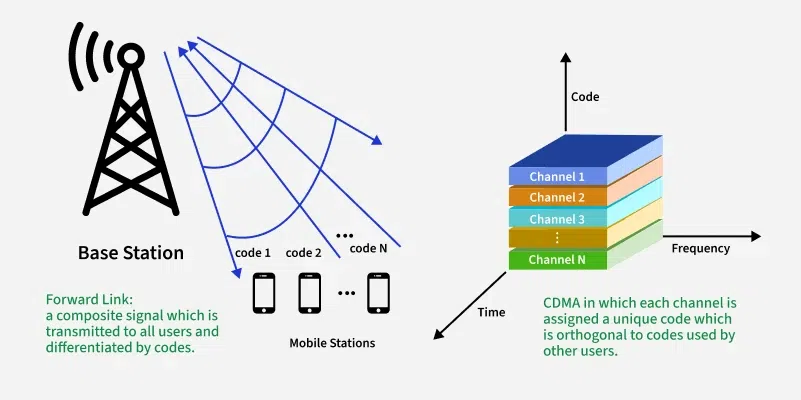
The CDMA Full Form is Code Division Multiple Access.
CDMA is a digital cellular communication technology in which multiple users can transmit data simultaneously over the same radio frequency using unique codes to avoid interference.
CDMA was widely used in 2G and 3G communication systems, satellite networks, military radios and GPS communication due to its security, high spectrum efficiency, and excellent call quality.
What is CDMA?
CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access) is a multiple access communication technique that allows many mobile users to communicate at the same time using one channel. Instead of dividing the channel by time (TDMA) or frequency (FDMA), CDMA uses codes.

How it works
- Each user is assigned a unique code
- All users transmit on the same frequency
- The receiver decodes the message using the unique code of the user
- Other signals are treated as noise and ignored
Because of this, the communication system can support more number of users without interference.
Characteristics of CDMA
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Technique | Spread Spectrum |
| Spectrum Usage | Shared among all users |
| Access Method | Code-based |
| Call Quality | High |
| Security | Very High |
| Network Capacity | High |
| Interference | Very Low |
Features of CDMA Technology
Below are the major features that made CDMA Full Form (Code Division Multiple Access) extremely popular:
- Multiple users can share the same carrier frequency
- No need for time slots or separate frequency bands
- High noise resistance and lower signal interference
- Excellent voice clarity
- Enhanced privacy and network security
- Better utilization of bandwidth (spectrum efficient)
- Power control mechanism to avoid signal clash
Applications of CDMA

| Field | Usage |
|---|---|
| Mobile Networks | 2G/3G voice & data |
| GPS (Global Positioning System) | Satellite communication |
| Military | Secure radio transmission |
| Satellite TV | Data communication |
| IoT Networks | Private enterprise communication |
| Wireless Broadband | CDMA-2000 & EV-DO services |
Types of CDMA
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Synchronous CDMA | Uses orthogonal codes, less interference |
| Asynchronous CDMA | Uses pseudo-random codes, more flexibility |
📡 CDMA vs GSM

| Parameter | CDMA | GSM |
|---|---|---|
| Full Form | Code Division Multiple Access | Global System for Mobile Communication |
| Technology Type | Spread Spectrum | TDMA/FDMA |
| SIM Card | Initially No (Later Yes) | Required |
| Signal Quality | Very High | Moderate |
| Network Switching | Difficult | Easy |
| Global Reach | Low | High |
| Security | High | Moderate |
| User Capacity | High | Moderate |
Advantages of CDMA

- Excellent voice and data clarity
- Support for large network capacity
- Efficient bandwidth usage
- Less dropped calls
- High security and privacy
- Good performance in indoor and rural coverage
Disadvantages of CDMA
- CDMA phones were mostly network-locked
- Limited global acceptance compared to GSM
- Expensive infrastructure
- Harder to switch devices between CDMA carriers
- Complex synchronization and interference management
But Why Did CDMA Decline?
If CDMA was so good, why did the world shift to GSM, LTE and 5G?
Let’s talk real.
Problems with CDMA
- Handsets were locked to the network
- SIM cards didn’t exist at the time (so switching networks was impossible)
- Infrastructure was expensive
- Not globally adopted like GSM
So even though CDMA Full Form = Code Division Multiple Access still represents a powerful technology, the world needed something uniform and global, and that’s where LTE and now 5G took over.
📶 Popular CDMA Standards
| Standard | Expansion |
|---|---|
| IS-95 | Interim Standard 95 |
| IS-2000 (CDMA 2000) | 3G CDMA Standard |
| EV-DO | Evolution Data Optimized |
| UMTS-WCDMA | Universal Mobile Telecommunication System – Wideband CDMA |
Conclusion
The CDMA Full Form (Code Division Multiple Access) refers to a powerful digital communication technology that changed the wireless world by demonstrating that many devices can communicate on the same frequency without interfering — simply by using unique codes.
While CDMA-based mobile networks are now replaced by modern LTE/5G systems, the fundamental principles of CDMA still define today’s wireless communication engineering.
Want to Learn More About Networking ? Kaashivinfotech Offers Networking Course, Cloud Computing Course, Cyber Security Course, Visit www.kaashivinfotech.com.