Introduction: Cryptography and You and Me.
Being blunt, I would say without cryptography our online world would fall apart.
Whenever you write something on WhatsApp, visit Amazon, or open your bank account, cryptography is at work in the background. It is that unseen superhero 🦸♂️ who does not demand to be acknowledged yet rescues you day in, day out.
The first time when I came across the term cryptography, I thought it was part of a James Bond film. However, as I began to investigate, I knew it had all been there around me. The password to my Wi-Fi, the PIN at the ATM, the OTPs on my phone, all those are instances of cryptography.

What is Cryptography?
Simply put, cryptography is the art of encrypting plain, understandable information into a coded text that can be deciphered by the right individual.
For example:
- When I send you a text saying, Meet me at 5 pm at Café blue, anyone can get the text and read it.
- But when I put it in cipher such as Xrru nf ng 5 cz ng Pnsr Oyhr – all of a sudden it makes no sense.
Cryptography is simply making information incomprehensible to others and understandable to the intended receiver.
Why Do We Need Cryptography?
You might say, Why be so complex? Why not just trust people?”
Well… because people steal, listen, and hack. The following are examples of why cryptography is necessary in real life:
- 💳 Banking: When it comes to debit cards, your money is encrypted, therefore no hacker can steal your money in the middle of transfer.
- 📱 Messaging applications: End-to-end encryption is used in WhatsApp, Signal and Telegram. The chats will be read by only you and your receiver.
- Image Healthcare: Records of patients are coded to protect their privacy.
- 🌐 Sites: Have you ever seen the little padlock 🔒 in the URL address of your browser? That is HTTPS, cryptography supercharged.
Cybercriminals would be feasting on your passwords, chats and bank information without cryptography. Scary, right?

Types of Cryptography
This is where it tends to get really technical. Nah, it will be easy, just like I do to my non-technical friends.
1. Symmetric Key Cryptography
This is the most ancient and the most basic form of cryptography.
- Both the recipient and the sender encrypt and decrypt messages with the same key.
- It’s fast but risky. When a person takes the key, he or she can read it all.
Example: Think of it like one house key. Share it with me and we can enter. But when a thief replicates it – it ends.

2. Asymmetric Key Cryptography (Public-Key)
This is wiser and safer.
- It relies on two keys, a public key (shared with everybody) and a private key (kept secret).
- Only the private key can decrypt what was encrypted with the public key and the other way round.
Example: Let me take a letter and put it in a box with your public padlock. It is for you to unlock it with a personal key. I can even lock it and cannot read it after.

That is the way digital certificates and online payments work.
3. Hashing
Hashing is a little bit different – it does not encrypt and decrypt. Rather, it transforms the data into a non-reversible fixed length string.
📌 Example: Your password. The password that you create is not saved on Instagram when you become an account holder. Instead a hash (5f4dcc3b5aa765d61d8327deb882cf99) is stored. Even Instagram does not know which password you have.

I was surprised when I was first told of it!
4. Digital Signatures
Always anxious about whether or not an email was actually sent by your bank or by a spammer? That is where digital signatures come in.
- They check the authenticity of messages.
- A digital signature indicates the message was not changed along the way.
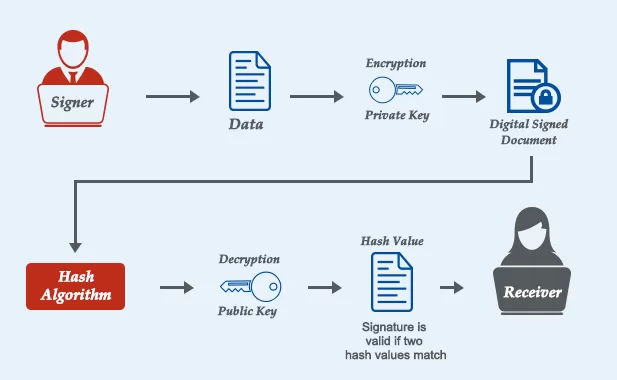
📌 Ex: It is like a cheque signature. Someone cannot forge your signature, even after copying the text.
Real-Life Examples of Cryptography That You Use Daily
Here I bring the strings of your life (and mine) together:
- Unlocking your phone with Face ID → cryptography.
- Using UPI in India or PayPal abroad → cryptography.
- Logging into Gmail with 2-step verification → cryptography.
- Even Netflix stopping you from sharing passwords? Yup, that’s cryptography too
Cryptography in the Future

The age of quantum computing is upon us, and the bad news is the cryptography used today might not pass the test. Minutes are enough to break existing encryption techniques with quantum computers.
But don’t panic. Scientists have already begun developing post-quantum cryptography to ensure things are safe again. The game never ends.
Quick Comparison of Cryptography Types
| Type | Key Used | Example | Security |
|---|---|---|---|
| Symmetric | One key | File encryption | Moderate |
| Asymmetric | Two keys | Online banking | High |
| Hashing | No key | Passwords | Very high (one-way) |
| Digital Signatures | Private + public | Emails, docs | High |
Conclusion:
Cryptography seems to me to be magic masquerading as math. We cannot see it but it offers security to all that we do over the net.
You are a beginner, you do not have to worry about phrases such as RSA, SHA-256, and AES. Start small. Play with Caesar ciphers. Cipher a word to your friend. And that is what I fell in love with.
Want to Learn About Cryptography? or Cyber Seurity Course Visit www.kaashivinfotech.com
And when you next visit a web site which displays that 🔒 symbol in your browser, smile a bit, now you know, it’s cryptography that protects you.





