what are the functions of operating system
If you’ve ever wondered what are the functions of operating system, think of it as the invisible manager running your computer or phone. The OS is the bridge between you and the hardware — it makes sure your apps launch, your files save correctly, and your system doesn’t crash when you open too many tabs.
In simple terms, the functions of operating system go beyond just “turning on the computer.” They include managing processes, memory, files, devices, and security — the very backbone of modern computing. Whether you’re preparing for exams, cracking technical interviews, or building a career in IT, understanding these OS functions is non-negotiable.
And here’s the best part: the same principles apply whether you’re working with Windows, Linux, macOS, or Android. By the end of this guide, you’ll know not only the main functions of operating system, but also how they matter in today’s world of cloud computing, mobile apps, and AI-driven systems.

🔑 Key Highlights
- ✅ Learn the 11 main functions of operating system with real-world use cases.
- 📌 Covers process, memory, file, device, and security management — simplified.
- 🚀 Updated for 2025: cloud-native OS, mobile platforms, AI-driven optimization.
- 🎓 Perfect for students, developers, and IT career aspirants.
🔹 1. Process Management
At its core, process management in operating system is about making sure every running program (process) gets a fair share of the CPU and resources. Imagine you’re streaming a movie, downloading a game update, and typing notes — all at the same time. Without process management, your system would freeze or give all attention to one task, leaving the others to starve.
📌 Key Functions of Process Management
- Process Scheduling 🕒
The OS decides which process runs when. Algorithms like Round Robin (used in time-sharing systems) or Priority Scheduling ensure no program is left behind. For example, your Spotify music playback doesn’t stop just because your antivirus starts scanning. - Process Synchronization 🔗
When multiple processes need the same resource (say, two apps writing to the same file), the OS steps in to coordinate. It uses locks, semaphores, and monitors to prevent race conditions. Without this, you’d end up with corrupted files or apps crashing randomly. - Deadlock Handling 🚫
A deadlock is when processes block each other forever, like two cars stuck on a one-lane bridge. The OS avoids this by smart resource allocation and can even recover by killing or rolling back processes. - Inter-Process Communication (IPC) 💬
Ever noticed how a browser lets a PDF viewer open directly inside it? That’s IPC at work — processes exchanging data smoothly, using shared memory or message passing.

💡 Real-World Insight
Developers often face issues like “thread starvation” or “race conditions” when writing code. Interviewers love to ask how operating systems prevent these problems. A solid grasp of process management shows that you not only understand theory but can also apply it when designing reliable software.
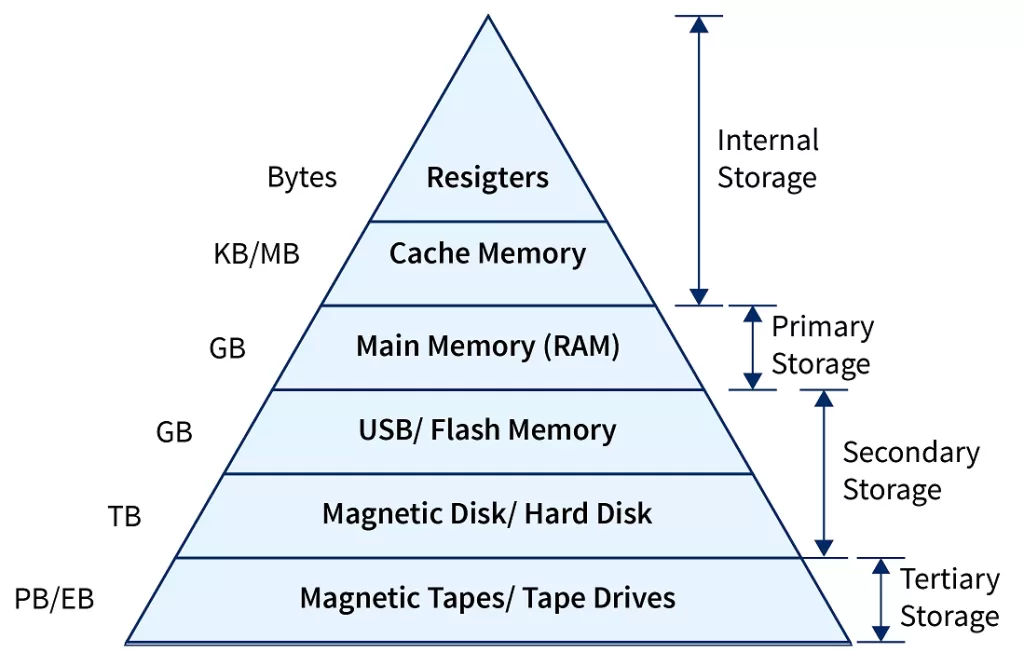
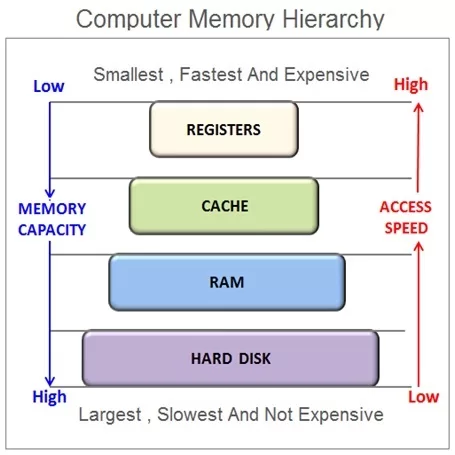
🔹 2. Memory Management
RAM is precious — especially when you have 20 Chrome tabs open. The OS manages memory so apps don’t overwrite each other’s data.
📌 Key Roles:
- Allocation & Deallocation: Assigns memory when a process starts, frees it when done.
- Virtual Memory: Lets you run programs larger than your RAM by using disk space.
- Protection: Prevents one program from touching another program’s memory.
- Fragmentation Handling: Organizes memory efficiently, reducing wasted space.
💡 Real-world example: When you switch between apps on your phone, the OS uses virtual memory and paging to keep apps “suspended” while freeing space for the active one.
🔹 3. File System Management
Imagine saving a document and finding it gone the next day. File management prevents that nightmare. The OS organizes files, directories, and permissions so your data is safe and accessible.
📌 Key Roles:
- File Attributes: Stores names, sizes, types, and permissions.
- File Operations: Create, read, write, delete.
- Access Methods: Sequential, direct, and indexed access.
- File Protection: Controls who can read, write, or execute.
💡 2025 update: Cloud-based OS like ChromeOS integrates with cloud storage so files are synced automatically across devices.

🔹 4. Device Management (I/O Management)
Every time you print a file, plug in a USB drive, or stream music, the OS handles the communication between hardware and software.
📌 Key Roles:
- Device Drivers: Special programs that let the OS talk to hardware.
- Buffering & Caching: Smooths out speed differences between CPU and devices.
- Spooling: Queues tasks (like print jobs) so the CPU isn’t stuck waiting.
💡 Example: On your phone, when you snap a picture, the OS buffers it in memory before saving it to storage. That’s device management in action.

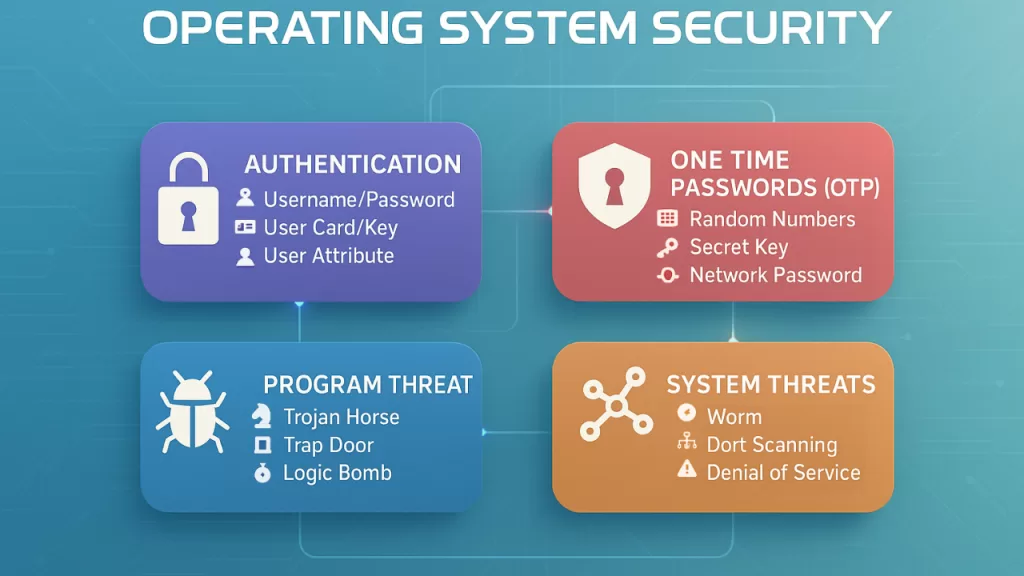
🔹 5. Protection & Security
With rising cyber threats in 2025, this is one of the most critical OS functions.
📌 Key Roles:
- Access Control: Ensures only authorized apps and users can access resources.
- Authentication: Verifies users with passwords, biometrics, or tokens.
- Resource Protection: Keeps files, memory, and devices safe from misuse.
- Defense Against Attacks: Shields against malware, ransomware, and phishing attempts.
💡 Real-world example: On Android and iOS, apps are sandboxed — meaning each app runs in its own safe space, protecting your data from malicious apps.
🔹 6. Performance Monitoring
The OS constantly tracks system performance — response time, throughput, and bottlenecks. It adjusts resource allocation to keep everything smooth.
💡 Example: Windows Task Manager or Linux top command shows real-time CPU and memory usage.
🔹 7. Job Accounting
In enterprise environments, the OS records how much CPU time, memory, or disk space each user or process consumes.
💡 Career tip: Cloud providers like AWS and Azure rely heavily on job accounting to bill customers accurately.
🔹 8. Error Detection & Handling
No system is perfect. When something goes wrong, the OS logs errors, generates dumps, and displays alerts.
💡 Example: That dreaded “Blue Screen of Death” on Windows is the OS catching a fatal error before damage spreads.
🔹 9. Networking Support
Modern OS functions also include networking — managing Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Ethernet, and VPN connections.
💡 2025 update: With 5G and edge computing, operating systems now optimize connections for low latency and energy efficiency.
🔹 10. Cloud & Virtualization Support 🌐
Operating systems now run not just on devices, but in the cloud. They support virtualization so multiple OS instances can run on the same hardware.
💡 Example: Kubernetes acts as an OS for containers, scheduling workloads across clusters.
🔹 11. User Interface (UI)
Finally, the OS provides a user interface — graphical (Windows, Android, macOS) or command-line (Linux). Without it, you’d still be typing binary codes.
🔹 FAQs About OS Functions
Q1: What are the 5 basic functions of operating system?
👉 Process management, memory management, file system management, device management, and security.
Q2: What are the 11 functions of the operating system?
👉 The ones covered in this article: from process management to UI support.
Q3: Which operating system is most used in 2025?
👉 Windows dominates desktops, Android dominates mobile, while Linux leads in servers and cloud infrastructure.
Q4: Why is security such a big deal in modern OS?
👉 Because OS is the first line of defense against malware, data theft, and system crashes.
🔹 Conclusion
The functions of operating system are the unsung heroes of modern computing. They keep your apps running, your files safe, your memory optimized, and your system secure.
In 2025, the OS is no longer limited to personal computers. It powers phones, cloud servers, IoT devices, and even AI platforms. Whether you’re a student, a developer, or an IT professional, understanding these functions will not only help you clear exams and interviews but also make you a smarter tech user.







