Has this ever happened to you? You’ve completed an equation and you’re not sure whether you got the right answer? 🤔 For example, you did 8 + 4 × 2 and you got 24, while your friend insists that the answer is 16. Who is right? Confusion like this is the reason the BODMAS rule exists.
The BODMAS rule (Brackets, Orders, Division, Multiplication, Addition, Subtraction) is more than just a mnemonic for teaching in a classroom; it is meant to serve everyone as a universal language of math and computing.
Whether you’re solving math problems in school, or writing code in Python, Java, or SQL, the fact that BODMAS governs the order of mathematical operations ensures that everyone does things in the same order — and lets everyone arrive at the same answer!
Key Highlights:
- 🧮 Understand the BODMAS rule with examples in math and programming from the real-world.
- 🧠 Understand why the BODMAS rule exists and the logic behind the hierarchy of operations.
- 💻 Understandoperator precedence in Python, Java, SQL and AI frameworks.
- ✏️ Workthrough BODMAS questions and answers (class 5–8).
- 🌍 BODMAS vs PEMDAS (UK/India vs US terminology).
- ⚠️ Understand what common mistakes areand when the BODMAS rule is not applicable.
- 📖 FAQs included to clarify any student and developer queries.
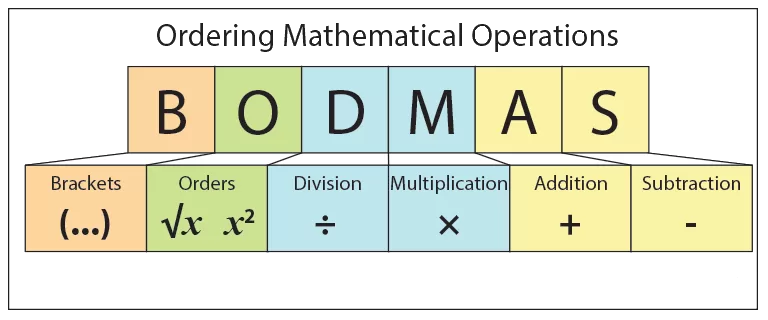
What is the BODMAS Rule? (Definition + Full Form)
If you ever wondered how a simple calculation like 5 + 2 * 10 can lead to a head scratchingly wrong answer of 25 (instead of 70), the BODMAS rule solves the puzzle.
BODMAS full form:
- B – Brackets
- O – Orders (powers, roots)
- D – Division
- M – Multiplication
- A – Addition
- S – Subtraction
Basically, BODMAS is about the order of operations. Computers, calculators, and cloud billing engines all operate on this logical convention. Forgetting it can turn simple math problems to even production code — into an impossible chaotic mess.
👉 Quick Example:10 + 5 * 2 → Apply BODMAS: Multiplication first → 10 + 10 = 20.
So when someone asks “what is BODMAS rule?”, you can tell them: it’s the logic behind how math, code, and machines evaluate expressions.
BODMAS Formula & Order of Operations
Here’s a quick table to help you remember the BODMAS formula:
| Order | Operation | Example |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Brackets | (2 + 3) * 4 = 20 |
| 2 | Orders | 2^3 + 4 = 12 |
| 3 | Division | 20 ÷ 5 + 2 = 6 |
| 4 | Multiplication | 2 * 3 + 4 = 10 |
| 5 | Addition | 5 + 2 = 7 |
| 6 | Subtraction | 10 – 3 = 7 |
💡 Pro Tip: Which bracket is solved first in BODMAS? — Parentheses ( ) always come first over [ ] or { }; it is always go from inside out.
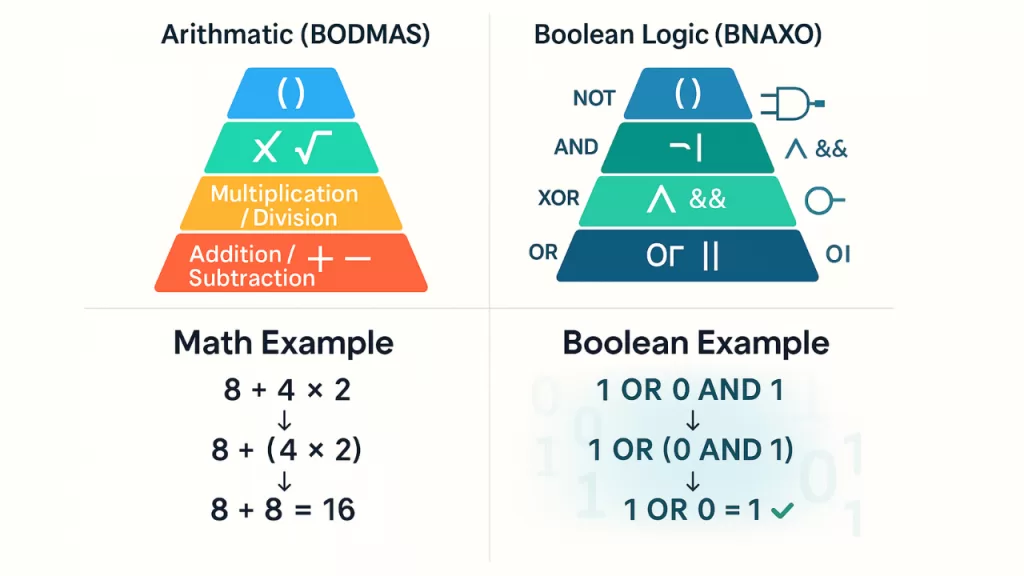
Why Does the BODMAS Rule Exist? (The Hierarchy of Operations Explained)
At first glance, BODMAS may feel like an arbitrary classroom trick. But it isn’t random at all — there’s a deep logic behind why it exists. The rule was designed to bring:
- Consistency → so everyone gets the same answer to the same expression.
- Hierarchy of operations → because math builds in layers, with complex operations made from simpler ones.
- Efficiency → to avoid writing brackets everywhere.
- Compatibility with computing & logic circuits → which rely on fixed precedence to execute operations.
The Hierarchy of Operations Step by Step
- Addition & Subtraction → The Foundation
These are the simplest operations: combining and removing.
Example: 5 + 3 = 8, 8 – 2 = 6. - Multiplication & Division → Repeated Addition/Subtraction
Multiplication is repeated addition: 3 × 4 = 3 + 3 + 3 + 3.
Division is repeated subtraction: 12 ÷ 4 = subtract 4 until zero.
Since they depend on addition/subtraction, they are ranked higher. - Orders (Powers, Roots) → Repeated Multiplication/Division
Exponents are repeated multiplication: 2³ = 2 × 2 × 2.
Roots are the reverse: √9 = 3 because 3 × 3 = 9.
Since they build on multiplication, they come even higher in the hierarchy. - Brackets → Manual Control Layer
Brackets exist to let humans override the hierarchy when needed.
Example: (5 + 3) × 2 vs 5 + (3 × 2).
✅ In short:
Addition is the base → multiplication is built on addition → exponents (or powers) are built on multiplication → brackets let you control the order.

This stacking is why the BODMAS rule feels natural — it mirrors how both humans and computers process calculations.
BODMAS Questions with Answers
Many learners first meet the BODMAS rule in school. Let’s solve a few BODMAS questions:
- Q: 15 – (6 + 2) × 2
A: 15 – 8 × 2 = 15 – 16 = -1 - Q: (25 ÷ 5) + 3 × 4
A: 5 + 12 = 17 - Q: 100 ÷ (10 – 5 × 2)
A: 100 ÷ (10 – 10) = Division by zero ❌ → Not applicable - Q: 6 + 18 ÷ 3 × 2
A: 6 + 6 × 2 = 6 + 12 = 18
👉 The BODMAS formula makes it clear what step to take at each stage of the operation and prevents confusion.
BODMAS Rule in Programming & IT (2025 Use Cases)
1. Full Stack Development
console.log(10 + "20" + 30); // Output: "102030"
console.log(10 + 20 + 30); // Output: 60
JavaScript illustrates how combining numbers and strings can lead to unexpected outcomes if you lose track of operator precedence.
2. AI & Data Science
a, b, c = 2, 3, 4
print((a + b) * c) # 20
print(a + b * c) # 14
In machine learning, a missing bracket can radically change the input and output of the original model.
3. Cloud & Networking
Automation scripts rely on conditional statements that account for:
if ((cpu > 80) && (memory > 70)) { alert(); }
Logical operators (&&, ||) are also subject to precedence.
4. Databases (SQL)
SELECT 10 + 5 * 2; -- 20, not 30
There is a priority difference between AND running before OR in SQL conditions; therefore, the brackets are important.
Common Mistakes Developers Make
- Mixing string + number operations.
- Forgetting logical operator precedence.
- Writing lengthy one-liners without parentheses.

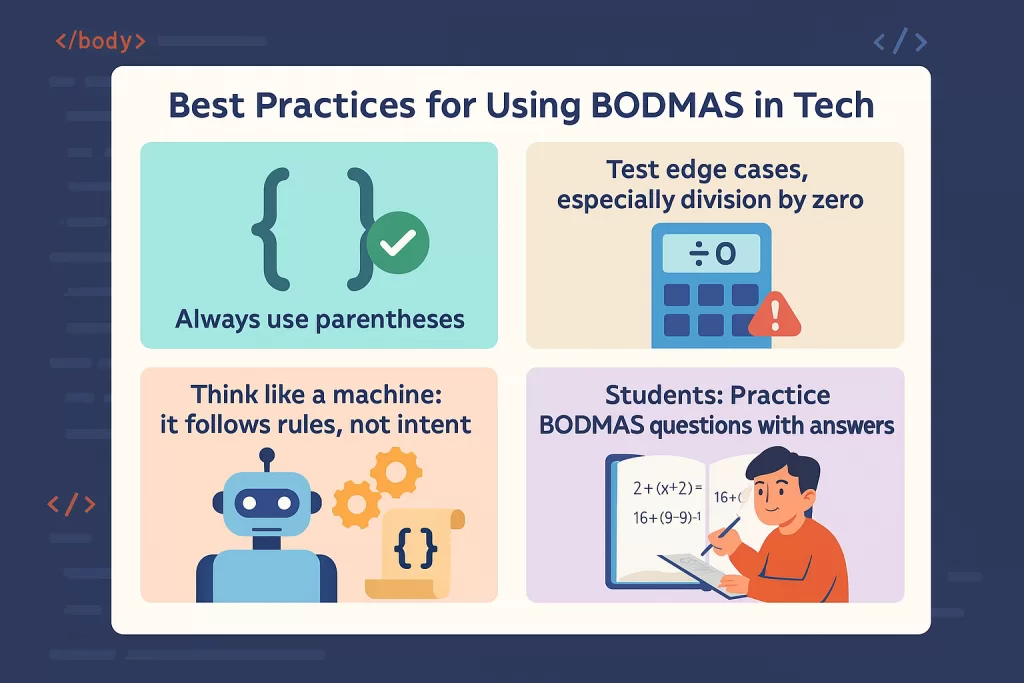
Best Practices for Using BODMAS in Tech
- Always use parentheses.
- Test edge cases, especially on division by zero.
- Think like a machine: it follows the rules, it does not follow intent.
- Students: Practicing bodmas questions with answers is helpful for developing reasoning both mathematically and programmatically.
When BODMAS Rule is Not Applicable
- – Division by zero scenarios.
- – Exceptions in specific languages (for example, string concatenation in Javascript).
- Mental math shortcuts humans use — machines don’t.

✍️ BODMAS vs PEMDAS (Are They the Same?)
You might also hear teachers or textbooks talk about PEMDAS instead of BODMAS. Don’t worry — they’re the same idea with different names:
| BODMAS (UK/India) | PEMDAS (US) | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| B = Brackets | P = Parentheses | ( ) grouping symbols |
| O = Orders | E = Exponents | Powers, roots |
| D = Division | D = Division | ÷ or / |
| M = Multiplication | M = Multiplication | × or * |
| A = Addition | A = Addition | + |
| S = Subtraction | S = Subtraction | – |
👉 BODMAS = PEMDAS.
The only difference is regional naming:
- UK/India = BODMAS
- US = PEMDAS
So, 10 + 2 × 5 will always be solved as 10 + (2×5) = 20 whether you call it BODMAS or PEMDAS.
FAQ: BODMAS Rule
Q1: What is the full form of BODMAS?
A: Brackets, Orders, Division, Multiplication, Addition, Subtraction.
Q2: What is BODMAS in maths?
A: It’s the order of operations rule that ensures everyone solves math expressions consistently.
Q3: When is BODMAS rule not applicable?
A: In division by zero, certain programming language quirks, or cases where operations aren’t clearly defined.
Q4: Which bracket is solved first in BODMAS?
A: Parentheses ( ) are solved first, followed by [ ] and then { }.
Q5: How to solve BODMAS step by step?
A: Always start with brackets → then orders → division → multiplication → addition → subtraction.
Q6: What is the meaning of BODMAS in programming?
A: It’s the operator precedence rules that compilers and interpreters use to evaluate code correctly.
Conclusion
The BODMAS rule is more than a school memory — it’s the backbone of calculations in math, programming, databases, and AI. Whether you’re a student solving bodmas questions, a coder writing SQL, or a data scientist building models, respecting this rule saves you from bugs, errors, and confusion.
👉 Next time someone asks “what is BODMAS rule?”, you can give them the BODMAS full form, walk them through a quick example, and even illustrate how BODMAS is running behind all the apps and AI systems we use every day.
📚 Related Reads
- Bayes’ Rule in Artificial Intelligence: The Beginner’s Guide to Smarter AI in 2025
Perfect companion for readers exploring logic and rule-based decision making—this guide breaks down how Bayes’ Rule updates beliefs in AI systems using real-world examples. - What is Normalization in DBMS – 1NF, 2NF, 3NF Explained with Examples (2025 Guide)
A practical dive into database fundamentals—just as BODMAS structures operations, normalization structures data. This post explains how to reduce redundancy and improve DB efficiency. - Master OOPS Principles in Java – Object-Oriented Programming Concepts (2025)
Delves into fundamental software design principles—encapsulation, abstraction, inheritance, polymorphism—building a strong parallel with operator precedence in code logic. - Random Number Generator Explained: How Computers Pick Numbers (With Python, Java & Excel Examples)
Covers important algorithmic thinking in programming and AI—deterministic versus truly random processes and examples in common languages.







