Consider the term dead lock. What do you think of? In computing, a dead lock in OS is one of the more difficult aspects of concurrent processing. A dead lock occurs when two (or more) processes are stuck waiting for resources where none of them can proceed. It’s like two people trying to cross a narrow bridge at the same time who won’t turn back. They are stuck forever.
What is Dead Lock?
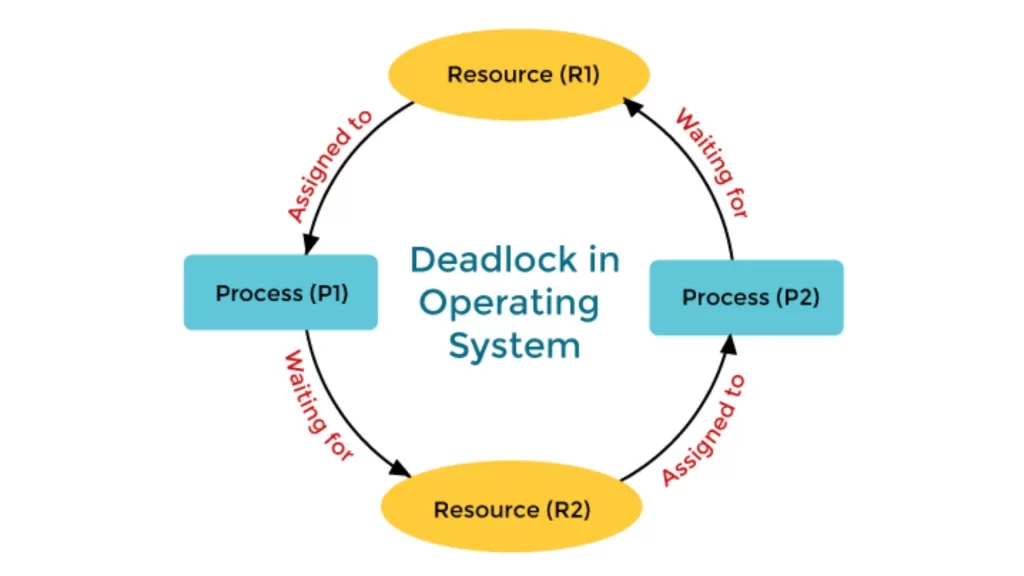
A dead lock in OS occurs when a few processes are blocked because each process holds a resource and is waiting for another resource held by a different process.
💡 Simple Example:
A useful analogy is two people having dinner together. One has a spoon, and the other has a fork. Neither of them has both a spoon and a fork to eat their spaghetti. If neither person gives up their utensil they will stay hungry forever! This is a dead lock in real life.
In operating systems, it happens with resources like the CPU, memory, files or I/O devices.
Dead Lock in OS: Key Characteristics
Four conditions must hold simultaneously:

1. Mutual Exclusion
Only one process can use a resource at a time.
2. Hold and Wait
A process holding at least one resource is waiting to acquire more resources.
3. No Pre-emption
Resources cannot be forcibly taken away; they must be released voluntarily.
4. Circular Wait
Processes form a circular chain, each waiting for a resource held by the next.
👉 If all four are true, dead lock is inevitable.
Real-Life Examples
- Generally being stuck at an intersection – Four cars block each other in a circular fashion and none can move forward.
- The Dining Philosopher’s problem – The classic computer science puzzle where philosophers are able to share forks and that leads to deadlock.
- Two database transactions where each is forever waiting on the other’s locked table of data.
Dead Lock in OS with Resource Allocation Graph

A resource allocation graph (RAG) can be a way to visualize deadlock.
- The processes are represented as circles.
- The resources are represented as squares.
- The edges determine allocation versus request.
Dead Lock Prevention Techniques
To prevent deadlock situation in the operating system, the system attempts to make at least one of the four necessary conditions never hold.

- Remove Mutual Exclusion – Allow resources to be shared (this is not always possible).
- Remove Hold and Wait – Only allow processes to request resources all at once.
- Remove No Pre-emption – Allow the OS to take resources back.
- Remove Circular Wait – Impose a strict ordering of resources.
Dead Lock Avoidance (Banker’s Algorithm)
Alternatively, it can be avoided. Instead of preventing this entirely, the OS checks whether specific allocations will lead to a safe state. The OS will only allocate resources if the state is safe!
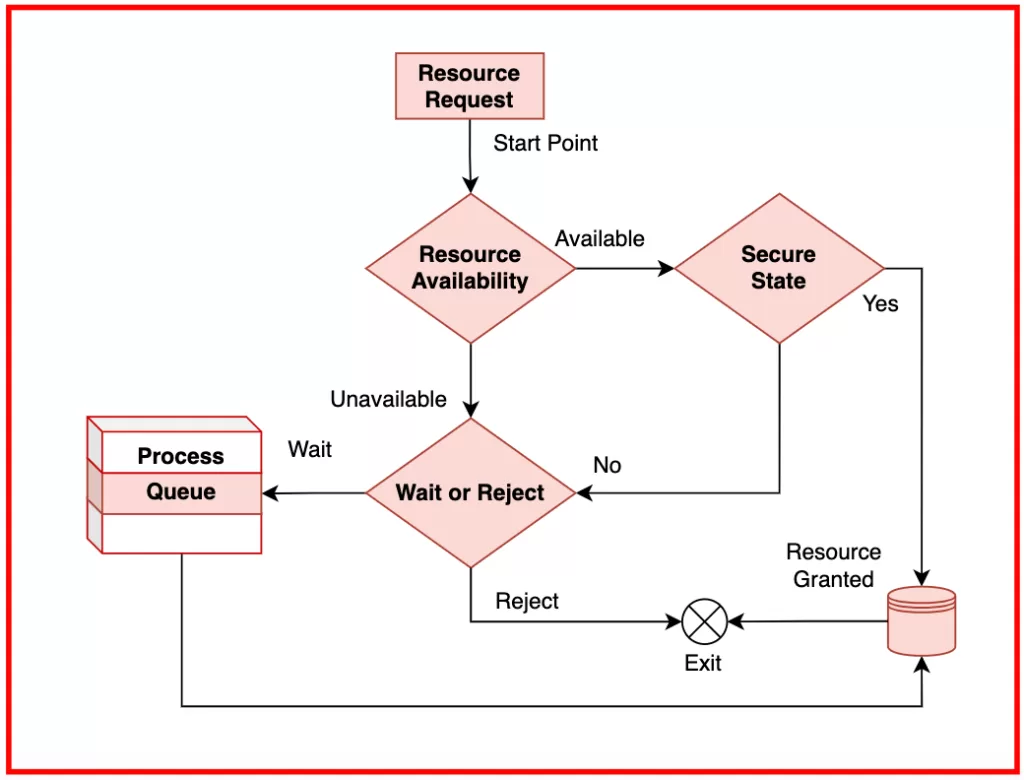
- The most famous algorithm is the Banker’s Algorithm
- The process declared its maximum.
- The system will only allocate resources if it does not lead to a deadlock.
Dead Lock Detection and Recovery
In some instances, the cost of preventing or avoiding this may be impossible, and thus, the OS will let dead lock occur but then will detect and recover it.
Dead Lock Detection: Check resource allocation graph for cycles over time.
Recovery Methods:
- Terminate process.
- Pre-empt resources.
Difference Between Dead Lock, Starvation, and Livelock
- Dead Lock: processes wait forever.
- Starvation: a process is waiting indefinitely for resources because other processes are getting the resources first.
- Livelock: process keeps changing states but is not making any progress.
Why Understanding Dead Lock in OS is Important
Understanding dead lock in an OS is important for:
- Writing efficient concurrent programs.
- Designing resource allocation models.
- Building reliability into the system.
Whether it is in preparation for an exam, an interview, or software development, being educated about dead lock concepts will help you avoid a costly bug or system failures.
Final Thoughts
A dead lock in OS is like a traffic jam for your computing processes, where no process can make any progress and resources are wasted. By learning about prevention, avoidance, detection, and recovery, not only will you prepare yourself to answer those dead lock questions provided in some interviews, but you will also create more reliable systems.
Thus, the next time that you see two processes fighting for a file, or database lock, remember, it may just be another dead lock waiting to happen!!




![Agile Model in Software Engineering [2025]](https://www.wikitechy.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/Agile-Model-in-Software-Engineering-2025-380x220.webp)


