Base 64 Encoding – The Basics First 🧩
Let’s cut straight to it.
Base 64 encoding is a way to represent binary data (like images, audio, or files) in plain text. Instead of dealing with unreadable machine code, base 64 encoding turns it into characters we can actually send over the internet.
Think of it as packing a messy room into a neat box so it fits through the door. The room is still the same (the data doesn’t change), but now it’s easier to carry. That’s what base 64 encoding does for data.

So, if you came here wondering “what is base 64 encoding and why do we even need it?”—the quick answer is:
👉 It makes data safe and simple to transfer between systems that only understand text.
Why Do We Even Need Base 64 Encoding? 🤔
Let me tell you a quick story.
Back in my early coding days, I tried sending an image over an email system that only allowed text. Guess what? The image got corrupted, and I spent hours scratching my head. Then I learned about base 64 encoding. It literally “translated” that binary image into text characters. Problem solved.
Here’s why base 64 encoding is necessary:
- 🌐 Safe Transmission: Many protocols (like email or JSON) are text-based. Raw binary just doesn’t play nice there.
- 🛠️ Compatibility: Different systems may interpret binary differently, but text? Almost every system understands text.
- 📩 Embedding Data: Sometimes you need to embed images or files inside HTML, CSS, or JSON. Base 64 makes it possible.
- 🔍 Readability: It’s not human-readable in a storytelling sense, but it’s at least text—not scary binary gibberish.
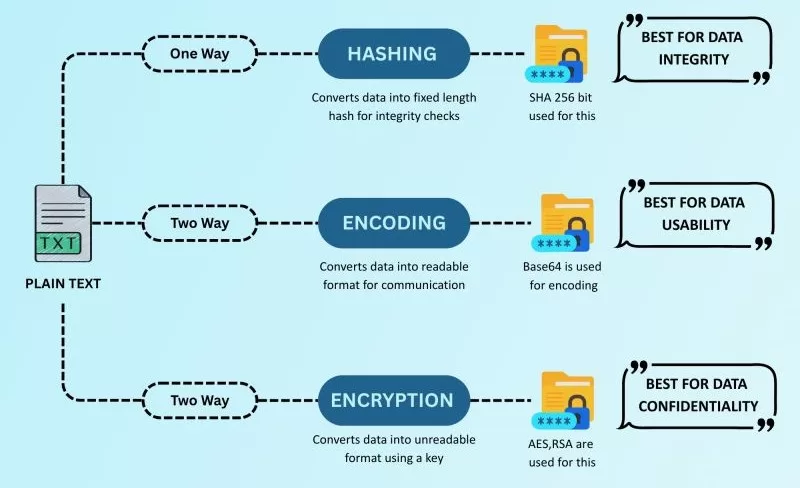
Base 64 Encoding vs Encryption vs Hashing ⚖️
This is a question I get a lot. People confuse base 64 encoding with encryption or hashing. But here’s the deal:
- Encoding (like base 64): Just transforms data into another format. No security.
- Encryption: Secures data by scrambling it with a key. Can be reversed with the right key.
- Hashing: Creates a unique fingerprint of data. One-way only.
👉 So remember: base 64 encoding is NOT encryption. If you put your password in base 64, it’s still visible to anyone who decodes it. Don’t make that mistake.
How Does Base 64 Encoding Work? 🔍
Okay, let’s break it down without getting too math-y.
- Computers use binary data (0s and 1s).
- Some systems can’t handle raw binary.
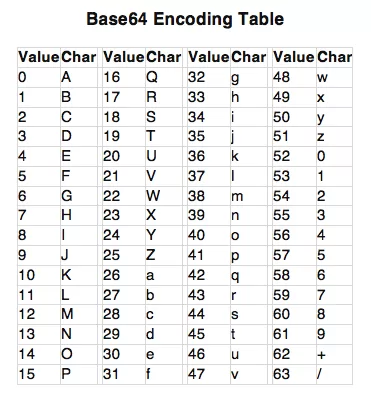
- Base 64 encoding maps those binary chunks into 64 readable characters (A-Z, a-z, 0-9, +, /).
- It also uses
=as padding when needed.
Example:
If you encode Man into base 64, it becomes TWFu. Simple as that.
You can try it yourself with free tools like Base64 Decode & Encode.
Where Do We Use Base 64 Encoding in Real Life? 🌍
You’d be surprised how often base 64 sneaks into our everyday digital lives.
- 📧 Emails (MIME): Attachments are base 64 encoded so they don’t break email systems.
- 🌐 Web Development: Embedding images into HTML/CSS with base 64 encoding.
- 🖼️ APIs & JSON: Sending files in text-based APIs often relies on it.
- 🔐 Authentication: Ever noticed
Authorization: Basic ...in HTTP headers? That’s base 64 encoding.
I once built a simple login system where I had to send credentials in an HTTP header. It blew my mind when I realized those weird characters were just username:password encoded in base 64. Of course, that wasn’t secure—but it worked for the system at that time.
Pros and Cons of Base 64 Encoding ⚡
Like everything in tech, base 64 encoding has its ups and downs.
✅ Advantages
- Universally supported.
- Makes binary safe for text-based systems.
- Simple and fast to implement.
❌ Disadvantages
- Bloats file size (around 33% bigger).
- Not secure at all (easy to decode).
- Can make code heavier if overused (like embedding large images in HTML).
Base 64 Encoding in Code
These are the kind of snippets I love keeping in my notes—they save me when I forget the exact functions.
Should You Use Base 64 Encoding in 2025? 🤷

Here’s my honest opinion.
Yes, base 64 is still super useful. I use it often when working with APIs, authentication headers, or embedding small assets. But, you should avoid using it for large files (performance issues) or anything related to security.
👉 For security, stick with encryption and hashing. Base 64 is just a helper, not a guard.
Final Thoughts
So, to wrap this up: base 64 is basically a translator. It helps systems “talk” to each other by converting binary into safe text. It’s not fancy encryption, but it’s practical, reliable, and everywhere once you start noticing it.
If you’re a beginner, experiment with online encoders/decoders. If you’re a developer, learn how to use base 64 in your favorite programming language.
And if you’re like me—you’ll eventually have that “aha!” moment when you realize base 64 encoding is quietly holding the internet together.
Want to learn more about this encoding, encryption, Cyber Security Course, Networking Course, Cloud Computing Course visit www.kaashivinfotech.com.







