Cloud Deployment Models in 2025 — The Core of Every Digital Strategy
If an app crashed during a busy sale time, customers wouldn’t care where your servers lived — AWS, Azure, or your own data center. They just expect it to work. That’s why choosing the right cloud deployment model can make or break your business.
In simple terms, a cloud deployment model decides where your data lives, who manages it, and how easily it can grow. It’s the foundation of every digital product you build.
And in 2025, this choice is more crucial than ever. With 95% of new digital workloads now running on cloud-native platforms (Gartner), companies that pick the wrong model can end up paying twice as much for the same performance.
For tech professionals, understanding cloud deployment models in cloud computing isn’t just a skill — it’s a career edge. It’s what separates teams that run apps from teams that keep them running flawlessly.
Let’s decode each model, explore their real-world use cases, and find out which one truly fits your business — and your growth.

What is a Cloud Deployment Model?
Think of cloud deployment models as blueprints that decide where your digital house is built — whether you rent an apartment (public cloud), own a villa (private cloud), or share a co-working space (community or hybrid cloud).
At its core, a cloud deployment model defines:
- Ownership: Who runs the servers — you, a cloud provider, or both?
- Access control: Who gets to use your resources and under what permissions?
- Scalability: How easily can your systems grow or shrink with demand?
- Governance: How your organization maintains compliance, monitoring, and data security.
Every cloud model is a trade-off between control, cost, and convenience. For instance, a startup might rely on a public cloud for affordability and speed, while a financial institution might stick to a private cloud to protect sensitive data.
🧠 Quick Analogy:
Imagine you’re running a company’s data like you’d manage your workspace:
- Public Cloud → Renting a shared co-working office. Cheap, flexible, but not 100% private.
- Private Cloud → Owning your own building. Expensive, but fully under your control.
- Hybrid Cloud → Having both — a private office and a flexible shared space when needed.
- Community Cloud → Sharing a campus with similar organizations (like universities).
- Multi Cloud → Using multiple office spaces across different cities for redundancy.
Each choice affects how you manage costs, data privacy, and scalability.

🌤️ Types of Cloud Deployment Models (2025 Update)
If you’ve ever wondered why one company swears by AWS while another insists on hosting everything in-house — it all comes down to their cloud deployment model. Each model represents a tradeoff between control, cost, compliance, and convenience.
Let’s break down the five major types of cloud deployment models in 2025 — and when each makes sense.
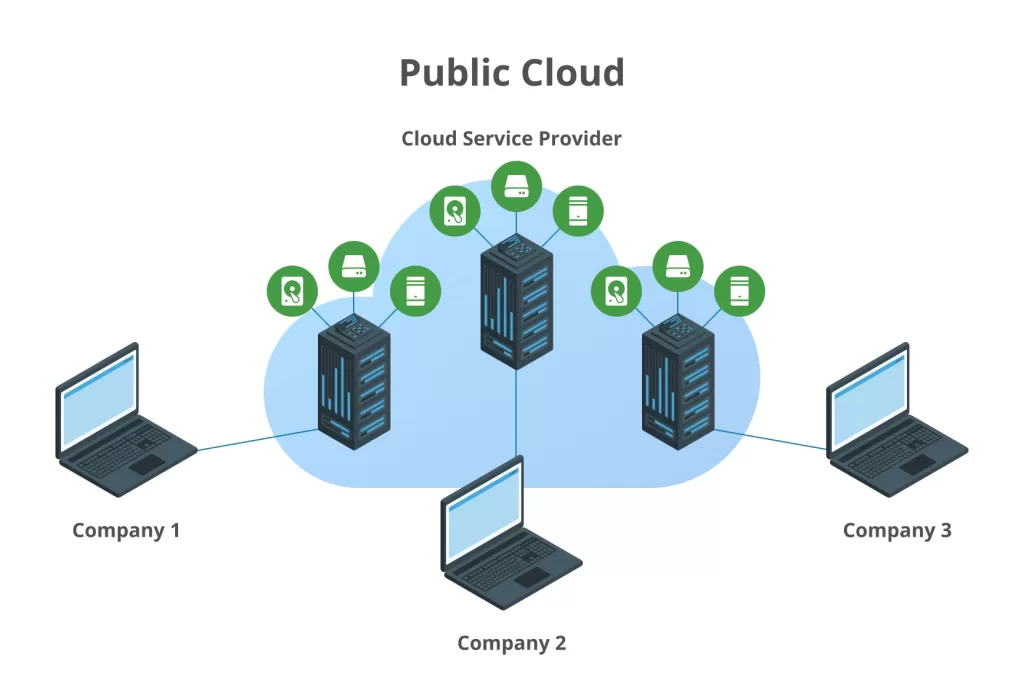
🏢 Public Cloud
Definition:
A public cloud is like renting a seat in a massive co-working space — you share the infrastructure with others, but the provider handles all the maintenance, power, and scalability.
Managed entirely by third-party providers such as AWS, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud Platform (GCP), it offers near-infinite capacity and global reach.
Best for:
Startups, SaaS companies, and businesses running short-term or high-traffic projects.
Example:
Netflix uses AWS to stream billions of hours of content globally without building its own data centers.
Advantages:
- 💰 Low upfront cost — pay only for what you use.
- 🔧 No maintenance — the provider handles updates and uptime.
- 🚀 Instant scalability — scale up or down within minutes.
Disadvantages:
- 🔐 Limited control over infrastructure configuration.
- ⚠️ Security concerns for industries with sensitive data.
📊 Stat:
As of 2025, 67% of SMBs rely solely on public cloud infrastructure for daily operations.
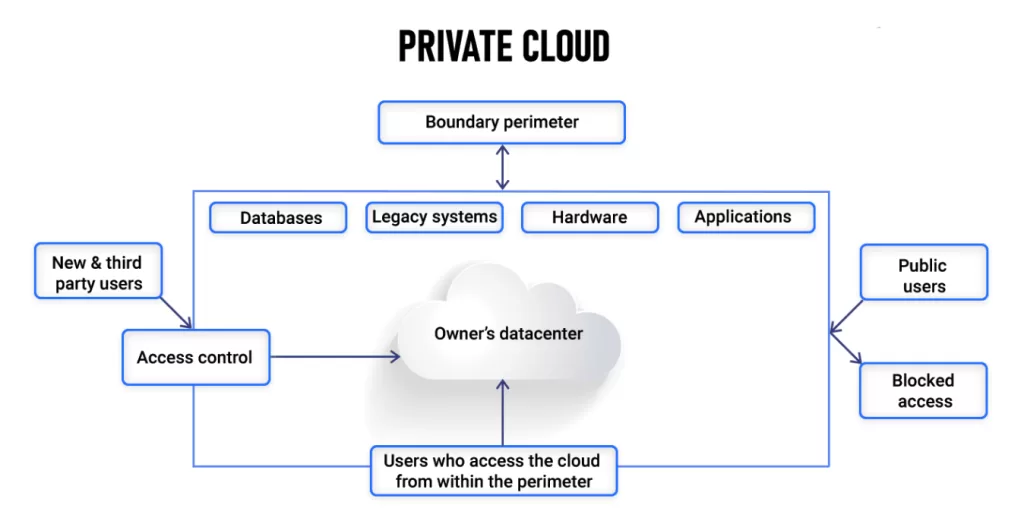
🔒 Private Cloud
Definition:
A private cloud gives you your own data center — the digital equivalent of owning a private office building. It’s dedicated to one organization, offering full control and customization.
Best for:
Large enterprises handling regulated or sensitive data, such as finance, defense, or healthcare sectors.
Example:
A bank running internal applications on VMware Cloud Foundation to ensure compliance and uptime.
Advantages:
- 🧩 High control and security — tailor your setup for compliance standards like HIPAA or PCI-DSS.
- ⚙️ Customizable architecture — fine-tuned for specific workloads.
Disadvantages:
- 💸 High initial setup and operational cost.
- 👨💻 Requires skilled IT teams for maintenance.
🧠 Developer Insight:
“Private clouds are often chosen when compliance and uptime matter more than elasticity.”
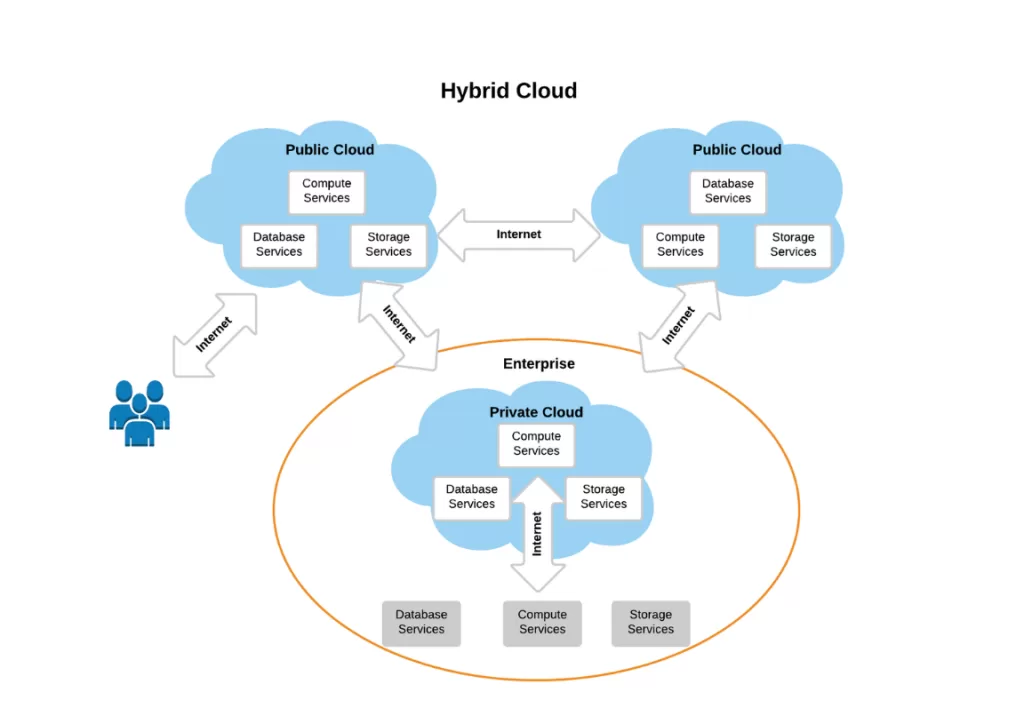
⚙️ Hybrid Cloud
Definition:
A hybrid cloud merges public and private environments, enabling workloads to move seamlessly between them. Think of it as owning an office (private) while occasionally renting coworking space (public) when demand spikes.
Best for:
Organizations with fluctuating workloads or partial regulatory requirements.
Example:
Spotify uses Google Cloud along with on-prem servers to balance performance and cost efficiency.
Advantages:
- ⚖️ Best of both worlds — cost savings with security.
- 🚀 On-demand scalability during traffic surges.
Disadvantages:
- ⚙️ Complex management across environments.
- 🌐 Latency issues during data transfer between clouds.
📈 Stat:
By 2025, 82% of mid-size companies are expected to adopt hybrid cloud architectures for flexibility.
👥 Community Cloud
Definition:
A community cloud is shared by multiple organizations with similar objectives — often in education, government, or research.
Example:
Several universities sharing an HPC (High Performance Computing) infrastructure for collaborative research.
Advantages:
- 💵 Cost sharing — reduces individual infrastructure costs.
- 🧾 Better compliance — aligned governance across partners.
Disadvantages:
- ⚙️ Limited customization due to shared governance.
- 🐢 Slower innovation — depends on collective decision-making.
💡 Best Practice:
Choose a community cloud when you need collaboration and compliance without the full cost of a private cloud.

🌐 Multi Cloud
Definition:
A multi cloud strategy uses multiple providers (AWS, Azure, GCP, etc.) simultaneously. It’s the digital version of diversifying your investment portfolio — reducing dependency on a single provider.
Best for:
Enterprises that need maximum uptime, geographical redundancy, and want to avoid vendor lock-in.
Example:
Adobe Creative Cloud operates across AWS and Azure to ensure global availability.
Advantages:
- 🔁 High availability and resilience.
- 🧠 Access to best-of-breed services from each provider.
Disadvantages:
- 🧩 Management complexity — requires integration expertise.
- 🔐 Security challenges across diverse environments.
🧩 Pro Tip:
Use multi-cloud management platforms like Google Anthos or Azure Arc for unified visibility and governance.

⚖️ Cloud Deployment Models Comparison Table (2025)
Here’s a quick snapshot comparing the five cloud deployment models side by side — designed for decision-makers who need clarity at a glance.
| Factor | Public Cloud | Private Cloud | Hybrid Cloud | Community Cloud | Multi-Cloud |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cost | 💰 Low | 💸 High | ⚖️ Medium | 💵 Shared | 💰💰 Variable |
| Scalability | 🔼 High | ⚙️ Moderate | 🔼 High | ⚙️ Fixed | 🔼 High |
| Security | 🟡 Medium | 🟢 Strong | 🟢 Strong | 🟢 Strong | 🟡 Depends |
| Control | Low | High | Medium | Shared | Medium |
| Example Use Case | Startups | Banks | SaaS/Enterprises | Universities | Global Enterprises |
🧭 How to Choose the Right Cloud Deployment Model
Choosing among the types of cloud deployment models can feel overwhelming — but it doesn’t have to be. The right choice depends on your team size, data sensitivity, scalability needs, and budget.
Here’s a quick decision guide to help:
✅ Small team or startup → Public Cloud
If your priority is speed, affordability, and global reach, go public. Services like AWS EC2 or Google Cloud Run let you deploy apps in minutes with minimal setup.
🏢 Large enterprise → Private or Hybrid Cloud
For industries that handle sensitive data (banking, healthcare, insurance), a private or hybrid cloud ensures compliance, control, and high availability.
🌎 Global service → Multi-Cloud
When uptime and regional redundancy matter — as in streaming or e-commerce platforms — a multi-cloud setup ensures no single provider outage can take you down.
🎓 Consortiums or educational networks → Community Cloud
If you’re collaborating on research or policy, community clouds offer shared governance and cost efficiency across institutions.
💡 Expert Tip:
Always start with hybrid or multi-cloud proof-of-concepts before committing to a full migration. This approach minimizes risk, reveals cost bottlenecks, and builds confidence in cloud scalability.
🌍 Real-World Use Cases & Industry Examples
Every industry now tailors its cloud deployment model to match its operational DNA. Here’s how leading sectors are doing it in 2025:
🏥 Healthcare — Private + Hybrid Clouds for Data Privacy
Hospitals and healthcare startups use private clouds for sensitive patient data and hybrid setups for analytics workloads. Platforms like IBM Cloud for Healthcare ensure compliance with global privacy laws like HIPAA and GDPR.
🛒 E-commerce — Multi-Cloud for Seasonal Scaling
Giants like Amazon and Flipkart rely on multi-cloud environments to handle regional sales peaks and improve latency. By distributing workloads across AWS, Azure, and GCP, they maintain uptime even during mega sales like Diwali or Black Friday.
🏛️ Government — Community Clouds for Unified Governance
India’s NIC Cloud (MeghRaj) runs on a community cloud model, allowing government departments to share secure infrastructure while maintaining data sovereignty. Similar models are used across the EU’s Gaia-X initiative for data collaboration.
These examples show that cloud deployment isn’t just an IT choice — it’s a strategic enabler for speed, compliance, and innovation.
🔮 2025 Trends in Cloud Deployment Models
As the world moves deeper into the digital era, the future of cloud deployment models in cloud computing is being shaped by four key trends:
🤖 1. AI-Driven Optimization
Clouds are getting smarter. Using machine learning, providers now offer predictive autoscaling that adjusts resources before traffic spikes — saving up to 30% in compute costs.
🌱 2. Sustainable Clouds
With enterprises focusing on ESG goals, carbon-aware computing is becoming mainstream. Providers like Google Cloud let users choose data centers based on renewable energy usage.
📡 3. Edge + Cloud Synergy
IoT devices, AR/VR systems, and autonomous vehicles demand ultra-low latency. Edge computing brings processing closer to the user, while the cloud handles orchestration — a perfect partnership for real-time applications.
🗺️ 4. Data Sovereignty and Compliance
New regional laws (like India’s Digital Personal Data Protection Act 2023) push organizations toward localized or hybrid cloud setups to ensure data residency and privacy compliance.
In 2025, the smartest cloud isn’t just scalable — it’s sustainable, compliant, and intelligent.
🧩 Models of Cloud Computing: IaaS, PaaS, SaaS
When you log into a cloud service, you’re interacting with one of three core service models — Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), or Software as a Service (SaaS).
Each defines how much control you have over the computing stack and how much responsibility the provider takes on.

Let’s break them down.
- ☁️ Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Gives you virtualized hardware resources like servers, networks, and storage. Ideal for developers who want flexibility and control.- Example: AWS EC2, Microsoft Azure VM.
- Ties to Deployment: Common in public and hybrid clouds for scalable hosting.
- 🧰 Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Offers pre-built environments for developing and deploying applications without managing infrastructure. Perfect for developers who value speed and convenience.- Example: Google App Engine, Heroku.
- Ties to Deployment: Found in public and multi-cloud setups.
- 💼 Software as a Service (SaaS)
Delivers ready-to-use software via the internet. Businesses love SaaS for its agility and zero maintenance.- Example: Salesforce, Microsoft 365.
- Ties to Deployment: Often runs on public or multi-cloud models for global reach.
Together, these service models power modern digital ecosystems, helping teams innovate faster while cloud providers handle the heavy lifting.

🏁 Conclusion: The Cloud You Choose Defines Your Future
In 2025, the cloud isn’t just infrastructure — it’s a business strategy. The right cloud deployment model can determine whether your app scales effortlessly or crashes under pressure.
From public clouds powering startups to multi-cloud strategies securing global uptime, each model has its place in the digital ecosystem.
The key is not just choosing the fastest or cheapest model — but the one that aligns with your goals, compliance needs, and growth vision.
If you’re unsure where to start, begin with a hybrid cloud pilot. It’s the sweet spot between cost, control, and innovation — and the perfect stepping stone into the future of cloud computing.
🔗 Related Reads You’ll Love
- Virtualization in Cloud Computing and Types: My Honest Take in 2025
Dive deeper into how virtualization powers cloud efficiency, isolation, and scalability. - Amazon Web Services (AWS) Explained in 2025: 7 Reasons Why AWS Cloud Still Dominates 🌍
Explore why AWS continues to lead the global cloud market — from innovation to ecosystem depth. - Krutrim Explained: Ola’s Bold Leap Into AI and Cloud Computing Revolution [2025 Update]
Discover how India’s homegrown AI cloud initiative is reshaping the future of intelligent infrastructure. - Network Switch Explained: 7 Powerful Insights for Smarter, Faster Networking in 2025
Learn the role of switches in modern networking and how they impact cloud and data center performance. - Computer Networks: The Complete Guide for 2025
A full-spectrum guide to understanding how networks, servers, and protocols come together in today’s connected world.



