Machine learning is the backbone of today’s technology, and we use machine learning every day via applications like Netflix’s recommendation systems, fraud detection at banks, and even medical image classification! The algorithms behind machine learning are at the forefront.
In this blog post, we’ll cover machine learning algorithms: what they are, the types of machine learning algorithms, and how to implement machine learning algorithms in Python. By the end, you will walk away with a good knowledge base on where and which algorithm you can use for a specific problem.
What Are Machine Learning Algorithms?
A machine learning algorithm is a mathematical model (or a set of rules) allowing a computer to recognize patterns in the data, thus making a prediction or a decision independent of human intervention.

As opposed to hard coding every possible scenario or doing everything manually, we provide an algorithm with data, and the algorithm learns the relationships between the data and uses them to make a prediction or decision.
👉 For example:
- Spam detection is a machine learning algorithm: an email is classified as spam or not spam.
- Self-driving cars use machine learning algorithms to make driving decisions based on sensor data.
- E-commerce uses machine learning algorithms to recommend products based on previous browsing history.
Types of Machine Learning Algorithms
In general, when someone speaks about the “types of machine learning algorithms“, they classify the algorithms into three types, which are:
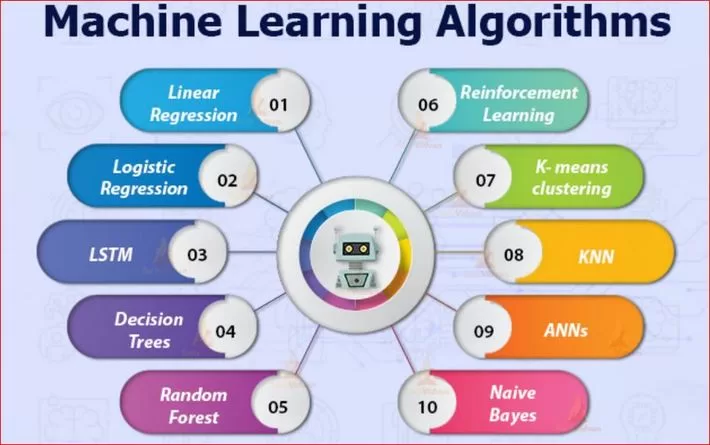
1. Supervised Learning Algorithms
Supervised Learning – uses labeled data , meaning the input is data that already has the correct output.
Goal: Predict responses based on historical examples.
Popular Algorithms:
- Linear Regression (e.g. predicting house prices)
- Logistic Regression (binary classification e.g. spam detection)
- Decision Trees
- Random Forest
- Support Vector Machines (SVM)
👉 E.g. predicting if a customer will buy a product based on their age, salary and past purchase history.
2. Unsupervised Learning Algorithms
Unsupervised learning is learned from unlabeled data, in which the system attempts to discover an underlying pattern, hidden structure, or grouping.
Goal: Find structure in the data.
Common algorithms:
- K-Means Clustering
- Hierarchical Clustering
- Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
👉 Ex. Customer segmentation based on shopping patterns (no labels given).
3. Reinforcement Learning Algorithms
Reinforcement learning involves an agent that learns by interacting with an environment and receiving rewards or penalties.
Goal: Learn a strategy to maximize rewards over time.
Popular algorithms:
- Q-Learning
- Deep Q-Networks (DQN)
👉 Example: Training a robot to walk or teaching AI to play chess.
Machine Learning Algorithms in Python
Python is a preferred language for applying machine learning because it has a strong ecosystem through a variety of libraries such as scikit-learn, TensorFlow, and PyTorch.

Examples of machine learning algorithms in Python are:
Example 1: Linear Regression in Python
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
import numpy as np
# Sample data
X = np.array([[1], [2], [3], [4], [5]])
y = np.array([2, 4, 6, 8, 10])
# Train model
model = LinearRegression()
model.fit(X, y)
# Predict
print(model.predict([[6]])) # Output ~ 12Example 2: K-Means Clustering in Python
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
import numpy as np
# Sample data
X = np.array([[1, 2], [1, 4], [1, 0],
[10, 2], [10, 4], [10, 0]])
# Train model
kmeans = KMeans(n_clusters=2, random_state=0).fit(X)
print(kmeans.labels_)
print(kmeans.cluster_centers_)Example 3: Decision Trees in Python
from sklearn import tree
# Training data
X = [[0, 0], [1, 1]]
y = [0, 1]
clf = tree.DecisionTreeClassifier()
clf = clf.fit(X, y)
print(clf.predict([[2, 2]])) # Output: [1]Real-Life Applications of Machine Learning Algorithms
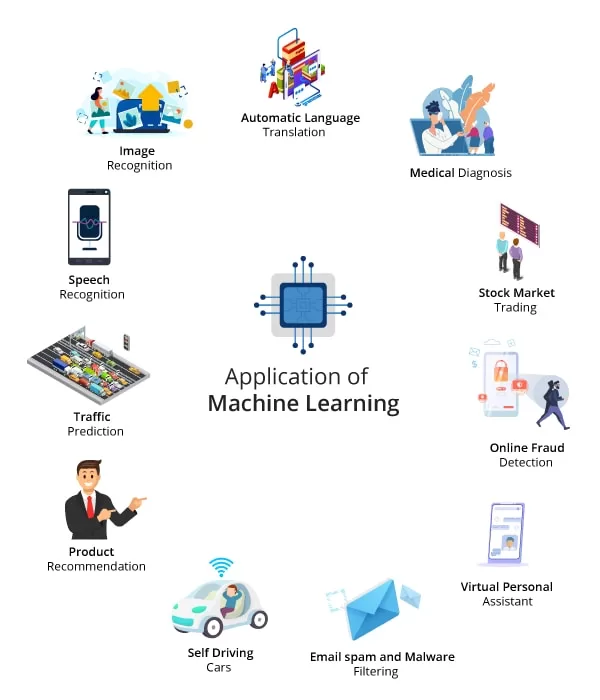
- Healthcare: Predicting diseases based on electronic medical records.
- Finance: Detection of fraud using classification algorithms.
- Marketing: Customer segmentation using clustering.
- Self-driving cars: Navigation using reinforcement learning.
- Voice assistants: Training natural language models using neural networks.
Choosing the Right Machine Learning Algorithm
Selecting the appropriate algorithm depends on:
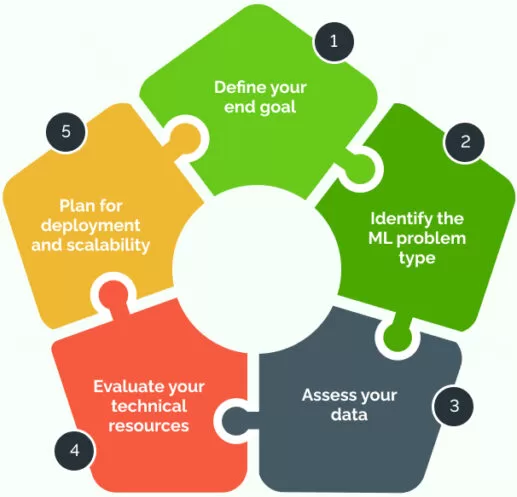
- Type of Data → Labeled or unlabeled?
- Problem type → classification, regression, clustering, or reinforcement?
- Accuracy vs. Interpretability → Some algorithms (like deep learning) are powerful but not easy to interpret.
FAQs on Machine Learning Algorithms
Q1: What is the easiest machine learning algorithm to start with?
👉 Linear Regression or Logistic Regression, since they’re easy to understand and implement.
Q2: What are the most used machine learning algorithms in Python?
👉 Decision Trees, Random Forest, K-Means, Linear Regression, Logistic Regression, and Neural Networks.
Q3: Can one algorithm solve all problems?
👉 No. The choice depends on your data, problem type, and performance needs.
Conclusion
Machine learning algorithms provide the foundation for artificial intelligence. If you’re familiar with the types of machine learning algorithms and have practiced using the machine learning algorithms in Python, then you can get started solving problems. You can use the algorithms to predict an outcome, classify an output, or cluster similar observations.
You will learn best by practicing and playing around — you can start practicing with datasets on Kaggle and use libraries such as scikit-learn.
🚀 So, whatever your level – student, beginner, or enthusiastic, if you learn these algorithms you will be on your way to be entering the realm of AI.