Call by Reference | C++ Call by Reference Using pointers With Examples - Learn C++ - C++ Tutorial - C++ programming
Learn c++ - c++ tutorial - call by reference in c++ - c++ examples - c++ programs
- In this article, you'll learn to pass pointers as an argument to the function, and use it efficiently in your program.
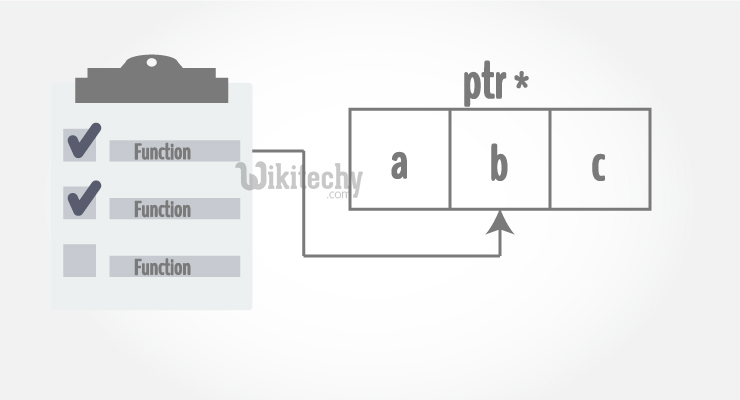
- In C++ Functions article, you learned about passing arguments to a function. This method used is called passing by value because the actual value is passed.
- However, there is another way of passing an argument to a function where where the actual value of the argument is not passed. Instead, only the reference to that value is passed.
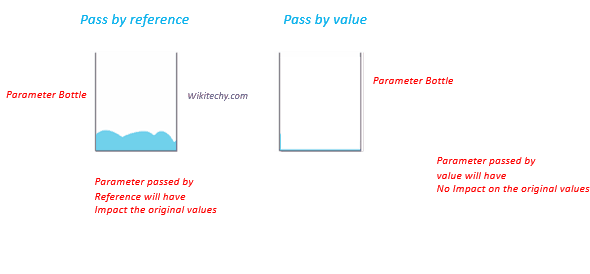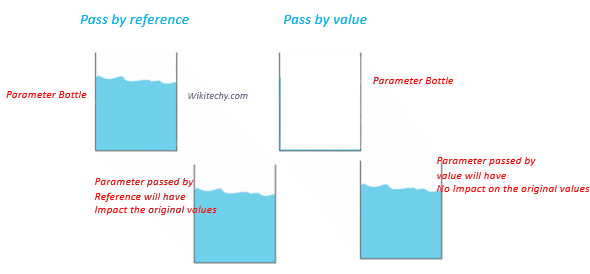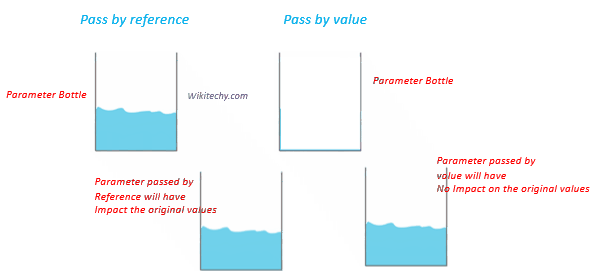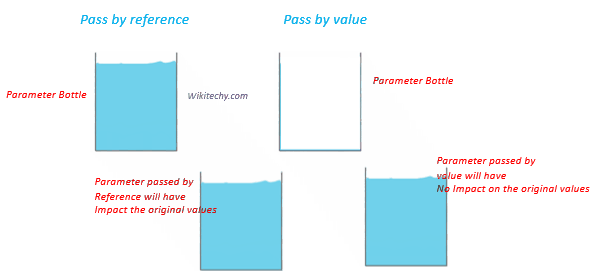
learn c++ tutorials - pass by value vs pass by reference in c++ Example
Learn C++ , C++ Tutorial , C++ programming - C++ Language -Cplusplus
Example 1: Passing by reference without pointers
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Function prototype
void swap(int&, int&);
int main()
{
int a = 1, b = 2;
cout << "Before swapping" << endl;
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
cout << "b = " << b << endl;
swap(a, b);
cout << "\nAfter swapping" << endl;
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
cout << "b = " << b << endl;
return 0;
}
void swap(int& n1, int& n2) {
int temp;
temp = n1;
n1 = n2;
n2 = temp;
}Output
Before swapping
a = 1
b = 2
After swapping
a = 2
b = 1
- In main(), two integer variables a and b are defined. And those integers are passed to a function swap() by reference.
- Compiler can identify this is pass by reference because function definition is void swap(int& n1, int& n2) (notice the & sign after data type).
- Only the reference (address) of the variables a and b are received in the swap() function and swapping takes place in the original address of the variables.
- In the swap() function, n1 and n2 are formal arguments which are actually same as variables a and b respectively.
- There is another way of doing this same exact task using pointers.
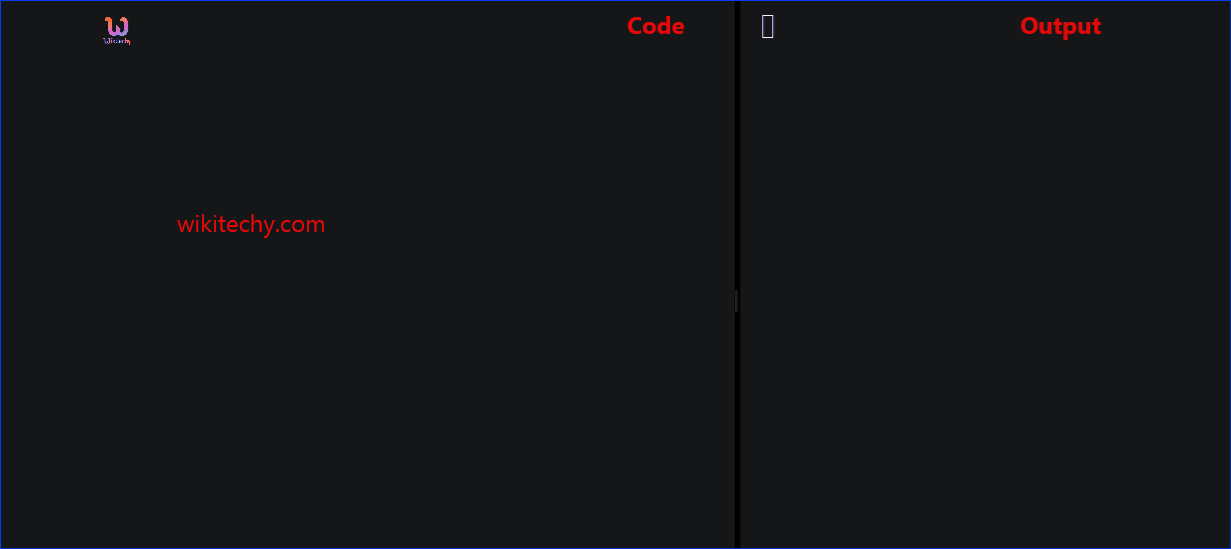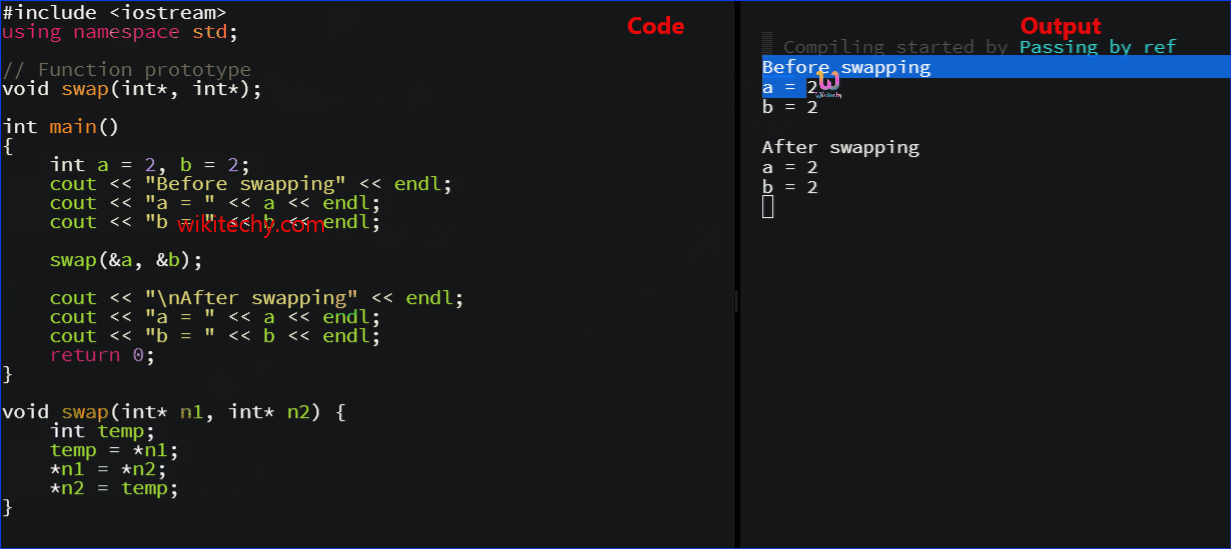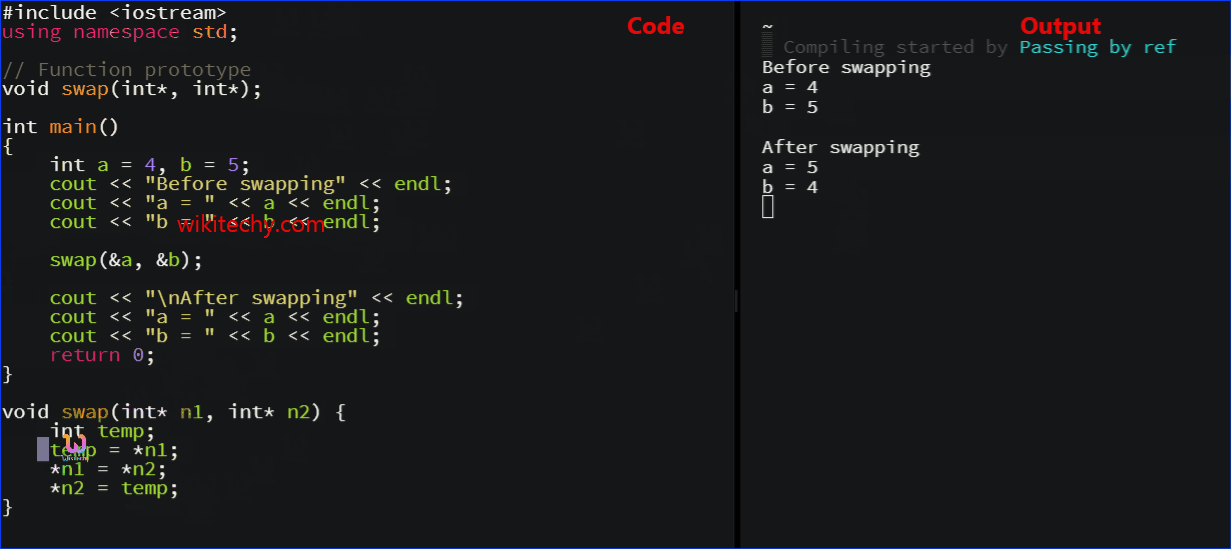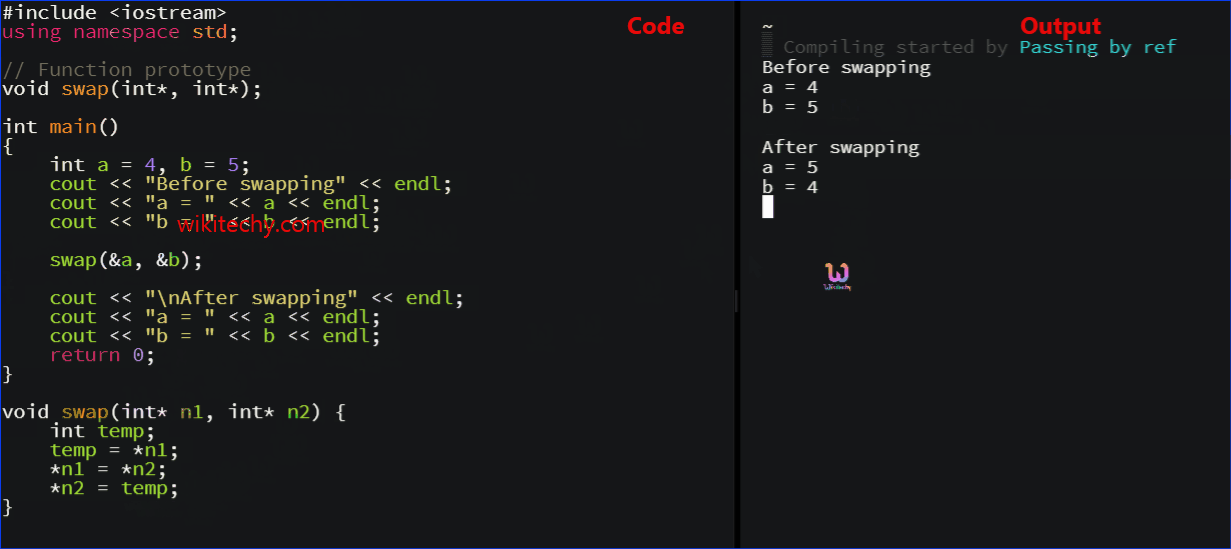
Example 2: Passing by reference using pointers
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Function prototype
void swap(int*, int*);
int main()
{
int a = 1, b = 2;
cout << "Before swapping" << endl;
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
cout << "b = " << b << endl;
swap(&a, &b);
cout << "\nAfter swapping" << endl;
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
cout << "b = " << b << endl;
return 0;
}
void swap(int* n1, int* n2) {
int temp;
temp = *n1;
*n1 = *n2;
*n2 = temp;
}
- The output of this example is same as before.
- In this case, the address of variable is passed during function call rather than the variable itself.
swap(&a, &b); // &a is address of a and &b is address of b
- Since the address is passed instead of value, dereference operator must be used to access the value stored in that address.
void swap(int* n1, int* n2) {
... .. ...
}- The *n1 and *n2 gives the value stored at address n1 and n2 respectively.
- Since n1 contains the address of a, anything done to *n1 changes the value of a inmain() function as well. Similarly, b will have same value as *n2.
