When you first hear about “hash in data structure,” you might feel a little overwhelmed. It sounds like a fancy, high-tech term that only computer scientists could understand. But here’s the thing: hashing is actually one of the most fundamental concepts in the world of programming and data management. If you want to get a handle on working with large datasets, solving lookup problems efficiently, or speeding up search queries, understanding hashing will take you a long way.
In this article, I’ll break down hash in data structure into digestible chunks, sharing real-life examples and insights along the way. Whether you’re new to programming or looking to brush up on your knowledge, you’re in the right place. Let’s dive in.
Key Highlights:
- What is Hashing? – The basics and why it matters.
- How Hashing Works – A simple explanation of hash functions and hash tables.
- Real-World Applications – How hashing is used in everything from databases to security.
- Common Hashing Techniques – Exploring various hashing strategies like linear probing and chaining.
- Performance Considerations – Why hash collisions happen and how to avoid them.
What is Hash in Data Structure?

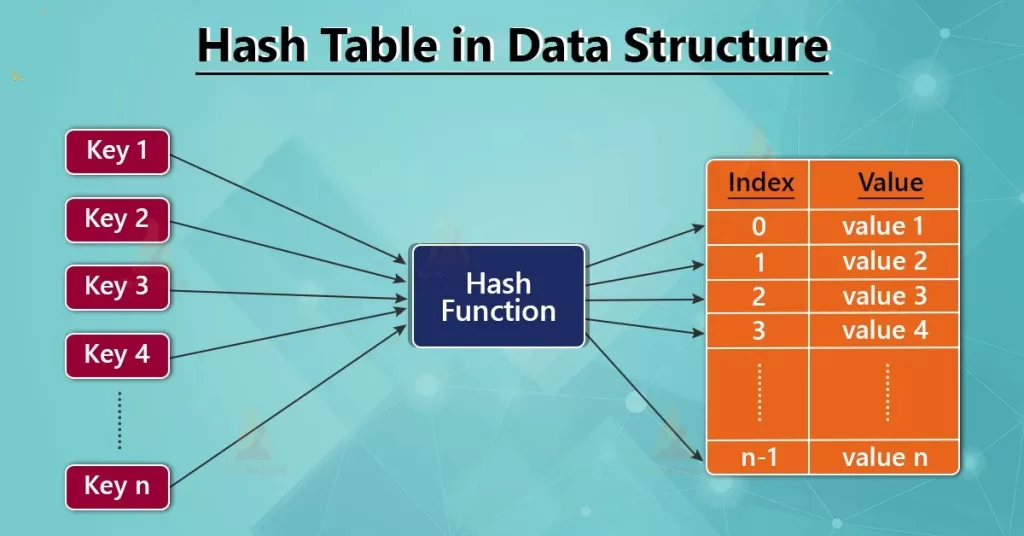
Alright, let’s start with the basics. At its core, hashing in data structure is a way of mapping data from a larger set into a fixed-size value, usually a number. Think of it like a clever shortcut that lets you quickly locate data without having to go through every single item. It’s kind of like using an index in a book—rather than flipping through every page, you just use the index to find what you’re looking for.
This “shortcut” is made possible by a hash function, which transforms an input (like a name or number) into a unique value, called a hash code. When you need to access the data later, the hash code serves as the key to quickly find it in the storage structure.
I’ve seen hashing come into play in databases and in situations where speed is absolutely crucial. Imagine a real-time app where you need to fetch user details based on a unique username. Instead of scanning every user profile one by one, hashing lets you jump straight to the right profile. Speed is everything!
How Does Hashing Work?
Now, you’re probably wondering: how exactly does hash in data structure work? Well, here’s the beauty of it: it’s both incredibly simple and surprisingly powerful.
- Hash Function: You input data (like a name or ID), and the hash function transforms it into a fixed-size number (hash code).
- Hash Table: The hash code is used to determine the position of that data in the hash table (think of it like a giant array). The idea is to store your data at the position indicated by the hash code.
- Retrieving Data: When you need the data later, you simply reapply the hash function to your search key (e.g., the username) and go straight to the position in the table.
Example: Let’s say you’re building a system to store user profiles based on usernames. A hash function like SHA-256 could take a username (say, “john_doe”) and return a hash code. The system uses that code to determine the index where the profile data should go.
Why Should You Care About Hashing?
Let me tell you, hash in data structure is more than just a cool concept you read about in textbooks. It’s in your everyday apps. Ever used a password manager? Yup, hashing is there. Browsing through Twitter or Instagram? They use hashing for their search and data retrieval processes.
In fact, it’s hard to find an area of tech that doesn’t rely on hashing in some way. Whether it’s file indexing, load balancing, or even data integrity checks like checksums—hashing is always lurking in the background.
Real-Life Application of Hashing:
- Database Management: In SQL and NoSQL databases, hashing helps locate rows or records without a complete scan.
- Cryptography: Hash functions are used to securely store passwords. Websites don’t store your actual password; they store a hashed version of it, making it harder for attackers to retrieve the original value.
- Distributed Systems: Hashing is widely used in load balancing (distributing workloads across multiple servers) and sharding (dividing large datasets).

Common Hashing Techniques
If you’ve heard of collisions in hashing and wondered what the fuss was about, let me explain.
A hash collision occurs when two different inputs produce the same hash value. Imagine if two people had the same exact hash code for their username. Not ideal, right? Fortunately, there are a couple of ways to handle this:
- Linear Probing: This is a technique where, if a collision occurs, the system checks the next available space in the hash table and places the data there. It continues checking subsequent spaces until it finds an empty one.
- Chaining: Another common approach is chaining, where each position in the hash table points to a linked list of entries that share the same hash code. It’s like having a “backup list” for each table slot.
Let’s use an example:
- Suppose we are storing book titles using hashing.
- The title “Harry Potter” and “Half-Blood Prince” might both get hashed to the same index. With linear probing, we’d move to the next available spot in the table. With chaining, we’d link these two book titles together at the same index, preventing data loss.

The Performance Considerations: Why Hash Collisions Happen
Here’s the thing: hash collisions are inevitable when you’re working with large datasets. The more data you store, the higher the chance two inputs will produce the same hash value. But don’t panic—there are strategies to minimize the impact.
- Load Factor: The load factor refers to the ratio of entries in the table to the size of the table. A high load factor increases the likelihood of collisions. By resizing the hash table (also known as rehashing) when it reaches a certain threshold, you can keep things running smoothly.
- Good Hash Function: A good hash function evenly distributes data across the hash table, reducing the likelihood of collisions. Think of it like creating a more efficient sorting algorithm for your data.

Why Hashing Should Be Your New Best Friend
By now, I hope you’re starting to see why hash in data structure is so crucial. From search optimization to secure data storage, hashing is a technique that touches almost everything we do with data. It’s fast, efficient, and—once you get the hang of it—something you’ll use constantly.
Here’s the deal: if you’re a software developer, you’re going to encounter hashing often. Whether you’re designing a search algorithm, optimizing a database, or building a secure login system, hashing will be in the mix. Understanding the ins and outs of hashing can make you a better, more efficient programmer.
Final Thoughts:
At first glance, hash in data structure might sound complex and abstract. But once you break it down, it’s actually one of the most practical and useful tools in the programmer’s toolbox. It’s like learning how to ride a bike—you might stumble at first, but once you get the hang of it, you’ll be cruising.
Want to learn more ??, Kaashiv Infotech Offers Data Analytics Course, Data Science Course, Cyber Security Course & More Visit Their Website www.kaashivinfotech.com.