apache hive - HiveQL Select Joins - hive tutorial - hadoop hive - hadoop hive - hiveql
What is Select-Joins in HiveQL ?
- Join queries can perform on two tables present in Hive. JOIN is a clause that is used for combining specific fields from two tables by using values common to each one.
- A JOIN locates related column values in the two tables.
- A query can contain zero, one, or multiple JOIN operations.
- It is more or less similar to SQL JOIN.
- There are different types of joins given as follows:
- JOIN
- LEFT OUTER JOIN
- RIGHT OUTER JOIN
- FULL OUTER JOIN
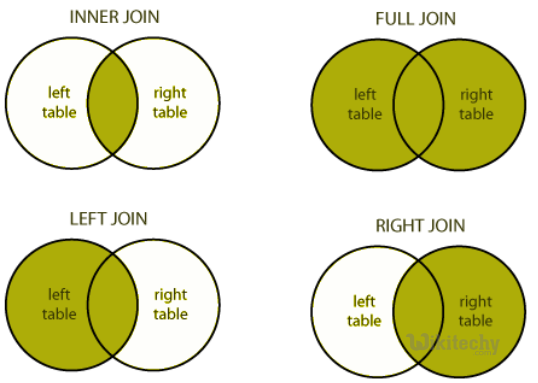
apache hive - learn hive - hive tutorial - different type of joins hiveql select joins - hive example
Syntax:
join_table:
table_reference JOIN table_factor [join_condition]
| table_reference {LEFT|RIGHT|FULL} [OUTER] JOIN table_reference
join_condition
| table_reference LEFT SEMI JOIN table_reference join_condition
| table_reference CROSS JOIN table_reference [join_condition]
Clicking "Copy Code" button will copy the code into the clipboard - memory. Please paste(Ctrl+V) it in your destination. The code will get pasted. Happy coding from Wikitechy hive tutorial team
Example:
We will use the following two tables. Consider the following table named WIKITECHY_CUSTOMERS.
| ID | NAME | AGE | ADDRESS | SALARY |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Arun | 32 | Ahmedabad | 2000.00 |
| 2 | Aarthi | 25 | Delhi | 1500.00 |
| 3 | Boomi | 23 | Kota | 2000.00 |
| 4 | Harikka | 25 | Mumbai | 6500.00 |
| 5 | Dharsanya | 27 | Bhopal | 8500.00 |
| 6 | Komal | 22 | MP | 4500.00 |
| 7 | Mirunalini | 24 | Indore | 10000.00 |
Consider another table WIKITECHY_ORDERS as follows:
| OID | DATE | CUSTOMER_ID | AMOUNT |
|---|---|---|---|
| 102 | 2009-10-08 00:00:00 | 3 | 3000 |
| 100 | 2009-10-08 00:00:00 | 3 | 1500 |
| 101 | 2009-11-20 00:00:00 | 2 | 1560 |
| 103 | 2008-05-20 00:00:00 | 4 | 2060 |
apache hive related article tags - hive tutorial - hadoop hive - hadoop hive - hiveql - hive hadoop - learnhive - hive sql
JOIN Clause :
- JOIN clause is used to combine and retrieve the records from multiple tables.
- JOIN is same as OUTER JOIN in SQL.
- A JOIN condition is to be raised using the primary keys and foreign keys of the tables.
- The following query executes JOIN on the WIKITECHY_CUSTOMER and WIKITECHY_ORDER tables, and retrieves the records:
learn hive - hive tutorial - hive sql datatypes - hive programs - hive examples
hive> SELECT c.ID, c.NAME, c.AGE, o.AMOUNT
FROM WIKITECHY_CUSTOMERS c JOIN WIKITECHY_ORDERS o
ON (c.ID = o.WIKITECHY_CUSTOMER_ID);
Clicking "Copy Code" button will copy the code into the clipboard - memory. Please paste(Ctrl+V) it in your destination. The code will get pasted. Happy coding from Wikitechy hive tutorial team
On successful execution of the query, you get to see the following response:
| ID | NAME | AGE | AMOUNT |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | Boomi | 23 | 2000.00 |
| 3 | Boomi | 23 | 2000.00 |
| 2 | Aarthi | 25 | 1500.00 |
| 4 | Harikka | 25 | 6500.00 |
learn hive - hive tutorial - apache hive - hive sql join - hive examples
learn hive - hive tutorial - apache hive - hive sql join map reduce - hive examples
Hive QL Multiple Tables Join with Map Reduce - Example 3 :
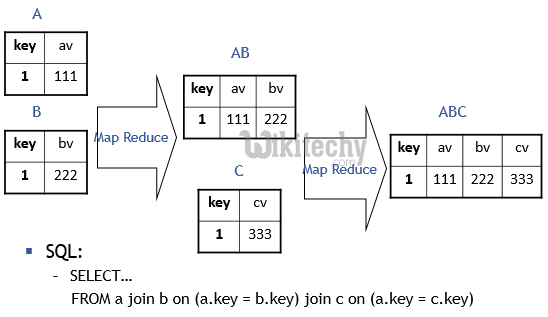
learn hive - hive tutorial - apache hive - hive sql multiple table join map reduce - hive examples
LEFT OUTER JOIN:
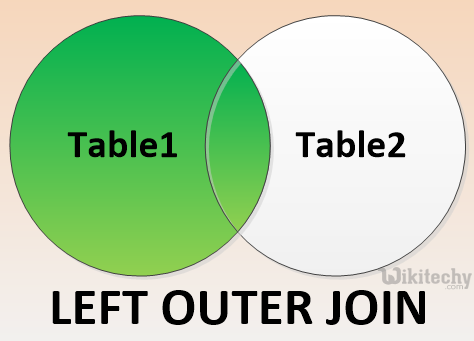
apache hive - learn hive - hive tutorial - left outer join in hiveql select joins - hive example
- The HiveQL LEFT OUTER JOIN returns all the rows from the left table, even if there are no matches in the right table.
- This means, if the ON clause matches 0 (zero) records in the right table, the JOIN still returns a row in the result, but with NULL in each column from the right table.
- A LEFT JOIN returns all the values from the left table, plus the matched values from the right table, or NULL in case of no matching JOIN predicate.
- The following query demonstrates LEFT OUTER JOIN between WIKITECHY_CUSTOMER and WIKITECHY_ORDER tables
hive> SELECT c.ID, c.NAME, o.AMOUNT, o.DATE
FROM WIKITECHY_CUSTOMERS c
LEFT OUTER JOIN WIKITECHY_ORDERS o
ON (c.ID = o.WIKITECHY_CUSTOMER_ID);
Clicking "Copy Code" button will copy the code into the clipboard - memory. Please paste(Ctrl+V) it in your destination. The code will get pasted. Happy coding from Wikitechy hive tutorial team
On successful execution of the query, you get to see the following response:
| ID | NAME | AMOUNT | DATE |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Arun | NULL | NULL |
| 2 | Aarthi | 1560 | 2009-11-20 00:00:00 |
| 3 | Boomi | 3000 | 2009-10-08 00:00:00 |
| 3 | Boomi | 3000 | 2009-10-08 00:00:00 |
| 4 | Harikka | 2060 | 2008-05-20 00:00:00 |
| 5 | Dharsanya | NULL | NULL |
| 6 | Komal | NULL | NULL |
| 7 | Mirunalini | NULL | NULL |
apache hive related article tags - hive tutorial - hadoop hive - hadoop hive - hiveql - hive hadoop - learnhive - hive sql
RIGHT OUTER JOIN:

apache hive - learn hive - hive tutorial - right outer join in hiveql select joins - hive example
- The HiveQL RIGHT OUTER JOIN returns all the rows from the right table, even if there are no matches in the left table.
- If the ON clause matches 0 (zero) records in the left table, the JOIN still returns a row in the result, but with NULL in each column from the left table.
- A RIGHT JOIN returns all the values from the right table, plus the matched values from the left table, or NULL in case of no matching join predicate.
- The following query demonstrates RIGHT OUTER JOIN between the CUSTOMER and ORDER tables.
- notranslate"> hive> SELECT c.ID, c.NAME, o.AMOUNT, o.DATE FROM WIKITECHY_CUSTOMERS c RIGHT OUTER JOIN ORDERS o ON (c.ID = o.WIKITECHY_CUSTOMER_ID);
- On successful execution of the query, you get to see the following response:
| ID | NAME | AMOUNT | DATE |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 | Boomi | 3000 | 2009-10-08 00:00:00 |
| 3 | Boomi | 3000 | 2009-10-08 00:00:00 |
| 2 | Aarthi | 1560 | 2009-11-20 00:00:00 |
| 4 | Harikka | 2060 | 2008-05-20 00:00:00 |
FULL OUTER JOIN:
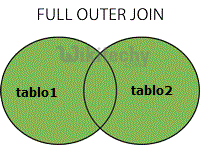
apache hive - learn hive - hive tutorial - full outer join in hiveql select joins - hive example
- The HiveQL FULL OUTER JOIN combines the records of both the left and the right outer tables that fulfil the JOIN condition.
- The joined table contains either all the records from both the tables, or fills in NULL values for missing matches on either side.
- The following query demonstrates FULL OUTER JOIN between WIKITECHY_CUSTOMER and WIKITECHY_ORDER tables:
hive> SELECT c.ID, c.NAME, o.AMOUNT, o.DATE
FROM WIKITECHY_CUSTOMERS c
FULL OUTER JOIN WIKITECHY_ORDERS o
ON (c.ID = o.WIKITECHY_CUSTOMER_ID);
Clicking "Copy Code" button will copy the code into the clipboard - memory. Please paste(Ctrl+V) it in your destination. The code will get pasted. Happy coding from Wikitechy hive tutorial team
On successful execution of the query, you get to see the following response:
| ID | NAME | AMOUNT | DATE |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Arun | NULL | NULL |
| 2 | Aarthi | 1560 | 2009-11-20 00:00:00 |
| 3 | Boomi | 3000 | 2009-10-08 00:00:00 |
| 3 | Boomi | 3000 | 2009-10-08 00:00:00 |
| 4 | Harikka | 2060 | 2008-05-20 00:00:00 |
| 5 | Dharsanya | NULL | NULL |
| 6 | Komal | NULL | NULL |
| 7 | Mirunalini | NULL | NULL |
| 3 | Boomi | 3000 | 2009-10-08 00:00:00 |
| 3 | Boomi | 3000 | 2009-10-08 00:00:00 |
| 2 | Aarthi | 1560 | 2009-11-20 00:00:00 |
| 4 | Harikka | 2060 | 2008-05-20 00:00:00 |
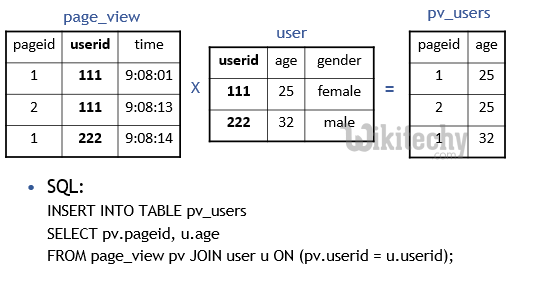
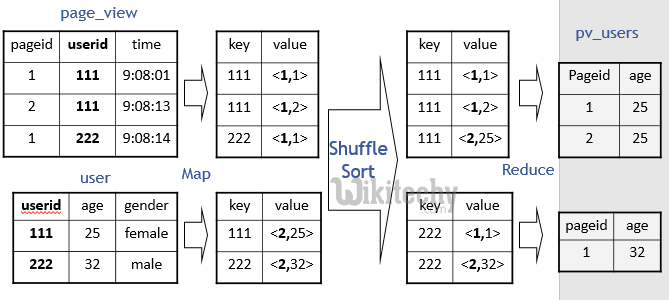
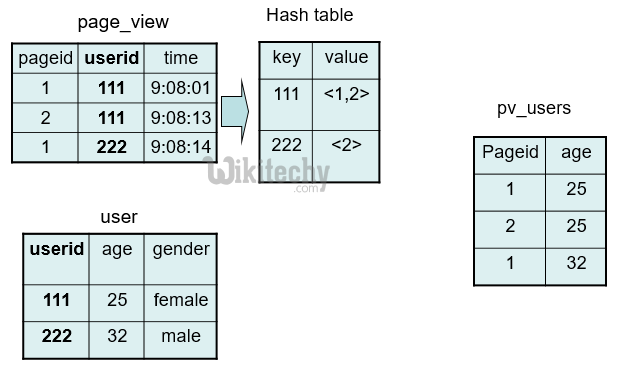
Hive QL Join :
SELECT pv.pageid, u.age
FROM page_view pv
JOIN user u
ON (pv.userid = u.userid);
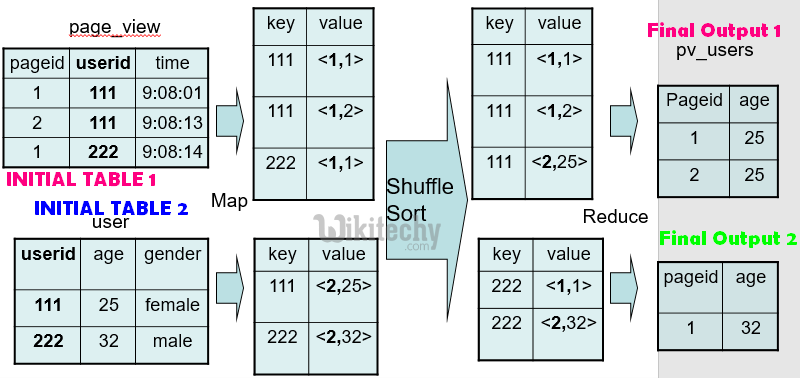
learn hive - hive tutorial - apache hive - hive mapreduce programming - hive examples
- Rightmost table streamed – whereas inner tables data is kept in memory for a given key. Use largest table as the right most table.
- hive.mapred.mode = nonstrict
- In strict mode, Cartesian product not allowed
Below is HiveQL Join, :
INSERT OVERWRITE TABLE pv_users
SELECT pv.pageid, u.age
FROM page_view p JOIN user u
ON (pv.userid = u.userid) JOIN newuser x on (u.userid = x.userid);
- Same join key – merge into 1 map-reduce job – true for any number of tables with the same join key. 1 map-reduce job instead of ‘n’
- The merging happens for OUTER joins also
SELECT pv.pageid, u.age
FROM page_view p JOIN user u
ON (pv.userid = u.userid) JOIN newuser x on (u.age = x.age);
Different join keys – 2 map-reduce jobs Same as:
FROM page_view p JOIN user u
ON (pv.userid = u.userid);
SELECT x.pageid, x.age
FROM tmptable x JOIN newuser y on (x.age = y.age);
Join Optimization - Map Joins :
SELECT /*+ MAPJOIN(pv) */ pv.pageid, u.age
FROM page_view pv JOIN user u
ON (pv.userid = u.userid);
- Optimization phase
- n-way map-join if (n-1) tables are map side readable
- Mapper reads all (n-1) tables before processing the main table under consideration
- Map-side readable tables are cached in memory and backed by JDBM persistent hash tables
Parameters for Join Optimization and Map Joins :
- hive.join.emit.interval = 1000
- hive.mapjoin.size.key = 10000
- hive.mapjoin.cache.numrows = 10000
apache hive related article tags - hive tutorial - hadoop hive - hadoop hive - hiveql - hive hadoop - learnhive - hive sql
Advanced Join Operations - Shuffle Join - Broadcast Join - Sort - Merge - Bucket Join :
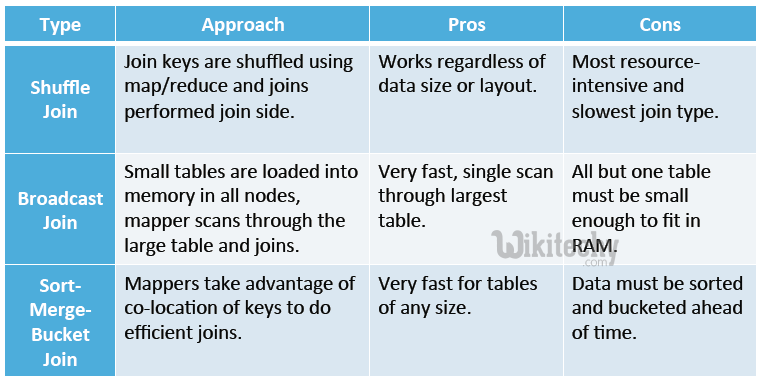
learn hive - hive tutorial - apache hive - hive join types - hive examples
apache hive related article tags - hive tutorial - hadoop hive - hadoop hive - hiveql - hive hadoop - learnhive - hive sql
Advanced Join Operations - Shuffle Joins in Map Reduce :
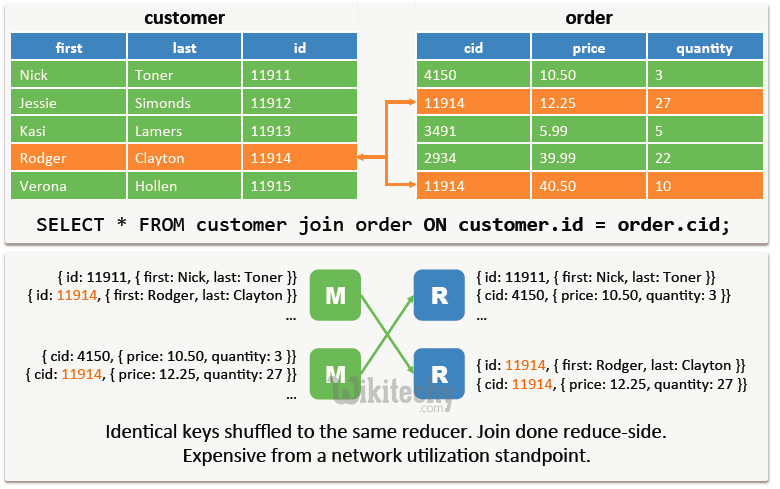
learn hive - hive tutorial - apache hive - hive Shuffle Joins in Map Reduce - hive examples

learn hive - hive tutorial - apache hive - hive Shuffle Joins in Map Reduce - hive examples
Advanced Join Operations - Broadcast Join :
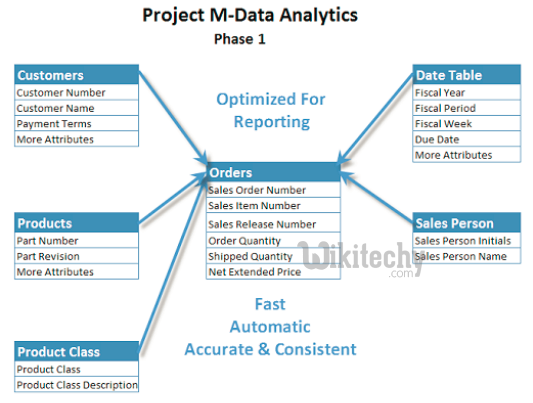
learn hive - hive tutorial - apache hive - hive broadcast join - hive examples
