When we write a C program, the compiler does not see it as one continuous stream of text. It separates the program into the smallest meaningful chunks referred to as tokens.
Token in C programming are the programming equivalent of words and the simplest fundamental building block of source code. Without tokens, the compiler wouldn’t know what you meant by a variable name, operator, or keyword.
You can think of tokens like words in the English language; just as you can form sentences using words, you can form C programs using tokens.
What is a Token in C Programming?
A token in the C programming language is the smallest meaningful part of a C program; that is, it is the smallest piece of information that can represent meaning to the compiler.
For example:
int age = 25;
This single line contains multiple tokens:
- int → keyword token
- age → identifier token
- = → operator token
- 25 → constant token
- ; → punctuator token
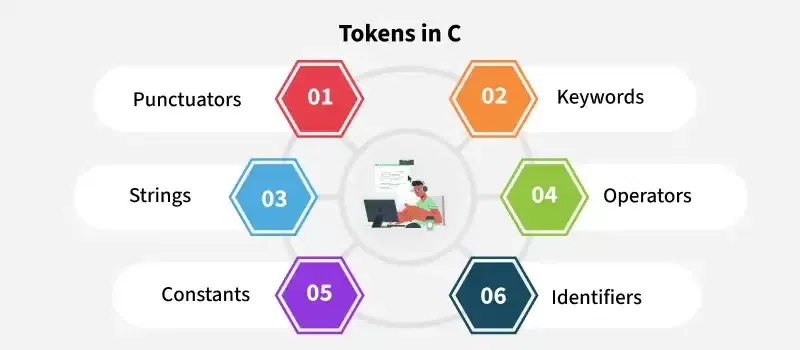
Types of Tokens in C Programming Language
The tokens in C programming language can be categorized into six major types:
| Type of Token | Example | Description |
| Keywords | int, return | Reserved words with predefined meaning |
| Identifiers | age, sum | User-defined names for variables, functions, etc. |
| Constants | 25, ‘A’ | Fixed values that do not change |
| Operators | +, -, * | Symbols that perform operations |
| Punctuators | ;, {, } | Symbols that separate statements or group code |
| Special Characters / Whitespace | space, newline | Used to separate tokens |
1. Keywords in C
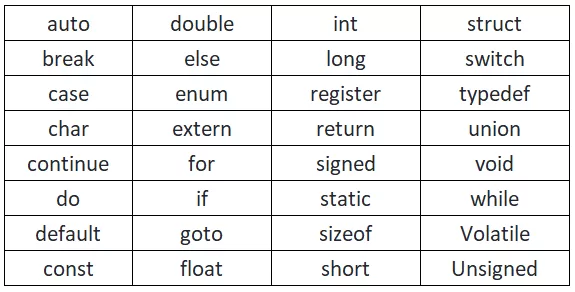
Keywords are reserved words, or statements, defined by the C language. Keywords cannot be used as identifiers.
Example:
int main() {
return 0;
}
Here int and return are keywords.
2. Identifiers in C
Identifiers are the names given to functions, variables, arrays etc.
Example:
int marks;
float average;
Rules for identifiers:
- Must start with a letter or underscore
- Cannot be a keyword
- Can contain letters, digits, and underscores
3. Constants in C

Constants represent unchangeable fixed values. A constant cannot be modified during program execution.
Example:
const int MAX = 100;
4. Operators in C

Operators are symbols, that tell the compiler what operation you want to perform.
Example:
sum = a + b;
Here + is an arithmetic operator.
5. Punctuators in C
Punctuators (you may also hear this referred to as separators) are symbols, that help to organize your code. Examples of punctuators include {}, ;, [].
Example:
int main() {
printf(“Hello World”);
}
6. Whitespace in C
Whitespace separates tokens and makes the code easier to read. The compiler completely ignores all whitespace except when it serves to separate tokens.
Example of Token in C Programming
Let’s break down this example:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int num = 10;
printf(“Number: %d”, num);
return 0;
}
Tokens here:
- #include
- <stdio.h>
- int
- main
- ()
- {
- int
- num
- =
- 10
- ;
- printf
- (“Number: %d”, num)
- return
- 0
- ;
- }
Why Tokens Are Important in C Programming
Without knowing what tokens in C programming, you’ll find syntax error debugging exceptionally difficult. The compilation errors you usually see, “unexpected token” or “missing semicolon”, means the compiler was expecting a certain token and the compiler was unable to find it.
Best Practices for Working with Tokens in C
- All statements must end with a ; (semicolon token).
- You can use whitespace to create clarity.
- You should never use keywords as identifiers.
- Tokens should be logically grouped in a way that is more readable.
FAQs about Tokens in C Programming
Q1: What are the types of tokens in C?
A: There are six types of tokens: keywords, identifiers, constants, operators, punctuators, and whitespace.
Q2: Is a semicolon a token in C?
A: Yes, it is a token of punctuator.
Q3: What is the difference between an identifier and a keyword?
A: A keyword has a defined meaning; an identifier is a name you define.
Final Thoughts
Knowing what token in C programming and understanding tokens in C programming language are critical for writing clean, error-free code. When you understand these smallest pieces of C code, you’ll improve coding speed, coding efficiency, and debugging abilities. This knowledge will be essential for anyone starting their way through programming or studying for implements design interviews.







