calloc |
malloc |
| We need to split and pass the memory we want | We can pass how much memory we want. |
| Ex: p=calloc(5,sizeof(int) | Ex: p=malloc(5,sizeof(int) |
| Function return void | Functions Return void |
| Returns starting address but before allocating to us it will zero it. It will clear the previous garbage value. | Returns starting address. |
| Calloc is slower than malloc | Faster than calloc. |
| It is safe as compared to malloc | Not safe as calloc. |
| Dynamic memory allocation | A function which allocates block memory during run time.
|
| There are 4 library routines calloc(), free(), alloc(),and malloc() which is used to allocate memory and free it up during the program execution | Once when a memory space of specific size is allocated, it returns null pointer pointing to that allocated memory location.
|
| Calloc() initialized the allocated memory to zero | Malloc() doesn’t initializes the allocated memory. It contains garbage Values |
| It allocates multiple block of requested memory. | It allocates only single block of requested memory. |
Why use malloc()
- You can use malloc when you have to allocate objects which must exist beyond the execution of the memory block.
- Malloc can be used if we need to allocate memory greater than size of stack.
- Returns the pointer to the first byte of allocated space.
- Enables developers to allocate memory as it is needed in the exact amount.
- This function allocates memory block size bytes from the heap.
Syntax of malloc()
- In above syntax, ptr is a pointer of cast_type. Malloc function returns the pointer to the allocated memory of byte _size.
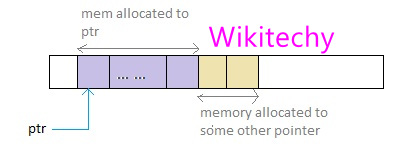
Example of malloc() in C
- When this statement is executed, malloc reserves a memory space of 50 bytes. The address of the first byte reserved space is assigned to the pointer
Why use calloc()
- When you have to set the allocated memory to 0.
- You can use calloc() that returns a pointer to get access to memory heap.
- Used when you need to initialize the elements to 0 to return a pointer to the memory.
- To prevent overflow that is possible with malloc()
- Use calloc() to request a page that is known to already be 0.
Syntax of Calloc()
- The above syntax is used to allocate n memory blocks of the same size. After the memory space is allocated, all the bytes are initialized to zero. The pointer, which is currently at the first byte of the allocated memory space, is returned.
