Vulnerability Analysis in Ethical Hacking
What is Vulnerability ?
It is defined as an issue in the software code that a hacker can exploit to damage the systems. It can be a gap in the execution of cyber security events or a weakness in the controls.
Table Of Content
- What is Vulnerability ?
- Examples of Vulnerability
- What is Vulnerability Analysis ?
- Objectives of the Vulnerability analysis
- Importance of Vulnerability Analysis
- Steps for the vulnerability Analysis
- Step 1 : Assess Critical Value of each device
- Step 2: Detailed of the Installed systems
- Step 3: Vulnerability Scanning
- Step 4: Report Creation
- Types of Vulnerability Assessment
- Models of Vulnerability in Ethical Hacking
- Protection from Hacking
Examples of Vulnerability
- Illegal network access by Hackers due to a weak Firewall
- Cracking of Wi-Fi Passwords
- Misconfiguration of passwords
- Insecure cryptographic storage
- Exposure of sensitive data due to lack of application security
What is Vulnerability Analysis ?
It is the next phase of Ethical hacking to find the security holes or vulnerabilities in your system or network.
A vulnerability assessment is a process of defining, identifying, classifying and prioritizing vulnerabilities in systems, network infrastructures, and applications.
This process provides organizations with the knowledge to know threats to their environment and react consequently which provides a way to detect and resolve security problems by ranking the vulnerabilities before someone or something can exploit them. It is important for the security of the organization.
Objectives of the Vulnerability analysis
- To identify vulnerabilities – Configuration, system, Design, Code, Process
- Supporting the vulnerabilities
- Preparation of guidance to mitigate the vulnerabilities
Importance of Vulnerability Analysis
- Deep dive visions of the security issues
- Helps us know the risks related with the entire ecosystem
- For security breaches
- Assets that are prone to cyber attacks
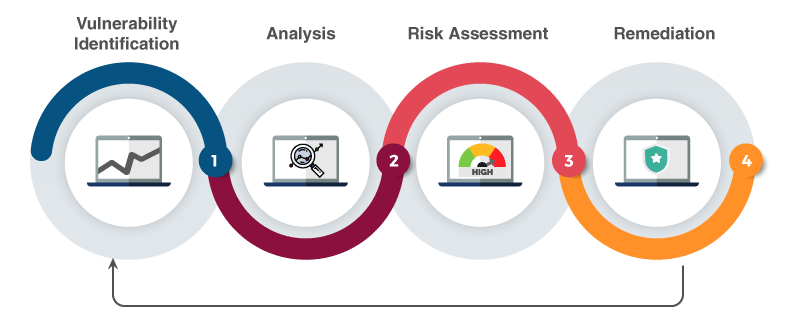
Steps for the vulnerability Analysis
Step 1 : Assess Critical Value of each device
- Review all the devices in the network
- Who are the people accessing the devices
- Capture the below information
- Risk Impact
- Risk threshold
- Risk strategy planning
- Mitigation
- Business Impact Analysis
Step 2: Detailed of the Installed systems
- Systems – What they do
- For whom the devices are installed
- Review – Device open ports
- Configuration of the devices
- Drivers of the devices which are certified
- Device vendor, version details
- Software installed on the devices
Step 3: Vulnerability Scanning
- Compilance requirements checking
- Scan policy formation
- Scanning – Single or Multiple time
Step 4: Report Creation
- Vulnerability name
- Vulnerability Discover date
- Common Vulnerabilities
- Risk Score,Systems affected
- Method to fix them
Types of Vulnerability Assessment
Network Based Scans
- To identify network vulnerabilities. This scan helps to find the weak systems in the wired and wireless networks
Host Based Scans
- To identify vulnerabilities in the ports, configuration, server workstations, other hosts and patch history
Wireless Network Scans
- Complete scan on wireless networks to find the vulnerabilities
Application Scans
- To test all gateways and mobile applications for vulnerabilities
Database Scans
- To scan all the databases for potential vulnerabilities.
Models of Vulnerability in Ethical Hacking
Firewall model
- Insider attacks – A Outside firewall should be decided and this can take care of the outside attacks
- Missed security patches
- When the patch management of firewall has not happened
- Configuration issues
- If there are faults in the configuration of firewall
- DDOS attacks
- Only allow genuine traffic to avoid these attacks
Password model
Dictionary, Hybrid model and Brute force is used to crack the password by the hacker.
Logical Bombing
When the hacker uses a malicious code to inject the web application or the cloud infrastructure
Web Hijacking
when an unauthorized user tries to access the application bypassing the authorization mechanism
Protection from Hacking
Here are the steps to prevent hacking
- Updating of Operating systems
- Installation of the proper firewall to prevent intrusion
- Destroying all personal information from all the web sources
- No use of Open Wi-Fi
- Password – Strong password which is not easy to find out
- Smart emailing – Avoid opening of phishing mails
- Keep the sensitive data in the protected environment
- Ignore spam
- Shut down the systems after use
- Secure the network
- Back up the data

