Aggregation in Java
What is Aggregation ?
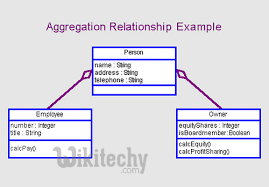
- Aggregation in Java is a relationship between two classes that is best described as a "has-a" and "whole/part" relationship. It is a more specialized version of the association relationship.
- The aggregate class contains a reference to another class and is said to have ownership of that class. Each class referenced is considered to be part of the aggregate class.
- If Class A contains a reference to Class B and Class B contains a reference to Class A then no clear ownership can be determined and the relationship is simply one of association.
Learn Java - Java tutorial - Aggregation in Java - Java examples - Java programs
Example :
- Student class that stores information about individual students at a school. You want to assume a Subject class that holds the details about a particular subject (e.g., history, geography).
- If the Student class is defined to contain a Subject object then it can be said that the Student object has-a Subject object. The Subject object also makes up part of the Student object after all, there is no student without a subject to study. The Student object, therefore, owns the Subject object.
public class WikitechySubject {
private String name;
public void setName(String name)
{
this.name = name;
}
public String getName()
{
return name;
}
}
public class WikitechyStudent {
private Subject[] studyAreas = new Subject[10];
}
Why we need Aggregation ?
- There are two other classes College and Staff along with above two classes Student and Address. In order to maintain Student’s address, College Address and Staff’s address we don’t need to use the same code again and again.
Student Has-A Address (Has-a relationship between student and address)College Has-A Address (Has-a relationship between college and address)Staff Has-A Address (Has-a relationship between staff and address)
- Here, we can improve code re-usability by using Aggregation relationship.
- So if I have to write this in a program, I would do it like this:
class Address{
int streetNum;
String city;
String state;
String country;
Address(int street, String c, String st, String coun)
{
this.streetNum=street;
this.city =c;
this.state = st;
this.country = coun;
}}class StudentClass{
int rollNum;
String studentName;
//Creating HAS-A relationship with Address class
Address studentAddr;
StudentClass(int roll, String name, Address addr){
this.rollNum=roll;
this.studentName=name;
this.studentAddr = addr;
}
...}class College{
String collegeName;
//Creating HAS-A relationship with Address class
Address collegeAddr;
College(String name, Address addr){
this.collegeName = name;
this.collegeAddr = addr;
}
...}class Staff{
String employeeName;
//Creating HAS-A relationship with Address class
Address employeeAddr;
Staff(String name, Address addr){
this.employeeName = name;
this.employeeAddr = addr;
}
...}
- We didn’t write the Address code in any of the three classes, we simply created the HAS-A relationship with the Address class to use the Address code.
