When you learn to write Java programs, at some point in time you will need to store, manage, and manipulate multiple pieces of data. This is where the Collections Framework comes into play. The Collections Framework in Java is an exceptionally useful, flexible, and a key aspect of the Java Standard Library for handling data more simply and efficiently.
Regardless of whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned pro looking to refresh your mind ahead of your interviews, my mega guide will take you through all the fundamental technicalities of the collection framework in Java – with examples, real-world use cases, and productivity hacks.
📚 What is the Collections Framework in Java?

The Collections Framework is a unified architecture for manipulating (i.e., representing and manipulating) collections or groups of objects in Java. It first emerged with Java 2 and has since been a mainstay in Java programming. The framework consists of:
- Interfaces (List, Set, Map, Queue, etc.)
- Implementations (ArrayList, HashSet, HashMap, etc.)
- Algorithms (sorting, searching)
- Utilities (i.e., helper classes Collections and Arrays)
Simply put, the Java Collections Framework provides reusable and efficient ways to manipulate data.
🌳 Java Collection Hierarchy – Overview of the Structure
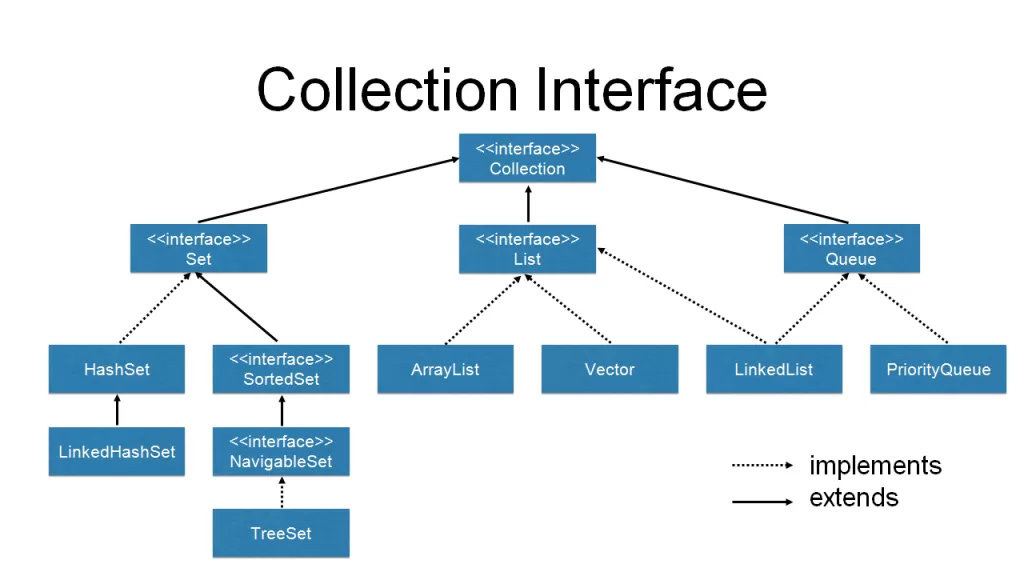
The Java collection framework is designed with interfaces above implementations, which are extended by abstract classes. Here’s a quick rundown:
Core Interfaces:
Collection – the parent interface
- List – ordered collection (ex. ArrayList, LinkedList)
- Set- uniqueness (ex. HashSet, LinkedHashSet)
- Queue – holds elements until they are processed (ex. PriorityQueue)
Map – key/value pairs (ex. HashMap, TreeMap)
Common Implementations:
- ArrayList, LinkedList
- HashSet, TreeSet
- HashMap, LinkedHashMap, TreeMap
- PriorityQueue
Understanding the Java collection class hierarchy helps you determine which type of data structure is appropriate for your use case.🧠
Why Use the Collections Framework in Java?
The Java Collections Framework offers:
- Reusability: Pre-built classes you can plug into your app
- Flexibility: Easily switch between implementations (e.g., from ArrayList to LinkedList)
- Performance: Optimized under the hood
- Interoperability: Collections can work across Java APIs
- Maintainability: Reduces boilerplate code and bugs
✅ Bonus: It saves you from having to reinvent the wheel every time you work with groups of data.
📌 Collection vs Collections in Java – Know the Difference
Many developers confuse these two:
- Collection: It’s the root interface for all collection types like
List,Set, andQueue. - Collections: It’s a utility class in
java.utilthat provides static methods for sorting, shuffling, reversing, etc.
Understanding this difference is key to mastering the collections framework java.
🧰 Most Used Java Collection Classes (With Real-World Examples)
📋 ArrayList – When You Need a Resizable Array
Use ArrayList when:
List<String> names = new ArrayList<>();
names.add("Alice");
names.add("Bob");
- You need fast access by index
- Insertion/removal is infrequent
🔗 LinkedList – When You Need Frequent Insertions/Deletions
Use when:
List<String> list = new LinkedList<>();
list.addFirst("Start");
list.addLast("End");
- You frequently insert or remove elements from the middle
#️⃣ HashSet – When Uniqueness Matters
No duplicates allowed. Good for:
Set<Integer> ids = new HashSet<>();
ids.add(101);
ids.add(102);
- Maintaining unique entries
- Checking presence quickly
🧭 HashMap – Store Key-Value Pairs
Use when:
Map<String, String> capitals = new HashMap<>();
capitals.put("India", "New Delhi");
- You need fast lookup by key
- Keys must be unique
ArrayList vs LinkedList – Which One Should You Use?
| Feature | ArrayList | LinkedList |
| Access time | Fast (O(1)) | Slow (O(n)) |
| Insert/delete | Slow (shifting needed) | Fast (no shift) |
| Memory usage | Less | More (due to pointers) |
👉 Use ArrayList for random access; LinkedList for lots of insertions/deletions.
🧪 Java Generics and Type Safety in Collections Frameworks in Java
With Generics, collections become type-safe:
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add("Hello");
// list.add(123); // Compile-time error!
Benefits:
- No need for casting
- Fewer runtime errors
- Cleaner, safer code
🔁 Iterable and Iterator in Java Collections
To traverse a collection, use Iterator:
Iterator<String> it = list.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(it.next());
}
Iterableis the interface allowing use of enhancedforloop.Iteratorgives you more control (e.g., remove while iterating).
🛠️ Common Algorithms Using Collections Framework in Java
Collections.sort(list)Collections.reverse(list)Collections.shuffle(list)Collections.min(list),Collections.max(list)Collections.binarySearch(list, element)
These are plug-and-play algorithms available via the Collections utility class.
🧩 Real-World Use Cases of the Collections Framework in Java

- Storing user input data dynamically
- Building LRU Cache (using
LinkedHashMap) - Implementing a task scheduler (using
PriorityQueue) - Counting word frequency (using
HashMap) - Creating a contact book (using
TreeMapfor sorted contacts)
📘 Best Practices When Using Collections Framework in Java
- Program to interfaces (e.g.,
Listinstead ofArrayList) - Avoid raw types – always use generics
- Pick the right collection for your use case
- Use
<strong>Collections.unmodifiableList()</strong>to make collections read-only - Use
<strong>ConcurrentHashMap</strong>for thread-safe maps
📝 Conclusion: Mastering Collections Framework Java is Non-Negotiable
If you are serious about Java development, you will need to fully learn and understand the collections framework java . Whether it be for interviews, building production applications or contributing to open-source, learning the collection of framework, will undoubtedly make you a better and more productive programmer.
View the collections framework java as something you can learn step by step. Start with the basics, then play around with different classes. As you build your mastery of the collections framework, you can continue zeroing in on each data structure.