What Is Sorting?
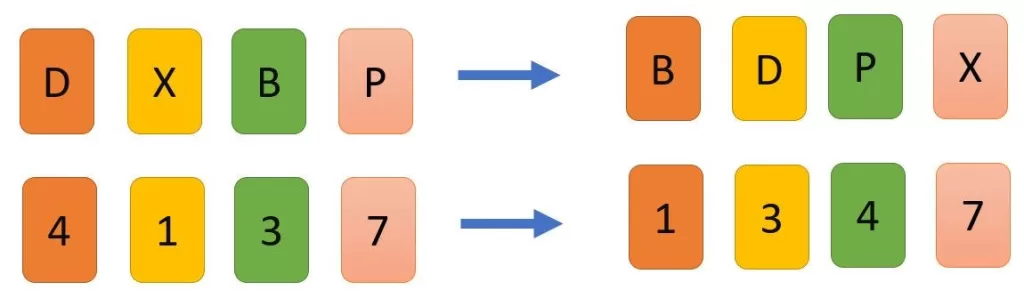
What is sorting in computer science?
Sorting is the process of arranging data in a particular order—most commonly ascending or descending. Whether you’re organizing names alphabetically, ordering numbers, or ranking search results, sorting algorithms make data processing faster and more efficient.
Why Sorting Matters
Efficient sorting techniques are a cornerstone of programming and data science. They help:
- Speed up searching (binary search requires sorted data).
- Present information in a user-friendly way.
- Optimize other algorithms such as graph traversal and database queries.
Without sorting, everyday applications like e-commerce product listings or social media feeds would be slow and chaotic.
Sorting Techniques Explained
Sorting methods are broadly divided into two categories:
1️⃣ Comparison-Based Sorting
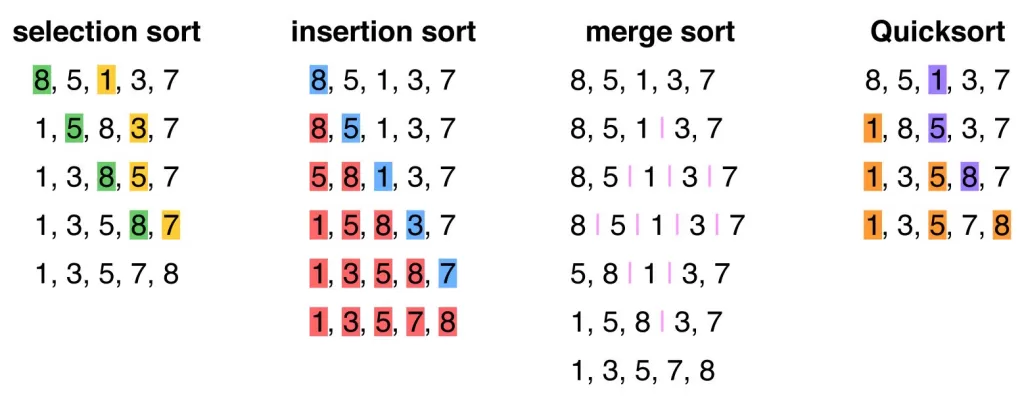
These algorithms compare elements to determine their correct order.
- Bubble Sort – Repeatedly swaps adjacent elements. Simple but inefficient for large lists.
- Insertion Sort – Inserts each item into its correct place in a growing sorted list.
- Selection Sort – Selects the smallest element and places it at the start.
- Merge Sort – Divides the list into halves, sorts them, and merges.
- Quick Sort – Uses a pivot to partition data; very fast on average.
2️⃣ Non-Comparison Sorting
Used when data has special properties:

- Counting Sort – Efficient when elements are within a limited range.
- Radix Sort – Processes digits from least to most significant.
- Bucket Sort – Distributes elements into buckets, then sorts each.
💡 Pro tip: Learn the input size and data characteristics before picking a sorting algorithm.
Big-O Analysis: Picking the Best Sorting Algorithm
Understanding time complexity is essential for choosing the best sorting algorithm:
| Algorithm | Average Case | Worst Case | Stable? |
| Bubble Sort | O(n²) | O(n²) | ✔ |
| Insertion Sort | O(n²) | O(n²) | ✔ |
| Merge Sort | O(n log n) | O(n log n) | ✔ |
| Quick Sort | O(n log n) | O(n²) | ✘ |
| Heap Sort | O(n log n) | O(n log n) | ✘ |
| Counting Sort | O(n + k) | O(n + k) | ✔ |
For general purposes, Quick Sort and Merge Sort often win. When stability matters (e.g., sorting records by name while preserving date order), Merge Sort is the safest bet.
Code Example: Quick Sort in Python
def quick_sort(arr):
if len(arr) <= 1:
return arr
pivot = arr[len(arr) // 2]
left = [x for x in arr if x < pivot]
middle = [x for x in arr if x == pivot]
right = [x for x in arr if x > pivot]
return quick_sort(left) + middle + quick_sort(right)
nums = [34, 7, 23, 32, 5, 62]
print("Original:", nums)
print("Sorted:", quick_sort(nums))
Output:
Original: [34, 7, 23, 32, 5, 62]
Sorted: [5, 7, 23, 32, 34, 62]Choosing the Best Sorting Algorithm
When performance matters:
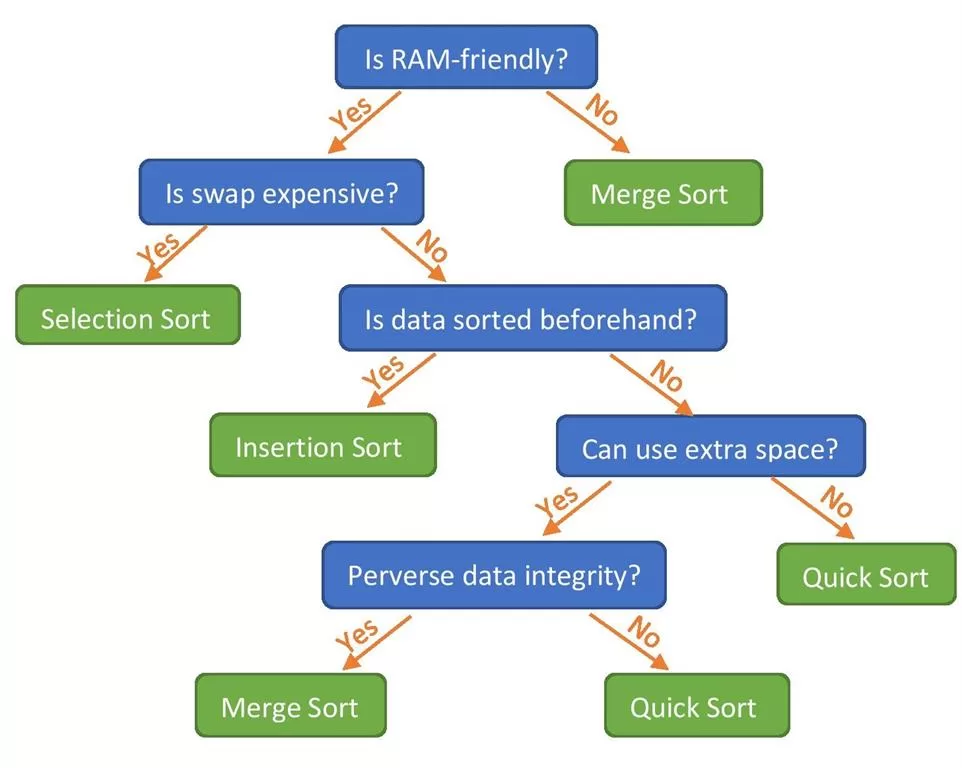
- For small datasets, use Insertion Sort (low overhead).
- For large datasets, Quick Sort or Merge Sort shine.
- For integer keys with limited range, Counting Sort or Radix Sort is unbeatable.
There’s no single “one size fits all.” The best sorting algorithm depends on dataset size, memory constraints, and stability requirements.
Applications of Sorting
- Databases – Sort query results (
ORDER BY), build indexes, remove duplicates. - Searching algorithms – Binary search and other search methods require sorted data.
- Operating systems – Job scheduling, paging, and memory management often depend on sorting.
- E-commerce & web apps – Sort products by price, rating, popularity, or relevance.
- Data science & analytics – Preprocess, group, and visualize data efficiently.
- Networking – Organize routing tables, reorder packets arriving out of sequence.
- Everyday apps – Sort playlists, contacts, emails, or messages alphabetically or by date.
- Education & sports – Rank exam scores, leaderboards, and sports statistics.
- Finance – Sort transactions, invoices, or stock data by amount or time.
- Graph algorithms – Kruskal’s MST and similar algorithms need edges sorted by weight.
FAQs About Sorting
Q1: What is the simplest sorting algorithm?
Bubble Sort is easiest to understand but not efficient for big lists.
Q2: Which sorting algorithm is fastest in practice?
Quick Sort is often fastest on average, but Merge Sort is more consistent.
Q3: Why are sorting techniques important for interviews?
Because they test problem-solving, data structure knowledge, and algorithmic thinking.
Conclusion
Sorting is more than an academic concept—it’s a foundation of computer science. By mastering sorting techniques and knowing when to apply the best sorting algorithm, you can write code that’s efficient, scalable, and ready for real-world challenges.