When building Java applications — whether small utilities or enterprise-scale systems — testing is not optional. It is a core part of professional software development. Among all Java testing tools, JUnit Framework has earned its place as the industry standard for unit testing.
This comprehensive guide walks you through JUnit’s history, architecture, core concepts, setup, features, best practices, integration techniques, and real-world usage — all explained clearly and practically.
📘 What is JUnit?

JUnit is an open-source framework designed for writing and running repeatable automated tests in Java. It allows developers to verify that individual units of code — typically methods or classes — behave as expected.
JUnit plays a central role in:
- Unit Testing
- Test-Driven Development (TDD)
- Continuous Integration (CI)
- Regression Testing
It is lightweight, easy to use, and tightly integrated with Java IDEs and build tools.
🧠 Why Unit Testing is Critical in Java Development

Before diving deeper into JUnit, let’s understand why unit testing matters:
1️⃣ Early Bug Detection
Testing small units of code helps catch logical errors before they grow into major system issues.
2️⃣ Safe Refactoring
When tests exist, developers can refactor confidently. If something breaks, tests fail immediately.
3️⃣ Better Code Design
Writing testable code naturally leads to:
- Loose coupling
- Clear separation of concerns
- Cleaner architecture
4️⃣ Documentation Through Tests
Well-written tests act as living documentation for how a method is expected to behave.
🏗 Evolution of JUnit Framework
JUnit has evolved over time:
| Version | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|
| JUnit 3 | Required inheritance from TestCase |
| JUnit 4 | Introduced annotations like @Test |
| JUnit 5 | Modular architecture, improved extension model |
JUnit 5 is the modern and recommended version today.
🧩 JUnit 5 Architecture
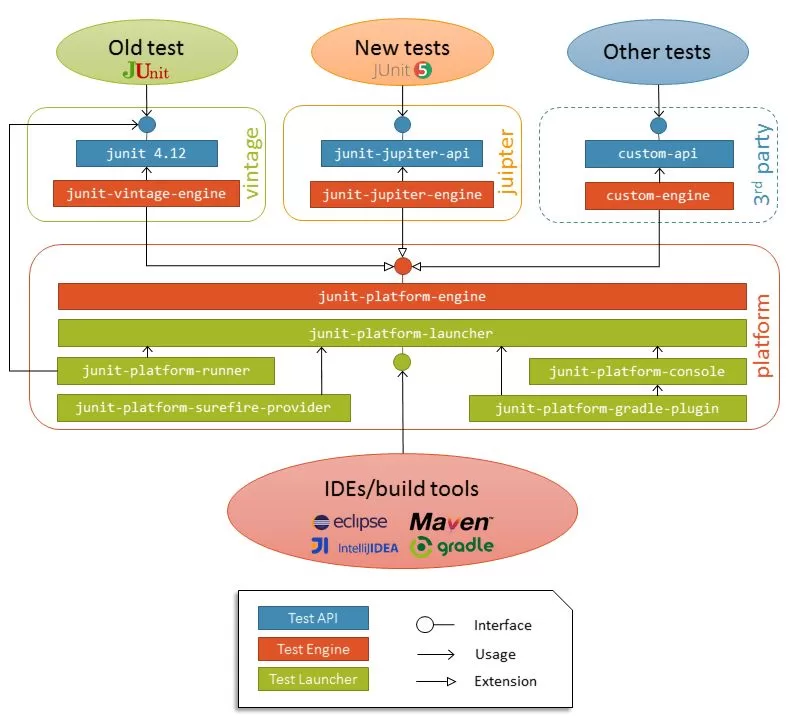
JUnit 5 consists of three main modules:
1️⃣ JUnit Platform
Launches testing frameworks on the JVM.
2️⃣ JUnit Jupiter
The new programming and extension model (what most developers use).
3️⃣ JUnit Vintage
Supports running older JUnit 3 & 4 tests.
🧪 Core Concepts in JUnit Framework
✅ Test Class
A class containing test methods.
✅ Test Method
A method annotated with @Test that verifies specific behavior.
✅ Assertions
Used to compare expected and actual results.
Example:
Assertions.assertEquals(10, calculator.add(7, 3));
✅ Test Lifecycle
JUnit provides hooks to run setup and cleanup code.
🏷 Important JUnit 5 Annotations

| Annotation | Purpose |
|---|---|
@Test | Marks a method as a test |
@BeforeEach | Runs before every test |
@AfterEach | Runs after every test |
@BeforeAll | Runs once before all tests |
@AfterAll | Runs once after all tests |
@DisplayName | Custom test name |
@Disabled | Skips a test |
🚀 Writing Your First JUnit Test
Step 1: Create a Class to Test
public class Calculator {
public int add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
} public int divide(int a, int b) {
return a / b;
}
}
Step 2: Create a Test Class
import org.junit.jupiter.api.*;class CalculatorTest { Calculator calculator; @BeforeEach
void setup() {
calculator = new Calculator();
} @Test
void shouldAddTwoNumbers() {
Assertions.assertEquals(5, calculator.add(2, 3));
} @Test
void shouldThrowExceptionWhenDividingByZero() {
Assertions.assertThrows(ArithmeticException.class,
() -> calculator.divide(5, 0));
}
}
📦 Adding JUnit to a Maven Project
Add this dependency inside pom.xml:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter</artifactId>
<version>5.10.0</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
🔁 Types of Assertions in JUnit Framework
JUnit provides multiple assertion methods:
assertEquals()assertNotEquals()assertTrue()assertFalse()assertNull()assertNotNull()assertThrows()assertAll()(group multiple assertions)
Example:
Assertions.assertAll(
() -> Assertions.assertEquals(4, 2 + 2),
() -> Assertions.assertTrue(5 > 3)
);
📊 Parameterized Tests
Instead of duplicating test methods, JUnit supports parameterized tests.
@ParameterizedTest
@ValueSource(ints = {2, 4, 6, 8})
void shouldBeEven(int number) {
Assertions.assertTrue(number % 2 == 0);
}
This runs the test multiple times with different inputs.
⏱ Timeout Testing
You can ensure a method completes within a given time:
@Test
void shouldCompleteWithinTime() {
Assertions.assertTimeout(Duration.ofSeconds(2), () -> {
Thread.sleep(1000);
});
}
🔄 Repeated Tests
Run the same test multiple times:
@RepeatedTest(5)
void repeatedTestExample() {
Assertions.assertTrue(true);
}
🧵 Nested Tests
JUnit 5 supports grouping related tests:
@Nested
class AdditionTests { @Test
void shouldAddPositiveNumbers() {
Assertions.assertEquals(5, calculator.add(2, 3));
}
}
🧪 JUnit + Mockito (Mocking Dependencies)
In real-world applications, classes often depend on databases, APIs, or services. Instead of calling real services, you mock them.
Popular mocking framework:
- Mockito
Mocking improves:
- Speed
- Isolation
- Reliability
🔁 JUnit in Continuous Integration
JUnit integrates seamlessly with CI tools like:
- Jenkins
- GitHub Actions
- GitLab CI/CD
Whenever code is pushed, tests automatically run.
🧪 JUnit vs Other Testing Frameworks
| Framework | Language | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| JUnit | Java | Most widely used |
| TestNG | Java | More configuration-heavy |
| Spock | Groovy | Expressive DSL |
JUnit remains the default choice in most enterprise Java projects.
🏆 Best Practices for Writing Clean JUnit Tests
✔ Use Descriptive Test Names
Example:
shouldReturnFalseWhenPasswordIsInvalid()
✔ Follow AAA Pattern
- Arrange
- Act
- Assert
✔ Keep Tests Independent
Each test should run in isolation.
✔ Avoid Testing Multiple Behaviors in One Test
✔ Mock External Systems
📌 Common Mistakes Developers Make
❌ Writing overly complex tests
❌ Testing implementation details instead of behavior
❌ Ignoring edge cases
❌ Not maintaining tests
🌍 Real-World Use Cases of JUnit Framework
JUnit is used in:
- Enterprise banking systems
- E-commerce platforms
- Microservices architectures
- Open-source Java projects
Almost every professional Java developer uses JUnit.
🧠 How JUnit Supports Test-Driven Development (TDD)
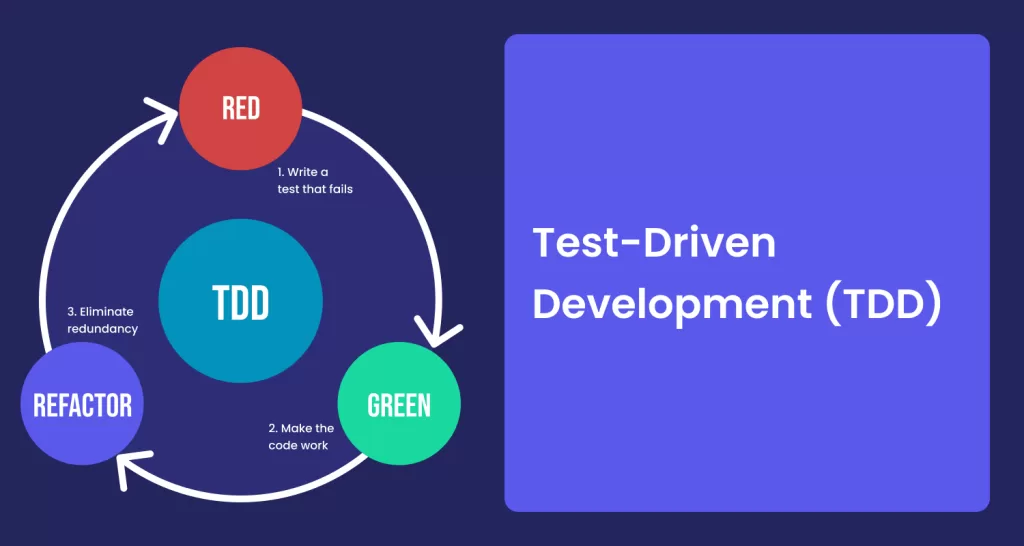
TDD workflow:
- Write a failing test
- Write minimal code to pass
- Refactor
- Repeat
JUnit enables this cycle seamlessly.
🔮 The Future of JUnit
JUnit continues evolving with:
- Improved extensions
- Better IDE integration
- Enhanced parallel test execution
- Modular test engines
It remains the backbone of Java testing.
🎯 Final Thoughts
If you are serious about Java development, mastering JUnit is non-negotiable.
It improves:
- Code reliability
- Developer confidence
- Application stability
- Long-term maintainability
From small utility classes to enterprise-scale systems, JUnit empowers developers to build robust and dependable software.
Want to Learn More About Java ?, Kaashiv Infotech Offers, Full Stack Java Course, Java Course, Data Science Course, Internships & More, Visit Their Website www.kaashivinfotech.com.



![Agile Model in Software Engineering [2025]](https://www.wikitechy.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Agile-Model-in-Software-Engineering-2025-380x220.webp)