Computers are an irreconcilable part of our daily lives. From giant computers that filled a room to the smartphone in your pocket, the generation of computer reflects one of the fastest technological evolutions in human history.
In this blog, I will guide you through the generation of computer 1st to 5th. I will explain how each generation was unique the technologies that were used and how each generation transformed computing. If you ever wondered how we got from punch cards, to artificial intelligence, this article will bring the ultimate perspective.
What Does “Generation of Computer” Means?
The generation of computer means to describe stages of development/computing. The generations of computing each represent a major technological advancement in computer hardware, software, and architecture. Each generation represented a change in how computers looked and operated and how it transformed industries, businesses, and life.

Computers, while developed and used in many countries, can be noted by five main generations:
- First Generation (1940–1956) – Vacuum Tubes
- Second Generation (1956 – 1963) – Transistors
- Third Generation (1964 – 1971) – Integrated Circuits
- Fourth Generation (1971 – 1980) – Microprocessors
- Fifth Generation (1980’s to present) – Artificial Intelligence
Now let’s take a closer look at each generation.
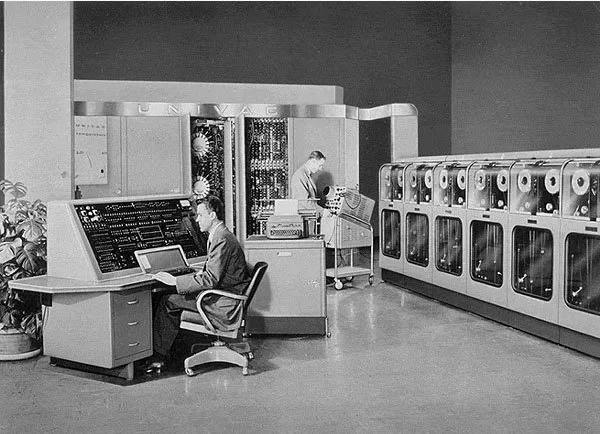
First Generation of Computer (1940–1956): The Beginning
It all began the first generation of computer. These machines used vacuum tubes for digital circuitry and magnetic drums for memory.

Key Features:
- Very large in size, often room-sized
- Extremely expensive to build and maintain
- Consumed a lot of electricity and generated heat
- Input through punch cards and output via printouts
- Slow processing speed
Examples:
- ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer)
- UNIVAC (Universal Automatic Computer)
👉 While bulky and inefficient, these machines laid the foundation of modern computing.
Second Generation of Computer (1956–1963): Rise of Transistors
The second generation of computer used transistors instead of vacuum tubes. Transistors were smaller, faster, and much more reliable than vacuum tubes.

Key Features:
- Much smaller and cheaper than first-generation computers
- More energy-efficient and produced less heat
- Use of assembly language and machine language
- Faster processing power
Examples:
- IBM 1401
- CDC 1604
👉 This was the era when computers began to be used in businesses and industries for the first time.
Third Generation of Computer (1964–1971): Integrated Circuits
The third generation of computer was characterized by the introduction of integrated circuits (ICs). ICs allowed for thousands of transistors to be put onboard a single chip.

Key Features:
- Smaller, faster, more powerful, and more reliable than the second generation
- Development of high-level programming languages like COBOL and FORTRAN
- Lower cost made computers more widely accessible
- More sophisticated operating systems
Examples:
- IBM 360 series
- Honeywell 6000
👉 Computers became commercially viable for wider markets, marking a true technological leap.
Fourth Generation of Computer (1971–1980s): The Microprocessor Revolution
The fourth generation of computer introduced the microprocessor. With microprocessors thousands of integrated circuits were employed in one silicon chip. this paved the way for the personal computer (PC) epoch.

Key Features:
- Extremely compact compared to earlier generations
- Dramatic improvement in processing speed and storage capacity
- Use of graphical user interfaces (GUIs), mouse, and keyboards
- Cheaper and available for households and small businesses
Examples:
- Apple II
- IBM PC
- Commodore 64
👉 This is when computers truly became part of everyday life.
Fifth Generation of Computer (1980s–Present): Artificial Intelligence and Beyond
Fifth generation of computer exists now and is defined by artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and natural language processing (NLP).

Key Features:
- Use of AI-based systems capable of learning, reasoning, and decision-making
- Parallel processing and quantum computing research
- Cloud computing and high-speed internet integration
- Voice recognition, robotics, and advanced user interfaces
Examples:
- IBM Watson
- Google AI systems
- Supercomputers and quantum computers
👉 Fifth-generation computers are shaping the future of technology, from smart assistants like Alexa to self-driving cars.
Comparison Table: Generation of Computer 1st to 5th
| Generation | Period | Technology Used | Size | Examples |
| First | 1940–1956 | Vacuum Tubes | Very Large | ENIAC, UNIVAC |
| Second | 1956–1963 | Transistors | Smaller | IBM 1401, CDC 1604 |
| Third | 1964–1971 | Integrated Circuits | Smaller | IBM 360, Honeywell 6000 |
| Fourth | 1971–1980s | Microprocessors | PC-sized | Apple II, IBM PC |
| Fifth | 1980s–Now | AI, Quantum, Robotics | Compact to Cloud | IBM Watson, Google AI |
Why Is Understanding the Generation of Computer Important?
- Aids our understanding of technology and its development.
- Benefits undergraduate and graduate students in computer science and competitive exams.
- Gives us insights into the manner in which the processing power of computers has fundamentally shaped modern society.
- Helps to situate what we are currently experiencing with AI and quantum computing.
Future Beyond the Fifth Generation
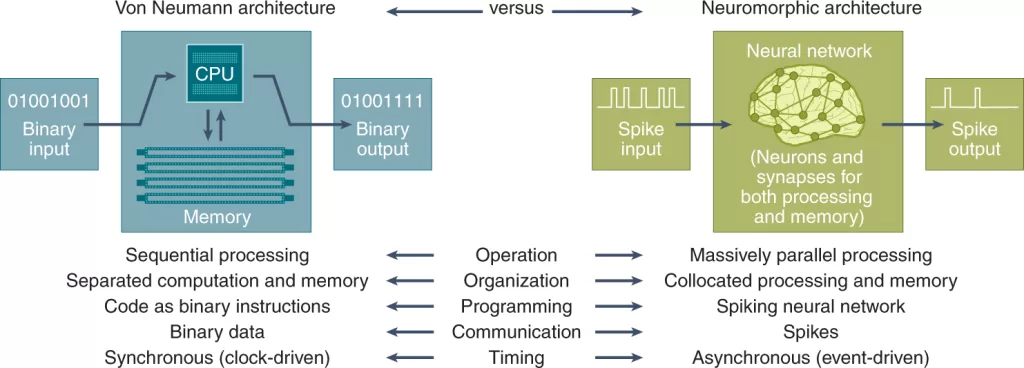
Many futurists suggest that the 6th generation of computer will be based on quantum computing and neuromorphic systems, or systems that are computer systems but modeled after the human brain. It is hard to imagine how the best computers in the world today will look dated.
✅ Final Thoughts
The generation of computer 1st to 5th tells us a compelling story of the human desire to innovate. From room-sized machines using vacuum tubes to systems employing AI to help solve the major problems facing our world today.
For students it is important to understand the generation of computer so they can see where we came from – and helps prepare them for an exciting future!







