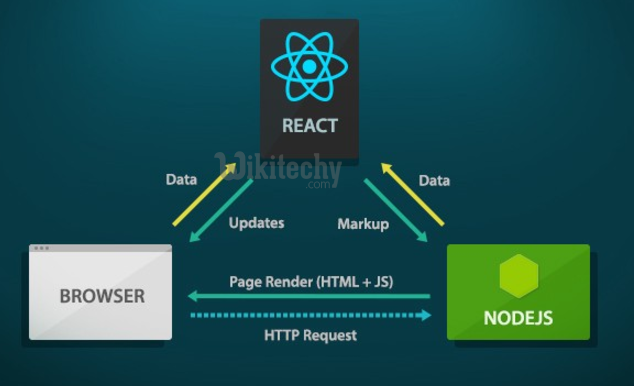
react - React vs Angular - react js - reactjs
Angular JS
- Angular has been around for a while now, with its initial release in 2009. Since then, it’s come a long way, and they’re up to version 1.3.8 now, with semi-regular releases.
- Lately, there’s been some buzz about Angular 2.0, which is going to change a lot about the framework, but it’s a long way off, and is scheduled for release sometime in 2016.
- The current Angular version uses various attributes and custom HTML elements to provide functionality on various DOM elements. These are called directives and are very versatile.
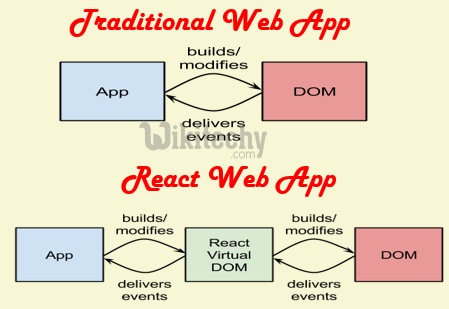
learn reactjs - reactjs tutorial - virtual dom
- reactjs example - react tutorial - reactjs - react
Here’s a breakdown of what we’re doing with the JavaScript.
- First, we’re initializing the Angular app by calling angular.module and giving it a name. The second argument in this call is the list of dependencies our module relies on. Since we don’t have any dependencies, we pass in an empty array.
- Next, we’re initializing the testController Angular controller. It’s not doing anything at the moment as our directive is handling all the “heavy” lifting.
- Finally, the directive is defined. All it’s doing is writing out a div containing the hello world text.
- An Angular app requires that the ng-app and ng-controller directives be set on various elements.
various elements rundown :
- The html tag has the aforementioned ng-app directive applied to it, indicating that the page reflects an Angular application named “testApp”.
- The body tag is annotated with the ng-controller directive, which tells Angular that the controller’s scope should reside within it.
- Finally, we’re rendering our hello-world directive as the only code in the body.
Article tag : react , react native , react js tutorial , create react app , react tutorial , learn react
React JS
- A lot of the heavyweight contenders for MVVM frameworks have a hard time rendering large amounts of data, like in lists and such.
- React doesn’t have that problem, as it renders only what’s changed.
- For example, if a user is viewing a list of 100 items rendered with React, and he or she changes the third one down somehow, only that item gets rerendered, leaving the other 99 items unchanged.
- It also uses what Facebook calls a “virtual DOM” for some increased performance by writing out a full render virtually, and then checking the difference between the virtual render and what’s actually on the DOM and creating a patch.
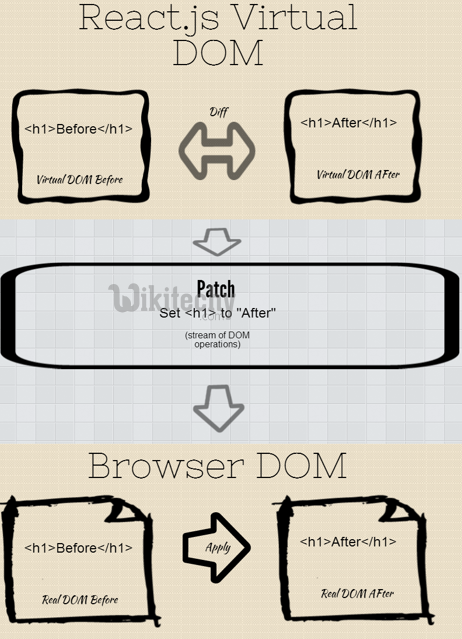
- React builds a new virtual DOM subtree
- Diff it with the old one
- Computes the minimal set of DOM mutations and puts them in a queue
- Batch executes all updates
- Note: React classes can be built in one of two ways: in raw JavaScript or in JSX, a language that combines HTML and JavaScript in one file format. I’m using JSX in the JavaScript sections of the examples below. If you’d like some more information, here’s the documentation.
Article tag : react , react native , react js tutorial , create react app , react tutorial , learn react
React requires that you build a class to define what HTML to render.
- We call React.createClass to (unsurprisingly) create a React class. This class is what gets rendered later on to be appended into an HTML element for the user to interact with.
- The createClass function takes an object which needs to contain a renderfunction, which is all that’s in our simple class so far. It returns a very simple JSX string to write out hello world.
- The last line of the JSX is used to render our hello world class into the document.body.
- The HTML for the React section isn’t noteworthy at all, and won’t change throughout this article, so you can stop looking at it.
Article tag : react , react native , react js tutorial , create react app , react tutorial , learn react
Mongodb Express Angularjs Nodejs (MEAN stack) :
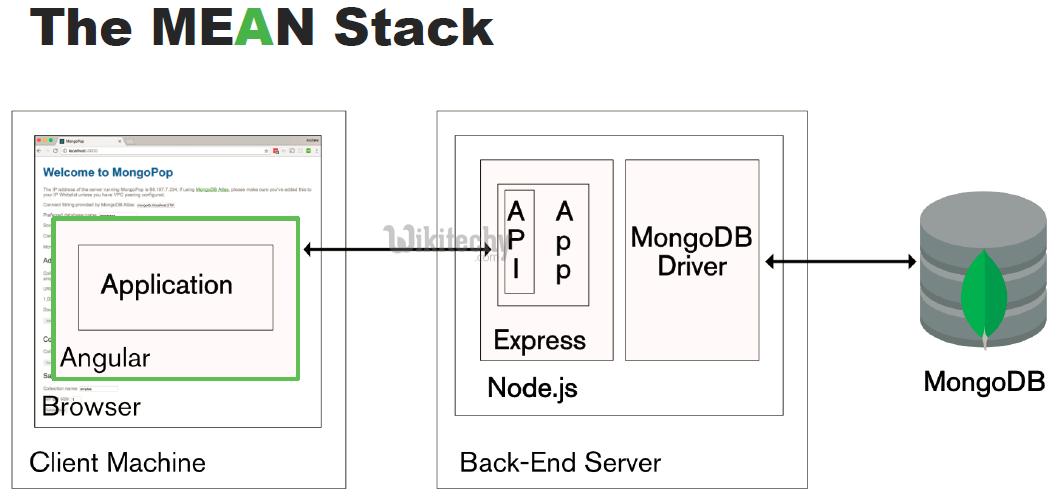
Article tag : react , react native , react js tutorial , create react app , react tutorial , learn react
Mongodb Express Reactjs Nodejs (MERN stack) :
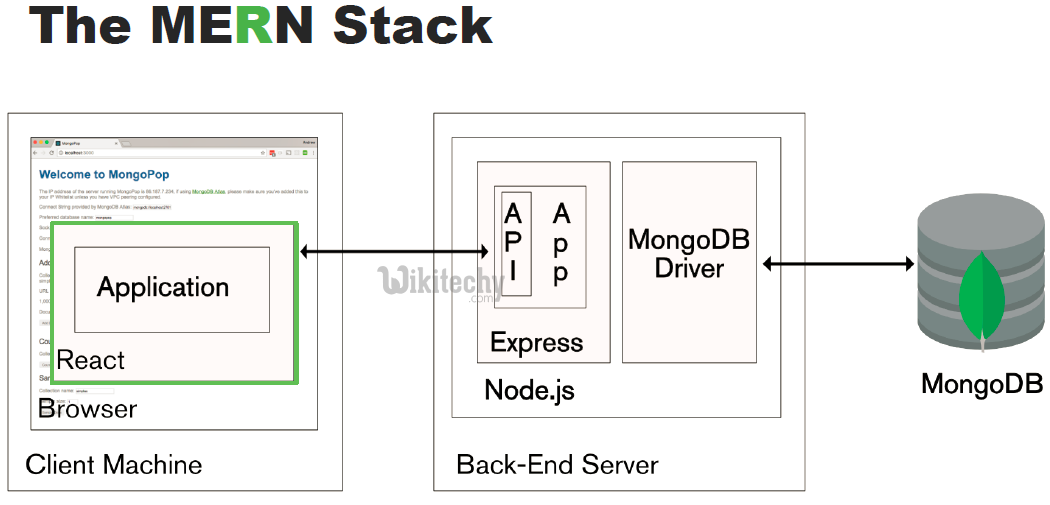
Article tag : react , react native , react js tutorial , create react app , react tutorial , learn react
Component data flow in reactjs :
- setState()
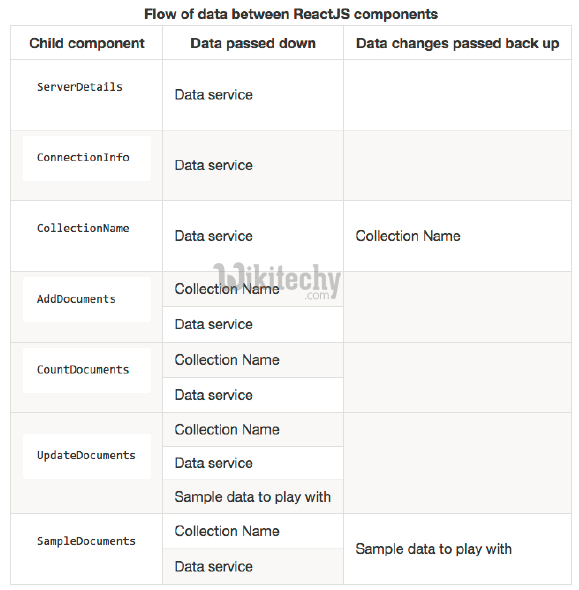
Component data flow :
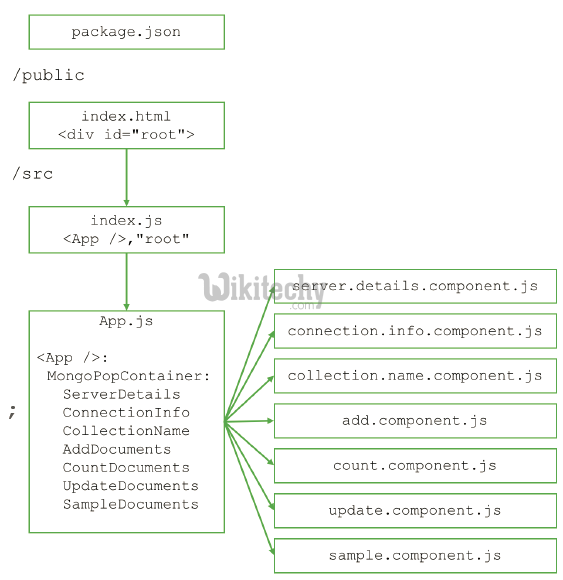
< div id="root"></div >click below button to copy the code. By reactjs tutorial team
import App from './App';
ReactDOM.render(
<App />,
document.getElementById('root'));click below button to copy the code. By reactjs tutorial team
import { CollectionName } from './
collection.name.component';
class MongoPopContainer
extends React.Component {
handleCollectionChange(collection) {
this.setState({MongoDBCollectionName:
collection});
}
render() {
return (
<CollectionName
dataService={this.dataService}
onColl={this.handleCollectionChange}
/>
)}
}
class App extends Component {
render(){return (
<MongoPopContainer />)}click below button to copy the code. By reactjs tutorial team
handleCollectionNameChange(event) {
this.setState({collection:
event.target.value});
this.props.onColl(event.target.value);
}
render() {
return (
<label>
Choose the collection:
<input type="text" size="20"
value={this.state.collection}
onChange={
this.handleCollectionNameChange}
/>
</label>) click below button to copy the code. By reactjs tutorial team
Angularjs vs Backbonejs vs Reactjs :
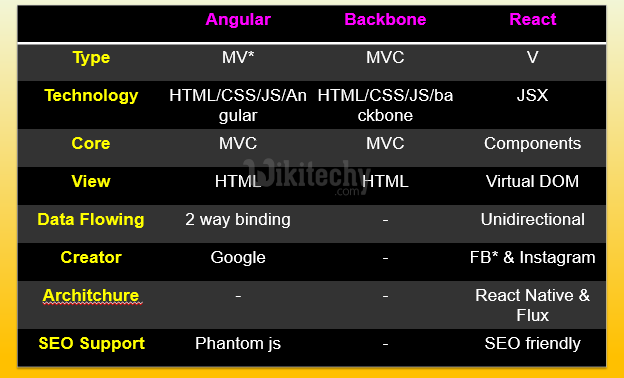
Injecting Data - AngularJS vs ReactJS
Angular JS
- The method Angular uses to inject data into directives is via scopes.
- A scope in the Angular world is just an object which contains data for various controls, like directives and controllers.
- On top of that, there’s a root scope object (injected with $rootScope) that functions as a top-level scope accessible by all other Angular components.
- A directive can have one of a few kinds of scope. First, there’s no directive scope, which means that it uses its parent’s scope (usually the controller’s scope).
properties come in three different flavours:
- Two-way binding: Indicates that changes made on either the parent or child scope are reflected in the other. It’s denoted by an equals sign (=) when building the scope.
- One-way binding: Data flows only from child to parent via a function. Denoted by an ampersand (&).
- Text binding: Just a string value that contains no binding information. Denoted by an at symbol (@).
React JS
- React injects data into its rendered views at construct time, be that when the root view is created or via a nested view. Inside the class, the data that’s passed in is accessed via the props property of the current context.
- We’ve added a { name: "Chris Harrington" } to the creation of our HelloWorldclass, which gets translated into the props property inside the class.
- The JSX now includes a reference to this.props.name so we can render a personalized hello message.
Article tag : react , react native , react js tutorial , create react app , react tutorial , learn react
Event Handlers - AngularJS vs ReactJS
Angular JS
- The ng-click directive is an attribute that can be placed on HTML elements that hooks up a click handler that already exists on the local scope.
- We’ve added a button to our directive template, which sets our greeting message on click. It has the ng-click directive set to fire the greet method.
- The link section to the directive has been added. This section is fired when the directive is rendered and is used to set up things like event handlers and default values, both of which are occurring here.
- The greeting property has been set to the empty string on the scope, and we’ve added a basic event handler (greet) to handle the button click.
React JS
- Event handlers in React work by setting various custom attributes on the HTML elements you’re building. Most of the common culprits have associated handlers.
- The getInitialState function is used to determine the initial state of the view. Without it, this.state will return null, potentially breaking the view. If you’re going to set any state during the operation of your class, you need to add this method. In our example, we’re just setting the greeting state property to the empty string.
- We’ve added a greet function to act as the event handler after the user has clicked on the button.
- Speaking of which, we’ve added a button to the HTML and are using React’s onClick event to hook up the handler, which is the greet function of the context.
Article tag : react , react native , react js tutorial , create react app , react tutorial , learn react
Nested Views - AngularJS vs ReactJS
Angular JS
- Nested views in Angular are accomplished using multiple directives. One directive can contain a reference to another without any problems.
- It’s worth noting that each of these directives can have their own isolated scope, and any level of nested directives will also have their own scopes.
- Angular uses the idea of transclusion to render child elements from a directive.
- Transclusion is a little complicated, so here’s the documentation if you need it. Here’s a quick example:
- Here, I’ve created a wrapper directive which (unsurprisingly) wraps our hello-worlddirective by adding some padding and a gray background colour. So, what’s changed in the code?
- First, some house keeping. I’ve moved the templates into script tags in our HTML to keep things neat. In our directive initialization, I’m now grabbing the template HTML from these script tags.
- There’s now a CSS class to set the style of the wrapper. Just a background and some padding; nothing fancy.
React JS
- Nested elements in React are much easier to put together, at least in my opinion. It’s as easy as declaring the various classes, and then referencing the child class in the render method of the parent class.
- Like in the Angular example, we’ve wrapped up the meat of our HelloWorld HTML in a new Wrapper class, which again provides a background colour and some padding.
- The Wrapper class comes before the HelloWorld class because it’s required in the HelloWorld‘s render method. It’s not necessary to do it this way, but I like it as it gives a natural order to where your classes sit.
- The Wrapper‘s render method contains a single div with a CSS class specified to give our wrapper the background and padding. Inside that div is a reference to a special variable: this.props.children.
- This variable contains all inner elements of the class when rendered in another class. Our HelloWorld class has the important parts of our greeting HTML inside the Wrapper, so that’s what gets rendered as a result of a call to the children props variable.
- Our HelloWorld class now contains a reference to the Wrapper class so as to provide the wrapping container.
Loops - AngularJS vs ReactJS
- Both Angular and React provide methods for rendering views by looping over some data. With Angular, it’s accomplished via the built-in ng-repeat directive. In React, nothing special is required, as we can just loop over various HTML elements and put them into an array; a benefit of using JSX.
Angular JS
- Here, we’re making use of the ng-repeat directive to add three greetings when clicking on the greet button.
- The hello-world directive now has a div after the button which uses the ng-repeat directive. It indicates that the marked div should be repeated for every greeting in the greetings array on the directive’s scope.
- The greet method on the directive’s scope now adds three separate greetings to the greetings array to be rendered on the view.
React JS
- Looping in React is relatively simple, as JSX is just JavaScript, so we can write a simple JavaScript loop to render what we want.
- The render method in the HelloWorld class has been refactored to reference a renderGreetings method, which renders all the greetings in the state. When I first started building React classes, I was under the mistaken impression that only the render method could contain HTML. That’s definitely not the case.
- The greet method now pushes three separate greetings onto the greetingsstate variable.
- The getInitialState method replaces the previous greeting variable with a new greetings variable, which is set to an empty array.
Article tag : react , react native , react js tutorial , create react app , react tutorial , learn react
React with nodejs :