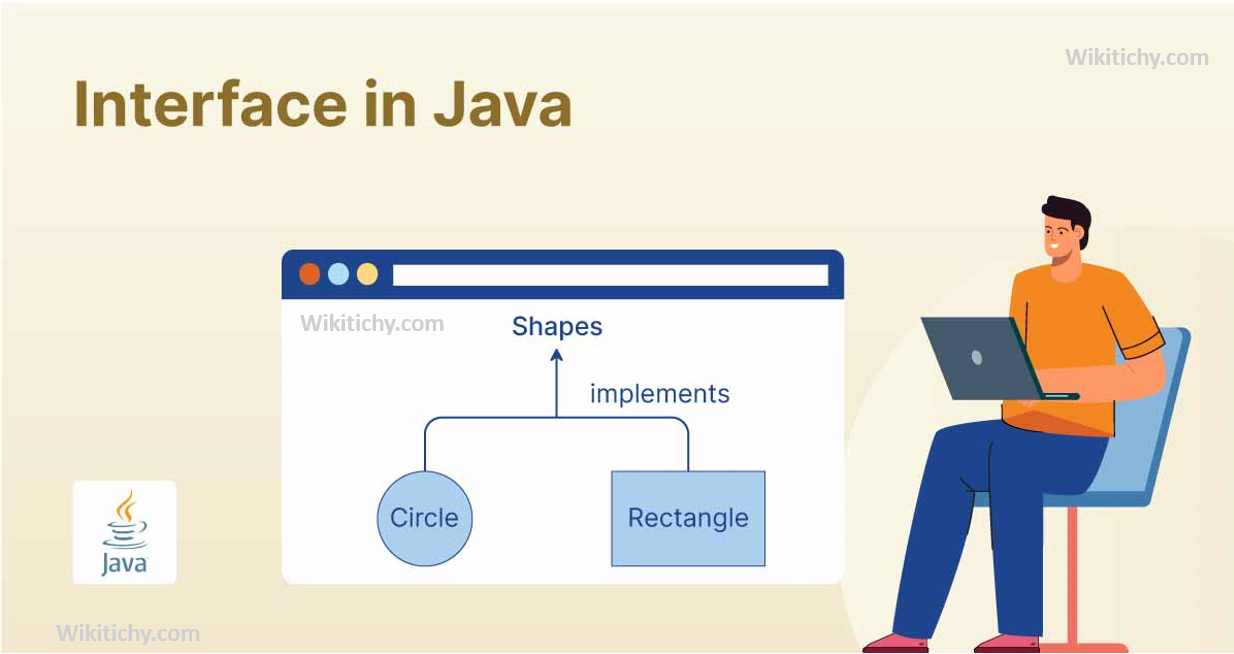
Definition:
An interface in Java is a reference type, similar to a class, that can contain only constants, method signatures, default methods, static methods, and nested types. Interfaces cannot contain method implementations (except default and static methods). They define a contract that classes must follow, specifying what methods a class must implement without dictating how the methods should be implemented. A class can implement multiple interfaces.
Example:
// Defining the interface
interface Animal {
// Abstract methods
void eat();
void sleep();
// Default method
default void breathe() {
System.out.println("Animal is breathing...");
}
}
// Implementing the interface
class Dog implements Animal {
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("Dog is eating...");
}
@Override
public void sleep() {
System.out.println("Dog is sleeping...");
}
}
class Cat implements Animal {
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("Cat is eating...");
}
@Override
public void sleep() {
System.out.println("Cat is sleeping...");
}
}
// Main class to demonstrate
public class InterfaceExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal dog = new Dog();
Animal cat = new Cat();
// Dog behavior
dog.eat();
dog.sleep();
dog.breathe();
// Cat behavior
cat.eat();
cat.sleep();
cat.breathe();
}
}
Output:
Dog is eating...
Dog is sleeping...
Animal is breathing...
Cat is eating...
Cat is sleeping...
Animal is breathing...
Features of Interfaces in Java:
- Interfaces can only have abstract methods (prior to Java 8). Starting from Java 8, they can also have default and static methods .
- Interfaces can only contain constants (final variables); they cannot store instance variables or object states.
- A class can implement multiple interfaces, thus providing multiple inheritance.
- Interfaces provide loose coupling between classes, promoting flexibility in code architecture.
- Starting from Java 8, interfaces can have default method implementations, allowing new methods to be added without breaking existing implementations.
Advantages of Using Interfaces:
- Java does not support multiple inheritance with classes but allows it with interfaces. A class can implement multiple interfaces, which helps in modularizing behavior.
- Interfaces define a contract that must be fulfilled, enabling abstraction by hiding implementation details from the user.
- Interfaces decouple the definition of behaviors from the actual implementation, making the system more modular and flexible.
- Interfaces make it easier to test code by allowing for dependency injection and mock implementations.
- Interfaces allow easy addition of new behaviors to a class without modifying its existing functionality.
Uses of Interfaces in Java:
- Interfaces are commonly used in APIs to define a contract that different classes (even from other developers) can implement without exposing the internal logic.
- Java GUI frameworks use interfaces (e.g., ActionListener) to handle events like button clicks.
- Interfaces are used in frameworks like Spring to inject different implementations of a service dynamically.
- Interfaces allow for polymorphism, where a single method or function can process objects of different classes that implement the same interface.
- Interfaces allow different modules or layers in a software application to interact while keeping their internal workings hidden.