java tutorial - Java LinkedHashMap class - java programming - learn java - java basics - java for beginners
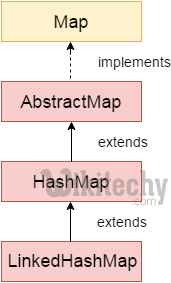
Java LinkedHashMap class is Hash table and Linked list implementation of the Map interface, with predictable iteration order. It inherits HashMap class and implements the Map interface.
The important points about Java LinkedHashMap class are:
- A LinkedHashMap contains values based on the key.
- It contains only unique elements.
- It may have one null key and multiple null values.
- It is same as HashMap instead maintains insertion order.
LinkedHashMap class declaration
Let's see the declaration for java.util.LinkedHashMap class.
public class LinkedHashMap<K,V> extends HashMap<K,V> implements Map<K,V> click below button to copy the code. By - java tutorial - team
LinkedHashMap class Parameters
Let's see the Parameters for java.util.LinkedHashMap class.
- K: It is the type of keys maintained by this map.
- V: It is the type of mapped values.
Learn java - java tutorial - linked-hashmap - java examples - java programs
Constructors of Java LinkedHashMap class
| Constructor | Description |
|---|---|
| LinkedHashMap() | It is used to construct a default LinkedHashMap. |
| LinkedHashMap(int capacity) | It is used to initialize a LinkedHashMap with the given capacity. |
| LinkedHashMap(int capacity, float fillRatio) | It is used to initialize both the capacity and the fillRatio. |
| LinkedHashMap(Map m) | It is used to initialize the LinkedHashMap with the elements from the given Map class m. |
Methods of Java LinkedHashMap class
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Object get(Object key) | It is used to return the value to which this map maps the specified key. |
| void clear() | It is used to remove all mappings from this map. |
| boolean containsKey(Object key) | It is used to return true if this map maps one or more keys to the specified value. |
Java LinkedHashMap Example
import java.util.*;
public class TestCollection14{
public static void main(String args[]){
LinkedHashMap<Integer,String> hm=new LinkedHashMap<Integer,String>();
hm.put(100,"Amit");
hm.put(101,"Vijay");
hm.put(102,"Rahul");
for(Map.Entry m:hm.entrySet()){
System.out.println(m.getKey()+" "+m.getValue());
}
}
} click below button to copy the code. By - java tutorial - team
Output
100 Amit
101 Vijay
102 RahulJava LinkedHashMap Example:remove()
import java.util.*;
public class LinkedHashMapExample {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// Create and populate linked hash map
Map<Integer, String> map = new LinkedHashMap<Integer, String>();
map.put(101,"Let us C");
map.put(102, "Operating System");
map.put(103, "Data Communication and Networking");
System.out.println("Values before remove: "+ map);
// Remove value for key 102
map.remove(102);
System.out.println("Values after remove: "+ map);
}
} click below button to copy the code. By - java tutorial - team
Output:
Values before remove: {101=Let us C, 102=Operating System, 103=Data Communication and Networking}
Values after remove: {101=Let us C, 103=Data Communication and Networking}Java LinkedHashMap Example: Book
import java.util.*;
public class Book {
int id;
String name,author,publisher;
int quantity;
public Book(int id, String name, String author, String publisher, int quantity) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.author = author;
this.publisher = publisher;
this.quantity = quantity;
}
}
public class MapExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Creating map of Books
Map<Integer,Book> map=new LinkedHashMap<Integer,Book>();
//Creating Books
Book b1=new Book(101,"Let us C","Yashwant Kanetkar","BPB",8);
Book b2=new Book(102,"Data Communications & Networking","Forouzan","Mc Graw Hill",4);
Book b3=new Book(103,"Operating System","Galvin","Wiley",6);
//Adding Books to map
map.put(2,b2);
map.put(1,b1);
map.put(3,b3);
//Traversing map
for(Map.Entry<Integer, Book> entry:map.entrySet()){
int key=entry.getKey();
Book b=entry.getValue();
System.out.println(key+" Details:");
System.out.println(b.id+" "+b.name+" "+b.author+" "+b.publisher+" "+b.quantity);
}
}
} click below button to copy the code. By - java tutorial - team
Output:
2 Details:
102 Data Communications & Networking Forouzan Mc Graw Hill 4
1 Details:
101 Let us C Yashwant Kanetkar BPB 8
3 Details:
103 Operating System Galvin Wiley 6