if anything, it’s expanded into tech, coding, and real-world problem solving.
So the next time you see an algebraic expression, remember: you don’t always need brute force. Sometimes, the formula is the shortcut. 🚀
❓ Frequently Asked Questions on a Square – b Square Formula
Q1. What is the a square – b square formula?
The a square – b square formula, also called the difference of squares formula, is written as:
Difference of Squares a and b can be written as (a+b)(a-b)
This means the difference between two squares is equal to the product of their sum and difference.
Q2. Why is the (a+b)(a-b) identity important in algebra?
This identity helps you factorize expressions quickly. Instead of expanding squares, you can reduce large equations in one step. For example, 49−3649 – 3649−36 can be seen as 72−627² – 6²72−62, which simplifies instantly using (7+6)(7−6)(7+6)(7-6)(7+6)(7−6).
Q3. Where is the a square – b square formula used in real life?
It shows up in geometry (finding the difference of two square areas), in physics (motion equations), and in coding optimizations (reducing computations by avoiding extra multiplications).
Q4. Is a square – b square the same as a square + b square?
No. While Difference of Squares is factorizes neatly into (a+b)(a−b), the a square + b square formula doesn’t break down in the same way. Instead, it’s expressed as: a² + b² = (a+b)² – 2ab.
Q5. How do you simplify expressions using the difference of squares formula?
Whenever you spot a pattern like x² – 25 or y² – 121, you can rewrite it as (x+5)(x−5) or (y+11)(y−11). This method saves time in exams and coding problems, especially when dealing with large numbers.
Q6. How useful is the a square – b square formula in learning algebra?
It’s one of the foundational algebraic expressions. Mastering it makes solving quadratic equations, factoring polynomials, and handling competitive exam questions much easier. Many higher-level math shortcuts are built on this single identity.







