🤔 What is Binary Arithmetic and Why Should You Care?
Before you think, “Oh no, more math,” hear me out.
I used to think binary arithmetic was just something computer science nerds dealt with in obscure programming problems. But once I realized how binary addition could literally crash rockets (true story – more on that soon), I saw it differently.
Binary arithmetic is the foundation of everything a computer does. Every search, click, video play, or AI prompt (even this one) is powered by simple binary math—a language of only 0s and 1s.

🔍 Key Highlights
✅ Learn binary arithmetic step-by-step — addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division
✅ Understand binary addition rules with real-life examples
✅ See how overflow errors once caused a $370 million rocket crash 🚀
✅ Use our recommended calculators to practice instantly
✅ Know how binary subtraction works using two’s complement
✅ Dive into binary multiplication and binary division tricks with examples
✅ Build a rock-solid base for computer science, electronics, AI & more!
📘 The Basics of Binary Arithmetic (In Plain English)
Binary arithmetic is the process of performing math using the binary number system — a system based on only two digits: 0 and 1.
In decimal (base-10), you have digits 0–9.
In binary (base-2), you have only two: 0 and 1.
But just with those two, computers perform billions of calculations per second.
This isn’t just abstract theory — it’s how your computer thinks.
So, let’s break down the four major operations of binary arithmetic:
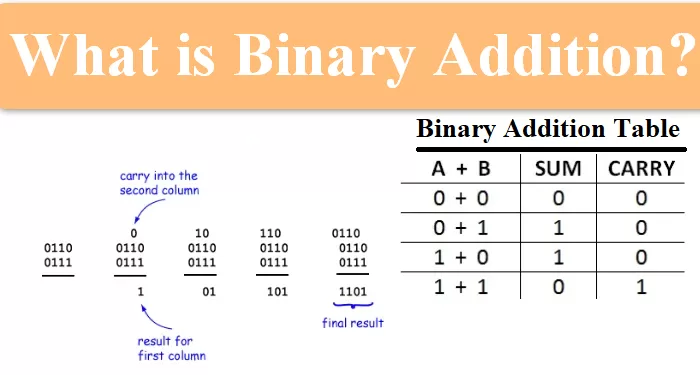
➕ Binary Addition (With Rules, Truth Tables & Real Examples)
Binary addition is very similar to decimal addition, but the rules are even simpler.
✨ Binary Addition Rules:
| Binary Add | Result | Carry |
|---|---|---|
| 0 + 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 + 1 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 + 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 + 1 | 0 | 1 |
Yes — when 1 + 1, the result is 0 with a carry of 1.
Let’s try this:
🧮 Binary Addition Example:
1101 <br>+ 1010 <br>= 10111 <br>Need more examples or confused about how this works?
🔗 Check out our full guide:
Decimal to Binary and Binary to Decimal Conversion – The Ultimate Beginner’s Guide
Or use a handy tool:
👉 Binary Addition Calculator – Free Tool
⚠️ Binary Overflow: The Bug That Crashed a $370 Million Rocket
In 1996, the Ariane 5 rocket exploded just 40 seconds after takeoff — because of a binary overflow error.
The rocket reused code from Ariane 4, which couldn’t handle higher speed values from the new model. The binary addition overflowed, and the guidance system shut down.
Boom. 💥
Binary math may seem simple — but even a tiny overflow in 32-bit or 8-bit systems can cause catastrophic failure.
🧠 Try This: What happens when you do 120 + 120 on an 8-bit system? You get 240, which is fine — but go further, say 200 + 100 = 300? Nope. That’s overflow, and you’ll get a wrong number.

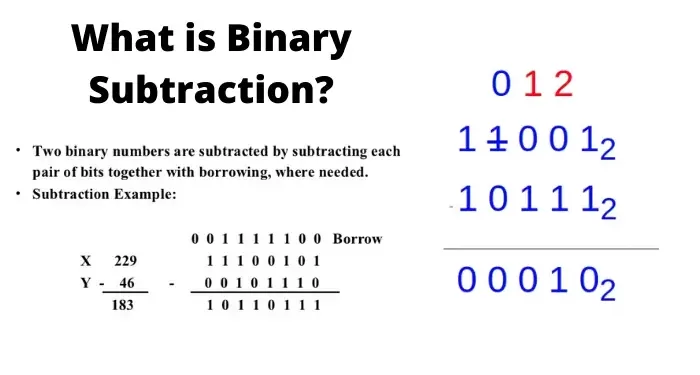
➖ Binary Subtraction (Using Two’s Complement & Real Examples)
Binary subtraction is a bit trickier than addition — especially when you try subtracting a bigger number from a smaller one.
To solve this, computers use something called two’s complement.
🧠 What is Two’s Complement?
It’s a clever way to represent negative numbers in binary.
Instead of subtracting, computers add the two’s complement of the number.
✨ Binary Subtraction Rules:
| Binary Sub | Result | Borrow |
|---|---|---|
| 0 – 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 – 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 – 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 – 1 | 1 | 1 (borrow) |
🧮 Binary Subtraction Example:
101001 <br>- 010110 <br>= 010011 <br>
🔗 Try it yourself with this Binary Subtraction Calculator With Steps
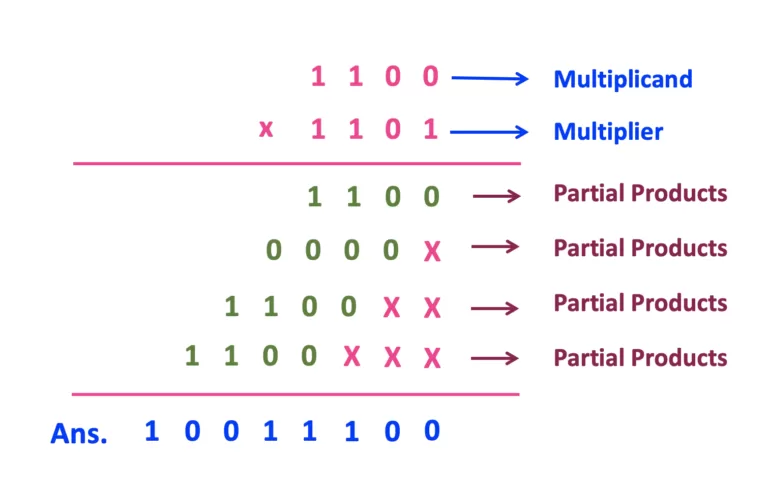
✖️ Binary Multiplication: Simpler Than It Sounds
Binary multiplication works like decimal multiplication — just with 0s and 1s.
The rules are easier than you’d expect.
🔢 Binary Multiplication Rules:
| Binary Multiply | Result |
|---|---|
| 0 × 0 | 0 |
| 0 × 1 | 0 |
| 1 × 0 | 0 |
| 1 × 1 | 1 |
But, multiplying large binary numbers often requires shift and add steps.
🧮 Binary Multiplication Example:
101 <br>× 11 <br>= 1111 <br>
Try our recommended Binary Multiplication Calculator to see the steps.
➗ Binary Division: How Computers Divide
Binary division is like long division in decimal but with simpler steps.
You keep subtracting the divisor, using binary subtraction, until you can’t anymore.
🧮 Binary Division Example:
1010 ÷ 10 = 101<br>Not bad, right?
Use this Binary Division Calculator with Steps if you want to play around.

💡 Truth Tables, Adders & the Inside of a CPU
Now let’s peek under the hood. How do computers actually add binary numbers?
They use logic gates to build circuits called:
- Half Adders – adds two 1-bit numbers
- Full Adders – adds two bits plus a carry
- Ripple Carry Adders – links full adders in a chain for multi-bit addition
But ripple carry adders are slow because each carry must ripple through.
Want to know how logic gates make this work?
🔗 Read our guide:
👉 Top 8 Logic Gates: Essential to Boost Your IT Career
🎓 Real-World Use of Binary Arithmetic (And Why You Should Learn It)
Every programmer, data scientist, and engineer relies on binary arithmetic operations — often without realizing it.
Here’s where it shows up:
- CPUs calculating pixel color in your video game
- AI adjusting neural weights in training
- Routers checking packet checksums
- Sensors sending binary signals in IoT devices
- Blockchain verifying transactions
🎓 Fact: Claude Shannon (yes, the “father of information theory”) introduced the concept of binary arithmetic in computers back in 1937 — and the world hasn’t been the same since.
🚀 Learn Binary Thinking with Real Projects
Want to go beyond theory?
👉 Check out these Internship for CSE Students or Internship for EEE Students to get hands-on experience in hardware, logic design, and binary operations!
📥 Download Binary Arithmetic Cheat Sheet (PDF)
Grab this free, printable Binary Arithmetic Cheat Sheet
🧾 Final Thoughts: Don’t Fear the 0s and 1s
You don’t need to be a math genius to understand binary arithmetic.
Whether you’re doing binary addition, subtraction using 2’s complement, binary multiplication, or just trying to understand how computers think — it all comes down to simple, logical steps.
The next time you send a text, open an app, or play a song — remember this:
Your device is doing millions of binary arithmetic operations in the background… and not once did it complain 😉