What is Spoofing ?
- Spoofing is that the act of disguising a communication from an unknown resource as being from a well-known, trusted resource.
- Spoofing will apply to emails, phone calls, and websites, or will be a lot of technical, like a pc spoofing an IP address, Address Resolution Protocol (ARP), or Domain name System (DNS) server.
- Spoofing will be used to gain access to a target’s personal information, describe malware through infected links or attachments, bypass network access controls, or distribute traffic to conduct a denial-of-service attack.
- Spoofing is usually the means a vulgar actor gains access so as to execute a bigger cyber attack like a complicated persistent threat or a man-in-the-middle attack.
- Successful attacks on organizations will cause infected pc systems and networks, data breaches, and/or loss of revenue-all vulnerable to have an effect on the organization’s public reputation.
- Additionally, spoofing that ends up in the rerouting of web traffic will overwhelm networks or lead customers/clients to malicious sites aimed at stealing info or distributing malware.

Email spoofing
- Email spoofing is that the fake of an email header so the message seems to have originated from somebody or somewhere apart from the particular source.
- Email spoofing may be a plan of action utilized in phishing and spam campaigns because people are more likely to open an email after they assume it’s been sent by a legitimate source.
- The goal of email spoofing is to need recipients to open, and probably even answer, a solicitation.

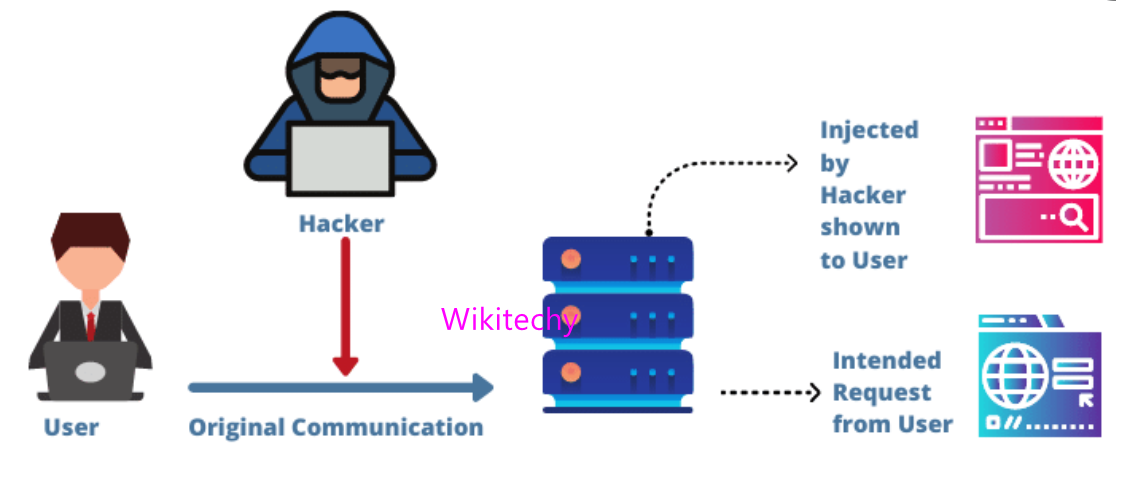
IP Spoofing
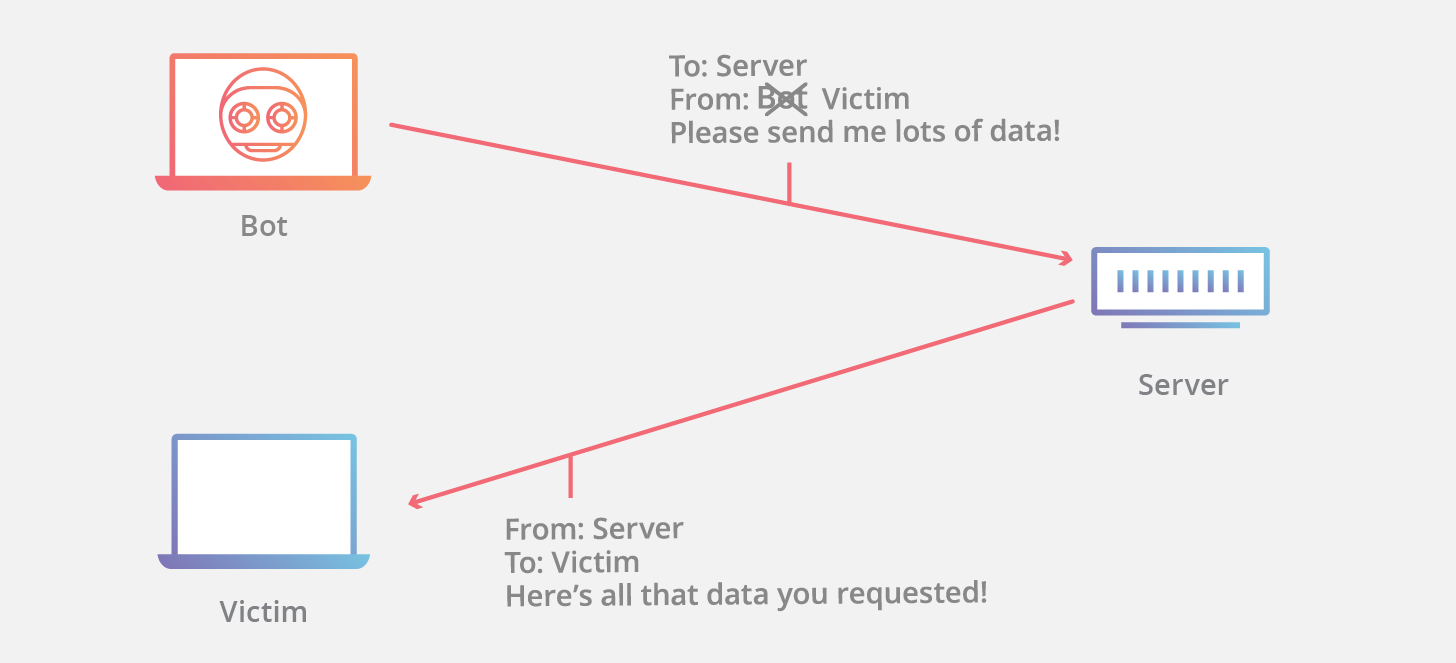
- IP (Internet Protocol) forms the third layer of the ISO model. It is the network protocol which is used for the transmission of messages over the internet. Every email message sent has details in the message header of the IP address of the sender (source address). Hackers and scammers alter the header details to mask their true identity by editing the source address. The emails then look to have been transmitted by a trusted source. There are two types of IP spoofing.
- Man in the Middle Attacks
- Denial of Service (DoS) Attacks
Caller ID Spoofing
- Caller ID spoofing is when a caller with intent fakes the information transmitted to your caller ID display to disguise their identity.
- Spoofing is often used as part of an attempt to trick someone into giving away valuable personal information so it can be used in fraudulent activity or sold illegally, but also can be used legitimately, for example, to display the toll-free number for a business.
ARP Spoofing
- ARP poison routing (APR) or ARP cache poisoning, a method of attacking an Ethernet LAN by updating the target computer’s.
- ARP cache with both a fake ARP request and reply packets in an effort to change the Layer 2 Ethernet MAC address (i.e., the address of the network card) to one that the attacker can monitor.
- Because the ARP replies have been fake, the target computer sends frames that were meant for the original destination to the attacker’s computer first so the frames can be read.
- A successful APR attempt is invisible to the user.

DNS Server Spoofing
- DNS (Domain Name System) servers resolve URLs and email addresses to corresponding IP addresses.
- DNS spoofing allows attackers to distract traffic to a different IP address, leading victims to sites that extent malware.

Website Spoofing
- Website spoofing means when a website is designed to copycat an existing site known and/or trusted by the user.
- Attackers use these sites to gain login and other personal information from users.
